Insertion Sort
 Akshay Biswal
Akshay BiswalTable of contents

Introduction
Initialization:
The function
insertionSortaccepts an arrayarras its argument.const end = arr.length;stores the length of the array in the variableend.
Element Comparison:
- The outer loop starts at the second element (
let start = 1) and iterates through the array until the end (start < end).
- The outer loop starts at the second element (
Inner Loop:
For each element
arr[start], it's stored in the variablecurr.The variable
previs initialized tostart - 1, representing the index of the element before the current element.
Shifting Elements:
The inner
whileloop comparescurrwith the elements before it (arr[prev]).If
arr[prev]is greater thancurr,arr[prev]is moved one position ahead to make space forcurr.This continues until
curris greater than or equal toarr[prev]orprevbecomes1.
Insertion:
- Once the correct position is found,
curris inserted at that position (arr[prev + 1]).
- Once the correct position is found,
Returning the Result:
- After all elements are processed, the sorted array
arris returned.
- After all elements are processed, the sorted array
function insertionSort(arr) {
const end = arr.length;
for (let start = 1; start < end; start++) {
let curr = arr[start];
let prev = start - 1;
while (prev >= 0 && arr[prev] > curr) {
arr[prev + 1] = arr[prev];
--prev;
}
arr[prev + 1] = curr;
}
return arr;
}
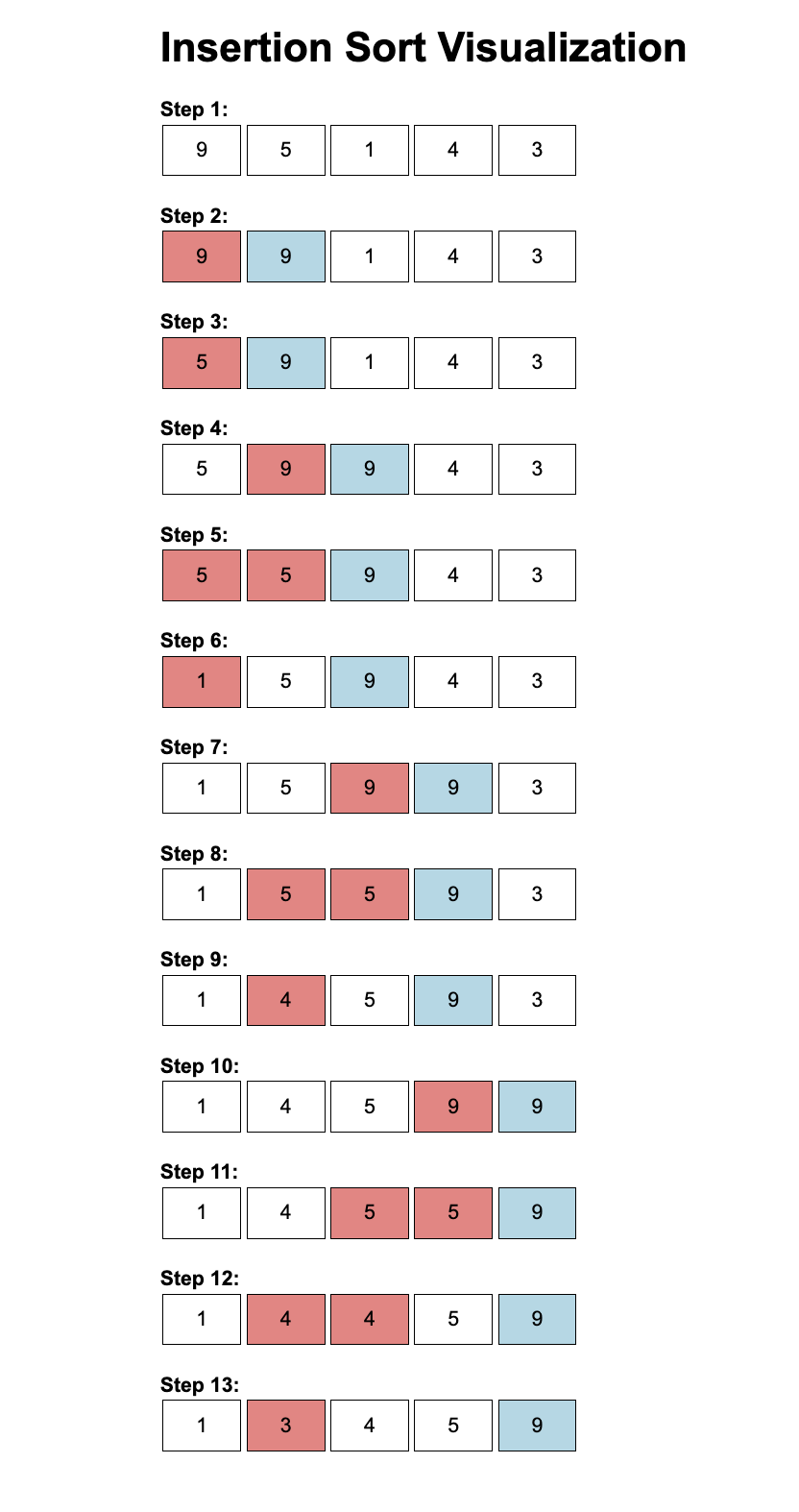
console.log(insertionSort([9, 5, 1, 4, 3]));
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Akshay Biswal directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Akshay Biswal
Akshay Biswal
Developer by day, globe-trotter by choice. Whether fixing bugs in the mountains or optimizing on the beach, each journey enhances both my code and life.🌍✈️