Introduction to JDBC
 Aniket Gudgal
Aniket Gudgal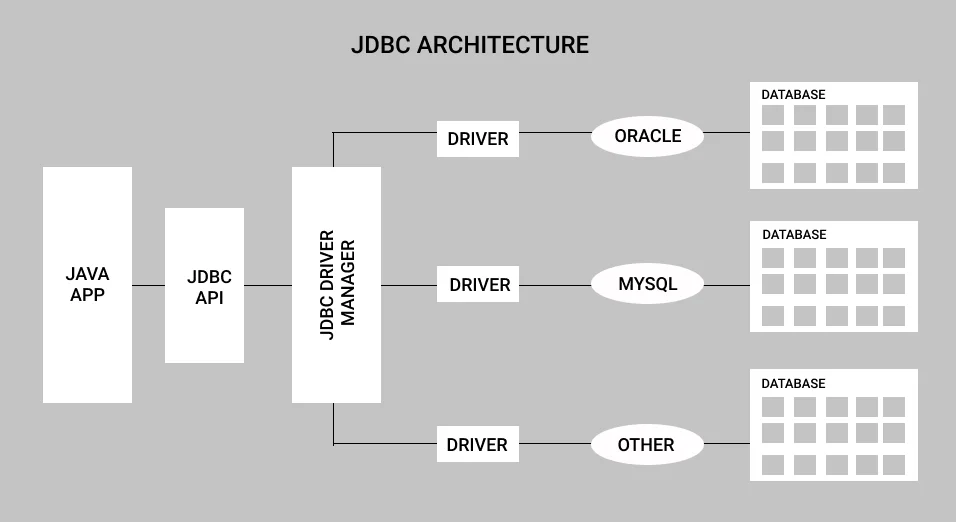
JDBC stands for Java Database Connectivity. It is a standard API provided by Oracle for Java applications to interact with different sets of database
Architecture of JDBC
Application: It is a Java applet or a servlet that communicates with a data source.
The JDBC API: The JDBC API allows Java programs to execute SQL statements and retrieve results. Some of the important interfaces defined in JDBC API are as follows: Driver interface, ResultSet Interface, RowSet Interface, PreparedStatement interface, Connection inteface, and classes defined in JDBC API are as follows: DriverManager class, Types class, Blob class, club class.
DriverManager: It plays an important role in the JDBC architecture. It uses some database-specific drivers to connect enterprise applications to databases effectively.
JDBC drivers: To communicate with a data source through JDBC, you need a JDBC driver that intelligently communicates with the respective data source.
Types of JDBC Architecture(2-tier and 3-tier)
Two-tier model: A Java application communicates directly to the data source. The JDBC driver enables the communication between the application and the data source. When a user sends a query to the data source, the answers for those queries are sent back to the user in the form of results.
The data source can be located on a different machine on a network to which a user is connected. This is known as a client/server configuration, where the user’s machine acts as a client, and the machine has the data source running acts as the server.Three-tier model: The user’s queries are sent to middle-tier services, from which the commands are again sent to the data source. The results are sent back to the middle tier and then to the user.
There are four types of JDBC drivers:
JDBC-ODBC Bridge Driver
Native Driver
Network Protocol Driver
Thin Driver
The java.sql package contains classes and interfaces for JDBC API
A list of popular interfaces of JDBC API are given below:
Driver interface
Connection interface
Statement interface
PreparedStatement interface
CallableStatement interface
ResultSet interface
ResultSetMetaData interface
DatabaseMetaData interface
RowSet interface
The question comes to mind why do we use the JDBC?
the simple answer is that communication between two different languages is not possible. java can not be communicated to the database language directly that's why the JDBC comes to solve this problem
I have installed the JDBC driver MySQL connector on my machine
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Aniket Gudgal directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
