Day 34 : Working with Services in Kubernetes
 Sahil Kaushal
Sahil Kaushal
On Day 32, we covered how to create a service for the application. Lets take it to a next level.
Make sure your Minikube is running.
minikube status
Create a ClusterIP Service for accessing the todo-app from within the cluster.
ClusterIP Service means the application is only accessible with Kubernetes cluster.
Create a ClusterIP Service definition for your todo-app Deployment in a YAML file.
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: todo-app labels: app: todo namespace: todo-group spec: replicas: 2 selector: matchLabels: app: todo template: metadata: labels: app: todo spec: containers: - name: todo image: trainwithshubham/django-todo:latest ports: - containerPort: 8000 --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: todo-app-service namespace: todo-group spec: selector: app: todo ports: - name: todo-app protocol: TCP port: 80 targetPort: 8000Apply the ClusterIP Service definition to your K8s (minikube) cluster.
kubectl apply -f YOUR_DEPLOYMENT_FILENAME.yml
- Deployment successfully created. Now we can see the deployment, pods, and service that are running by using the following commands.
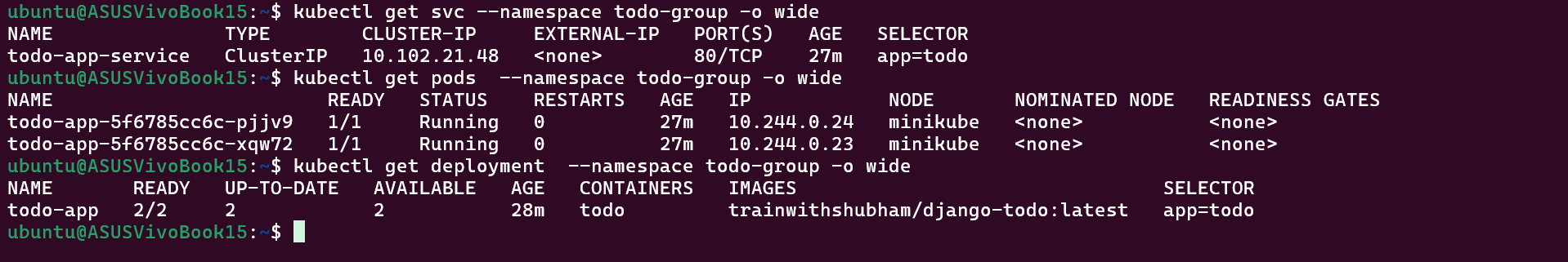
kubectl get svc --namespace todo-group -o wide
kubectl get pods --namespace todo-group -o wide
kubectl get deployment --namespace todo-group -o wide
To check if the application is up and running, we will use the command minikube ssh.
In the YAML file, in the service section, we haven't specified any "type of service," so by default, the type will be ClusterIP. Because of this, the app is running internally within the cluster. That's why we have to SSH into the minikube cluster to check whether the application is running or not.
minikube ssh
curl -L http://IP:8000
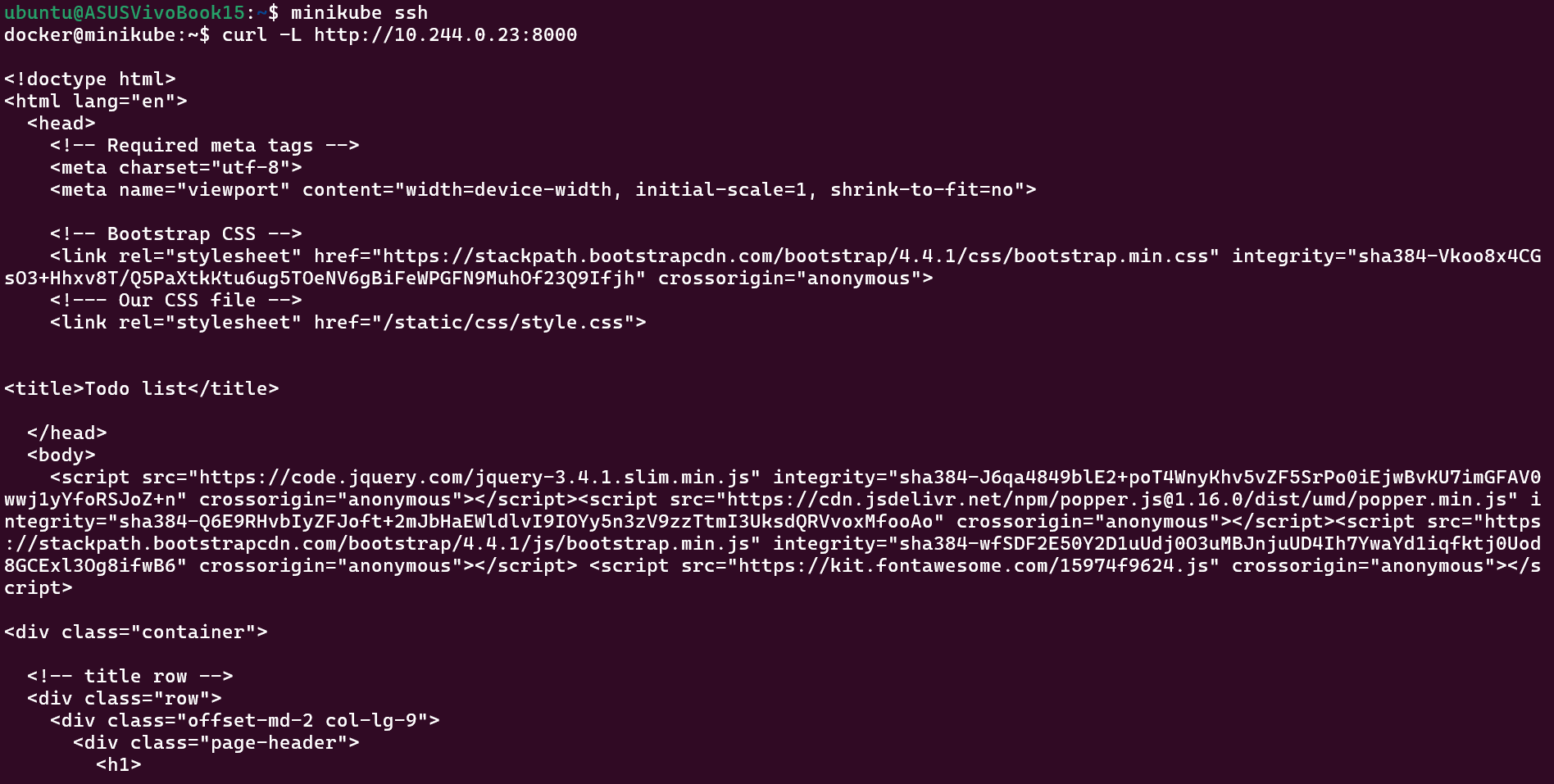
The app is running 😎.
Create a LoadBalancer Service for accessing the todo-app from outside the cluster.
A LoadBalancer service is used on an external cloud platform because the cloud provider gives you a publicly accessible Elastic IP address.
What is a LoadBalancer Service?
A LoadBalancer Service in Kubernetes is a type of Service that exposes your application to external traffic. It provides a stable IP address and routes traffic to the appropriate Pods within your cluster. This is particularly useful for applications that need to be accessible from outside the Kubernetes cluster, such as web applications or APIs.
Key Features
External Access:
The LoadBalancer Service provides an externally accessible IP address that clients can use to reach your application.
This IP address is stable, meaning it doesn’t change even if the underlying Pods do.
Load Balancing:
It distributes incoming traffic across multiple Pods, ensuring high availability and better performance.
This helps in handling high traffic volumes efficiently.
Integration with Cloud Providers:
When you create a LoadBalancer Service, Kubernetes interacts with the cloud provider’s API to provision a load balancer.
This is supported by major cloud providers like AWS, GCP, and Azure.
How It Works
When you create a LoadBalancer Service, Kubernetes provisions an external load balancer in your cloud environment. This load balancer forwards traffic to the nodes running the service. The traffic is then distributed to the appropriate Pods based on the service’s configuration.
Example
Let’s create a LoadBalancer Service for an example application.
Pod and service Definition:
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: todo-app labels: app: todo namespace: todo-group spec: replicas: 2 selector: matchLabels: app: todo template: metadata: labels: app: todo spec: containers: - name: todo image: trainwithshubham/django-todo:latest ports: - containerPort: 8000 --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: todo-app-service namespace: todo-group spec: selector: app: todo ports: - name: todp-app protocol: TCP port: 80 targetPort: 8000 type: LoadBalancerDeploy the Pod and Service:
kubectl get svc YOUR_SERVICE_NAME -n NAMESPACE
Finding the External IP
After deploying the LoadBalancer Service, you can find the external IP address assigned to your service using the following command:
kubectl get services YOUR_SERVICE_NAME
The output will show the external IP address under the EXTERNAL-IP column.
Use Cases
Web Applications: Exposing web applications to the internet.
APIs: Making APIs accessible to external clients.
High Traffic Applications: Distributing traffic across multiple instances to handle high loads.
Summary
A LoadBalancer Service in Kubernetes is a powerful way to expose your applications to external traffic, providing a stable IP address and load balancing capabilities. It integrates seamlessly with cloud providers to provision external load balancers, making it an ideal choice for applications that need to be accessible from outside the cluster.
Thank you for reading😉.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Sahil Kaushal directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
