Learn like a baby - Vendor Agnostic Hunting approaches for modern authentication abuse using AITM - 3
 raja mani
raja maniTable of contents

In this blog we have structured this into three parts The Act, The Analysis and The Detection and go through each part in very simplistic way to understand and approach them.
The Act talks about Modern authentication abuse using AITM
The Analysis talks about behind scenes of what happened in The Act and The Detection talks about the pseudocode to detect them agnostic to security vendors
The Act
Man in the middle framework named evilginx is available in github to perform this activity
https://github.com/kgretzky/evilginx2
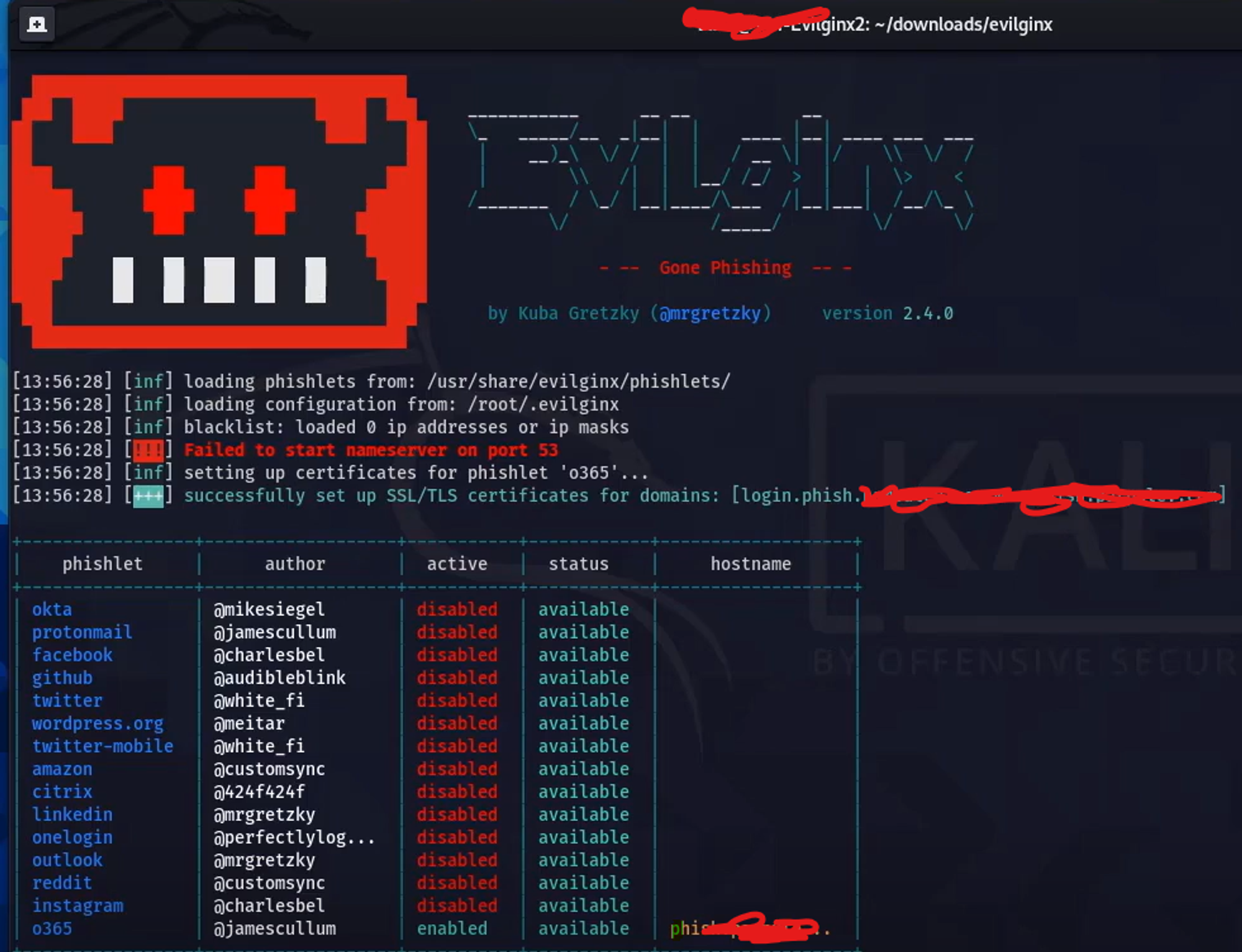
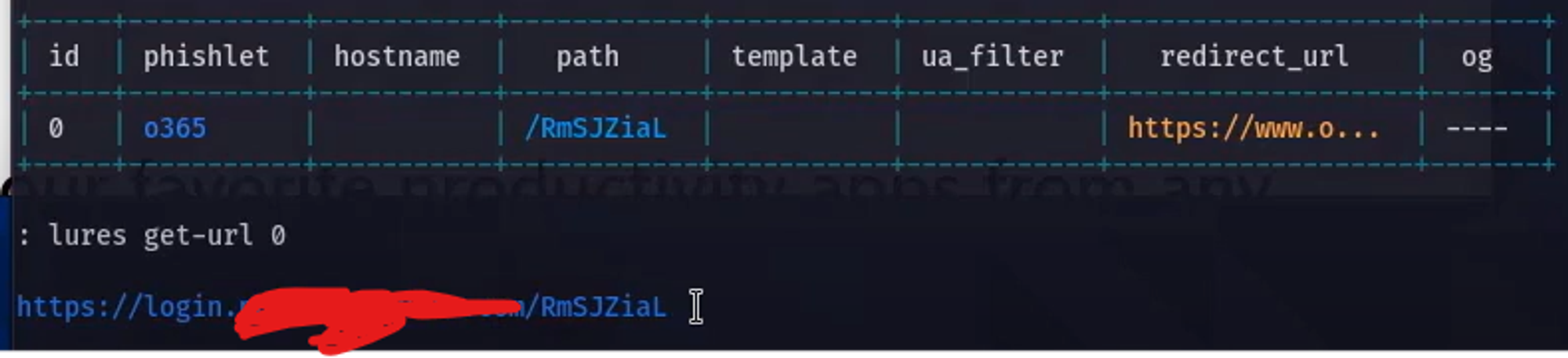
There are various templates of phishing available above screenshot has a o365 template. Attacker will need to own a domain to perform the AITM activity. To get the url where the interception happens use lures get-url command
1 - Assuming MFA is not configured
When an user visits the login page
you get the log in evilginx

Once signin is completed by entering the password by victim
Meanwhile in the evilginx screen you obtain the username and password
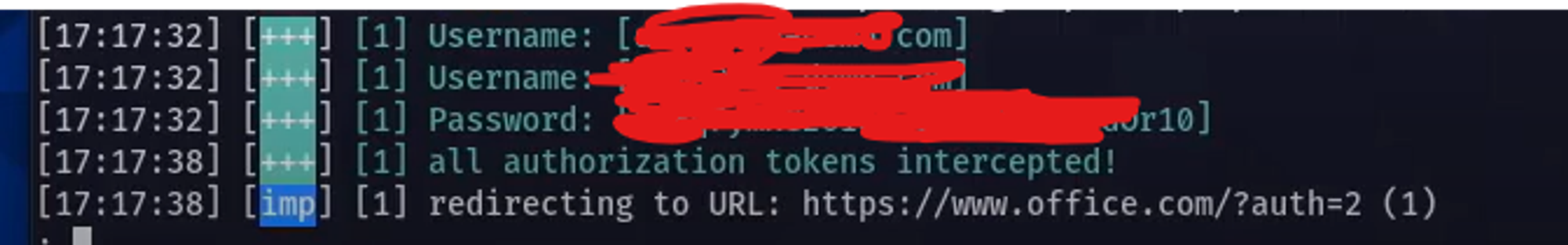
Because the credential is there attacker can use the credential and signin to org in single factor
2 - Assuming MFA is configured
Once the victim puts the signin MFA code
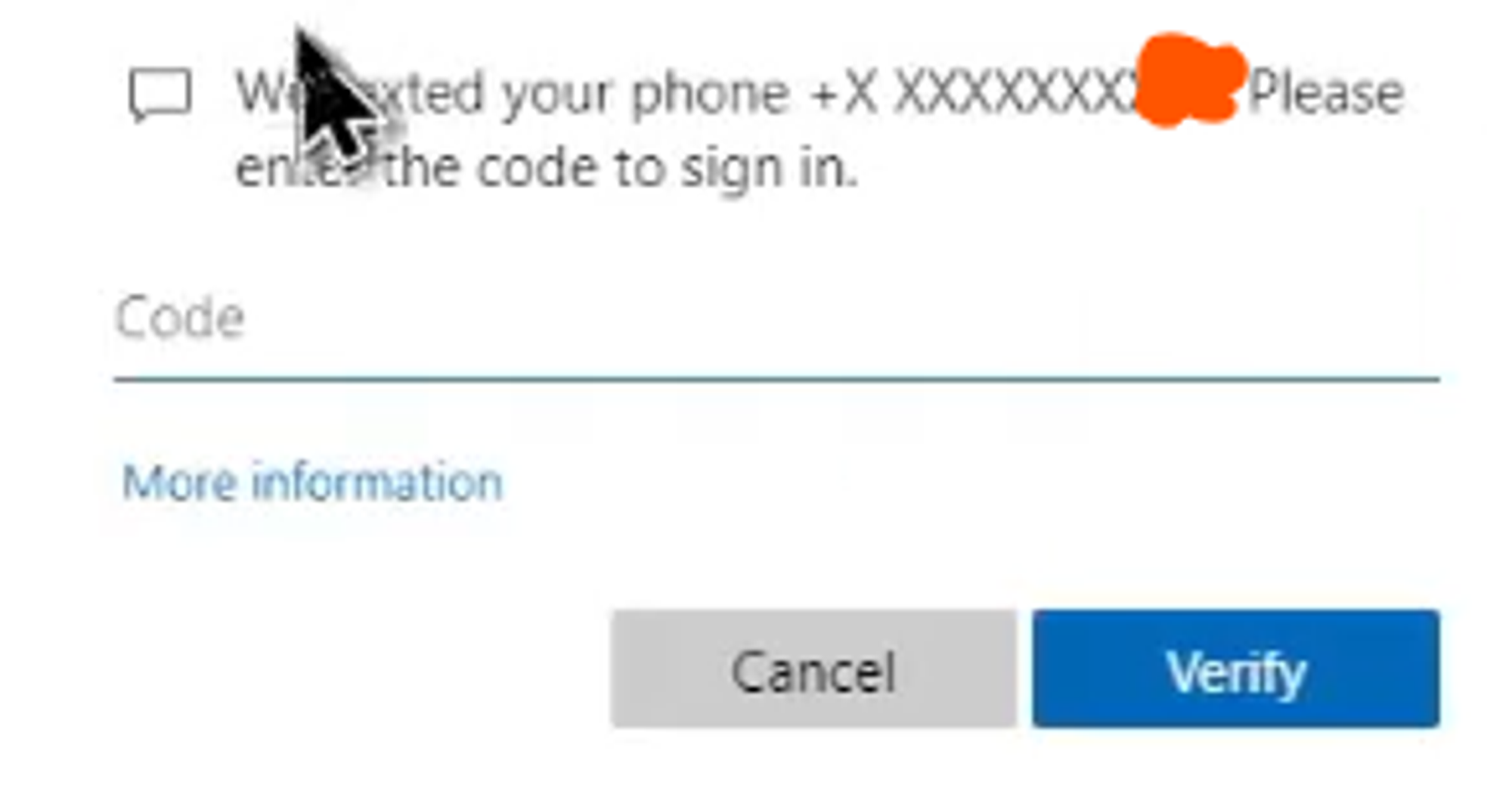
and signin
This is what attacker will observe in the evilginx user name and password and message that authorization was intercepted

you can view intercepted session information by typing session id
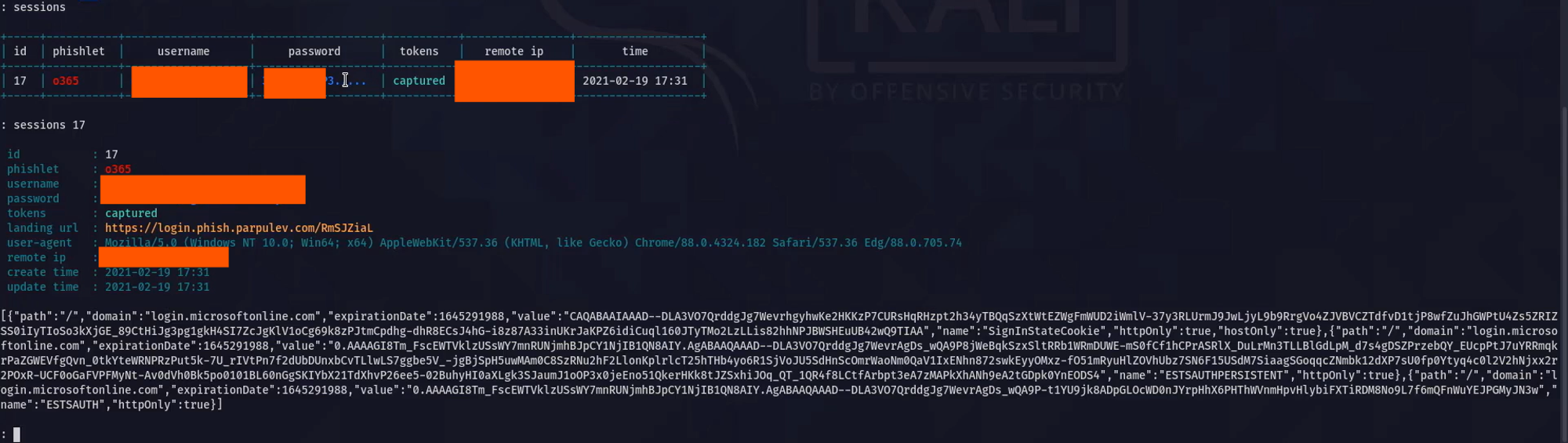
Now the attacker can copy the json like structure and reuse them. When you observe there three types of cookies for o365 based phishing. It will change based on the targets.
SignInStateCookie
ESTSAUTHPERSISTENT
ESTSAUTH
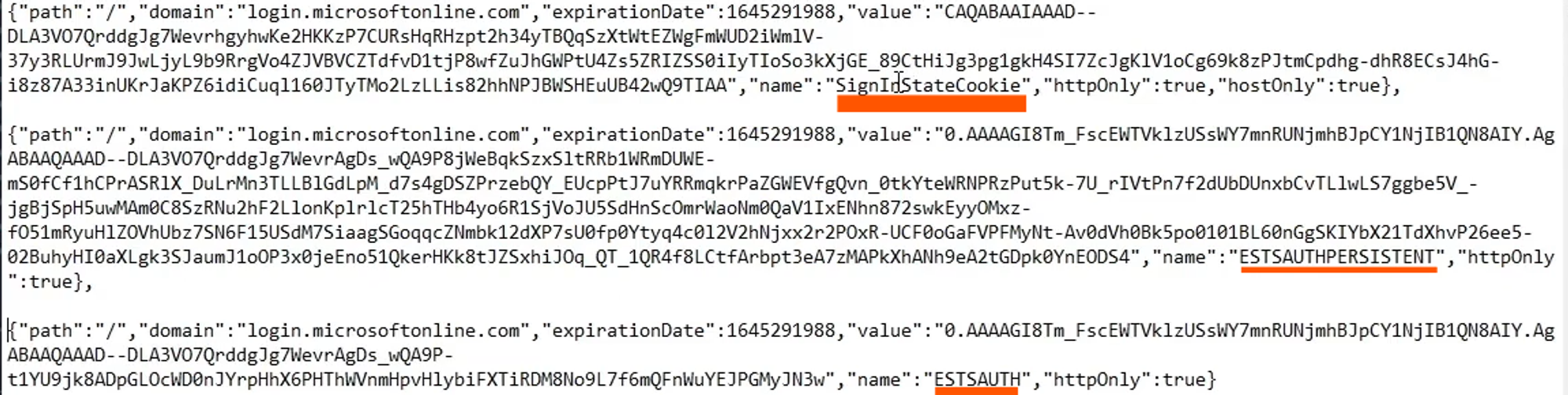
Understanding SignInStateCookie, ESTSAUTHPERSISTENT, and ESTSAUTH
SignInStateCookie
Purpose: Contains a list of services accessed to facilitate sign-out.
Data: No user information, but a record of accessed services.
Role: Security feature, aiding in controlled sign-out.
ESTSAUTHPERSISTENT
Purpose: Contains user session information for single sign-on (SSO).
Data: User session data.
Role: Maintains persistent SSO, allowing access to multiple services without re-authentication.
ESTSAUTH
Purpose: Similar to ESTSAUTHPERSISTENT, but for non-persistent sessions.
Data: User session data.
Role: Facilitates SSO for a specific browser session.
Additional Notes:
Other cookies like ESTSAUTHLIGHT, CCState, and buid also play roles in the authentication process.
The specific behavior and contents of these cookies might vary based on the authentication configuration.
Non-persistent sessions: Exist only for the duration of a browser or application session. Data is lost when the session ends.
Persistent sessions: Continue beyond the immediate browser or application session, allowing data to be retained for future us
There are numerous plugin to reuse the cookie, for example
https://chromewebstore.google.com/detail/fngmhnnpilhplaeedifhccceomclgfbg
attacker reuse SignInStateCookie, ESTSAUTH and ESTSAUTHPERSISTENT in order to get in with out MFA.
The Analysis. & The Detection.
How this has happened is a pretty simple to understand as highlighted by Microsoft adversary in the middle to steal the three tokens we discussed- SignInStateCookie, ESTSAUTH and ESTSAUTHPERSISTENT
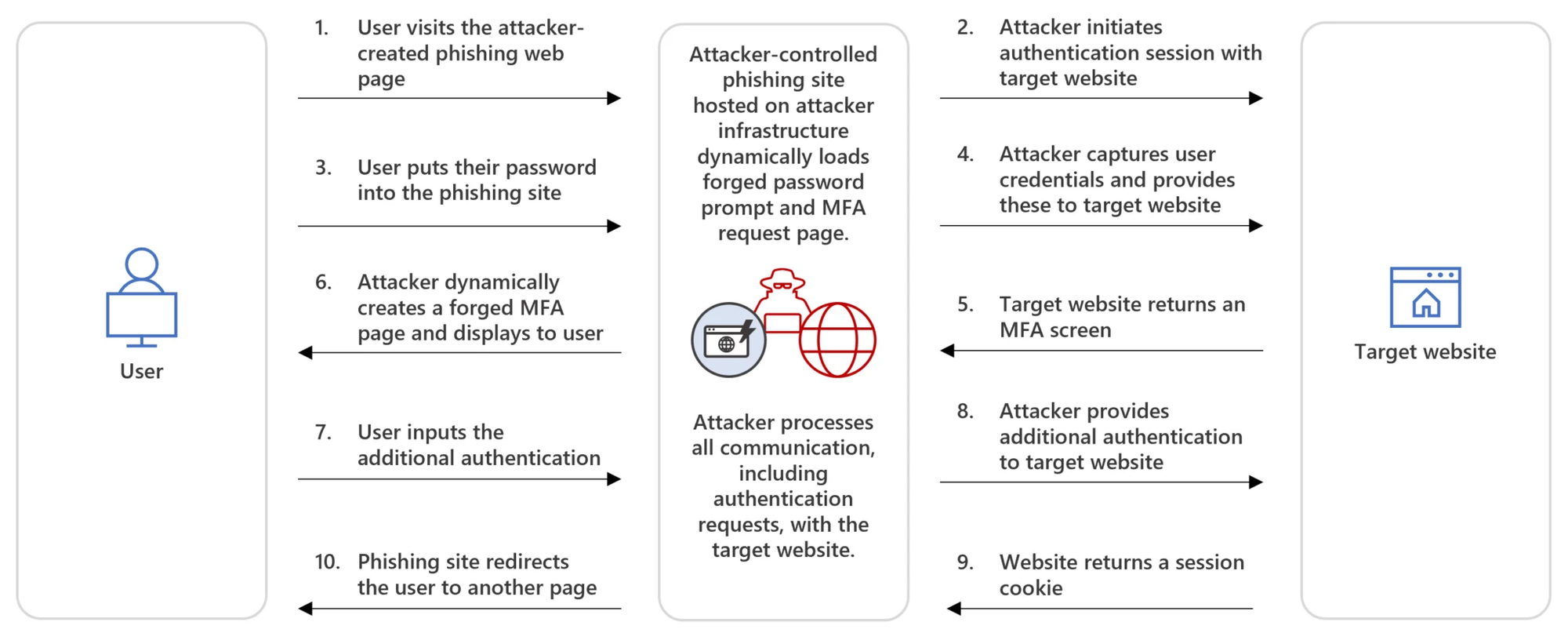
lets analyze a setup to discuss more on this and write detection.
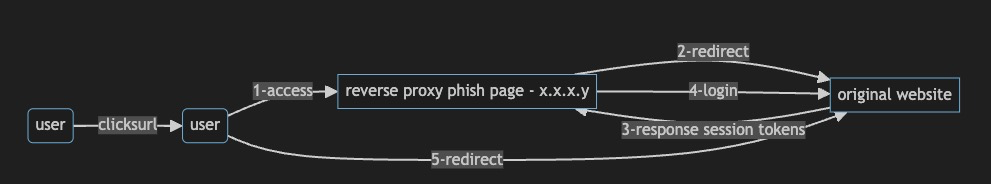
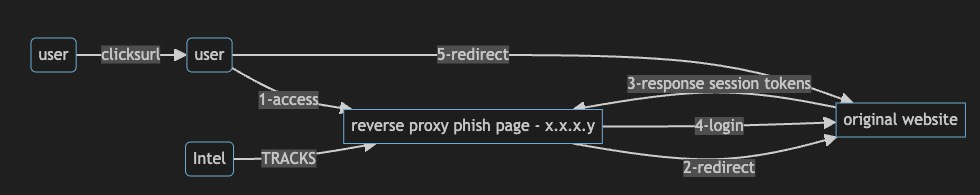
Scenario 1 - simple setup
where attackers hosting site contacts the final landing url instead of reusing the token from different infrastructure.
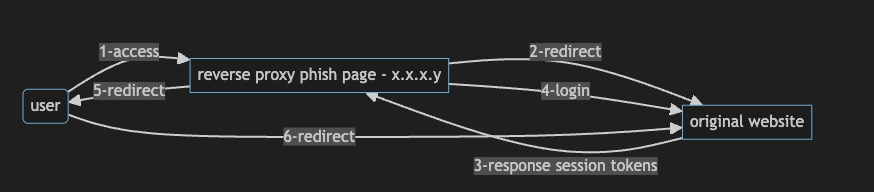
Lets develop the pseudo code for this detection being vendor agnostic here.
Trying to be vendor agnostic because not every dataset will be available from single source in most organization
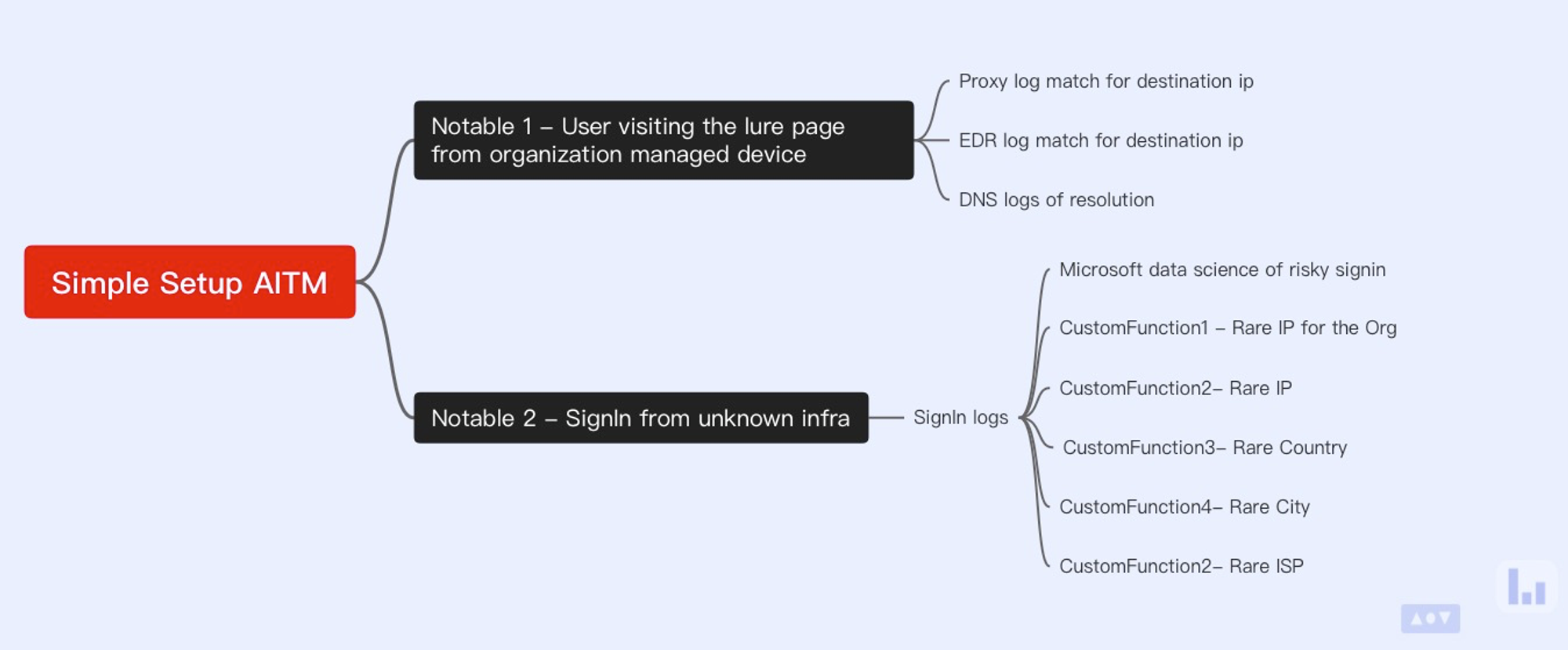
Highly recommend to orchestrate this detection by using Jupyter notebook solutions for a multi product environment.
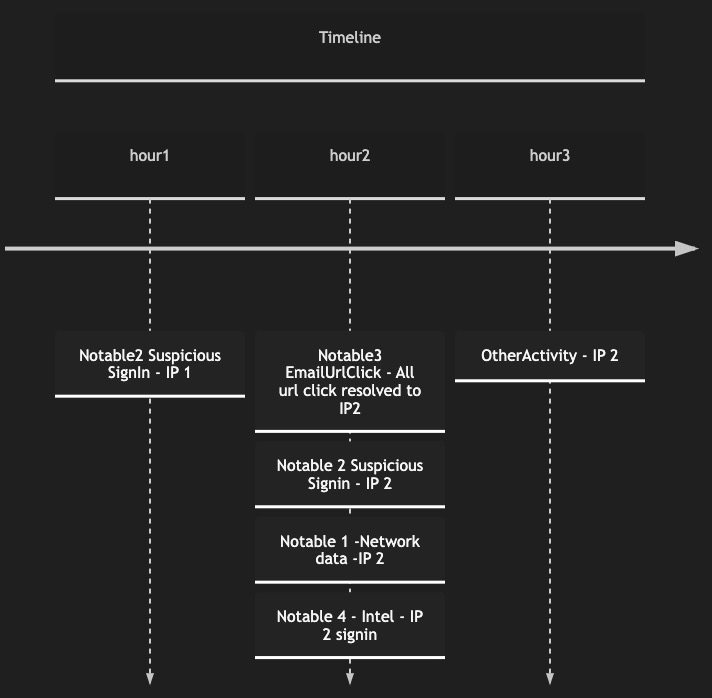
Recommended to timeslice the activity so it looks like the below
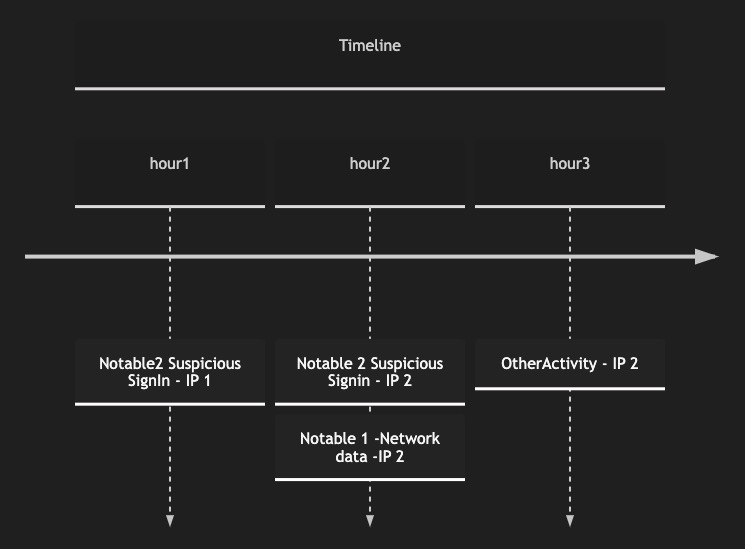
Clearly in the above timeline hour2 is interesting where the initial detection is present and all actions from the IP then on has to be analyzed deeply.
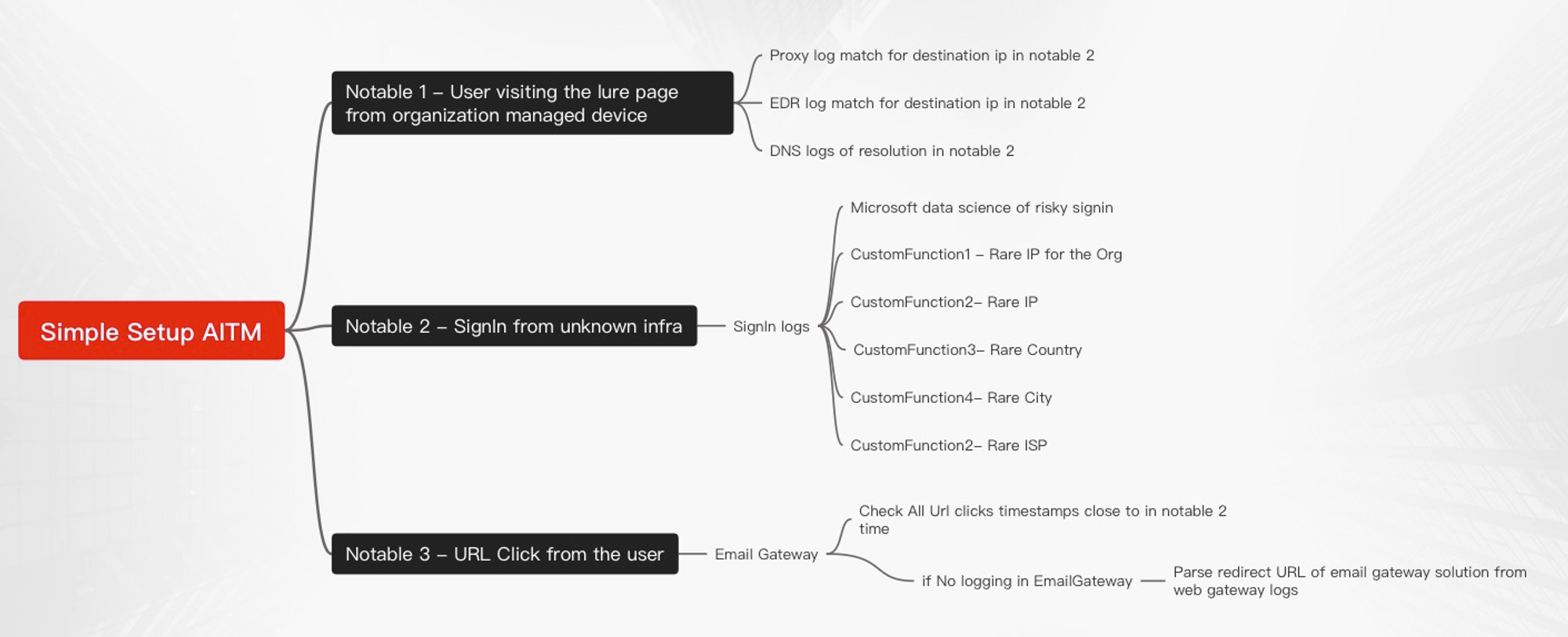
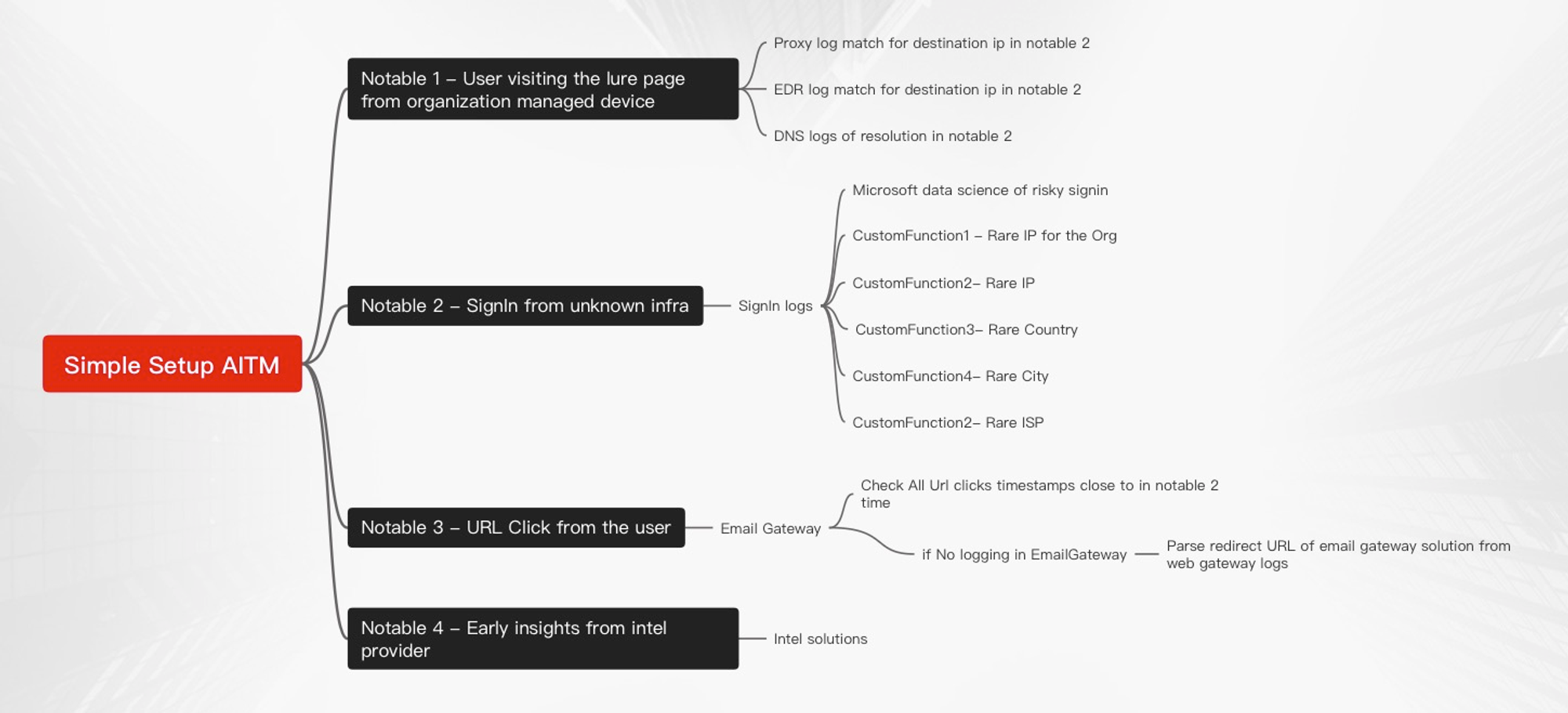
Scenario 2 - Correlation with URLclicks
now detection pseudocode changes, one more notable is in place. Its backtracking urlclicks via email gateway and webgateway logs
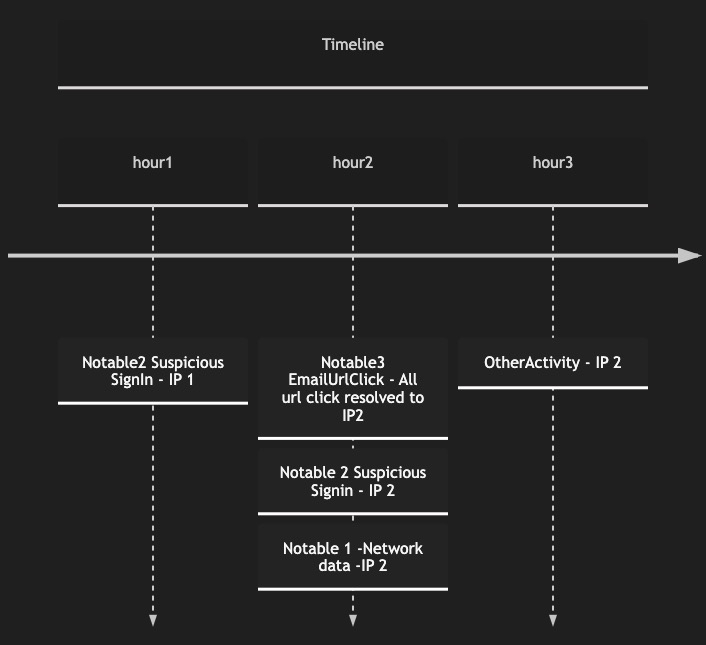
how timeline will look in timeslice
Scenario 3 - What if you are expecting signin from particular infrastructure
You may be expecting attackers using VPS providers
Popular VPS Providers:
There are numerous VPS providers available, each with its own strengths and pricing plans. Some well-known options include:
DigitalOcean: Known for its user-friendly interface and affordable plans.
Linode: Offers high-performance VPS solutions with a focus on simplicity.
Vultr: Provides flexible VPS options with various data center locations
May be you are subscribed to Insights of Intelligence solutions on both the cases this apply
Please see below how the pseudo code now changed
Also have a look and feel of how hour 2 timeline looks like during the attack
Now the challenge is
what if the url is in attachment ? there wont be url clicks ?
what if url is in QR code there wont be network connection if mobile infra is not monitored?
what if attacker reuse the token from different Infrastructure , network connection becomes irrelavent ?
what are attackers doing further more to evade our detections ?
hunting goes on and on! :)
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from raja mani directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

raja mani
raja mani
✨🌟💫Threat Hunter 💫🌟✨