Unlocking the Full Potential of Python's datetime Module: A Comprehensive Guide
 Shrey Dikshant
Shrey Dikshant
Working with dates and times is a common requirement in many applications, from logging events to handling time zones and calculating durations. Python’s datetime module provides a powerful suite of tools to handle date and time operations with ease and precision. This guide will walk you through the key features of the datetime module, helping you to unlock its full potential.
Getting Started with datetime
The datetime module includes several classes, each serving a specific purpose:
datetime.date: Represents a date (year, month, day).datetime.time: Represents a time (hour, minute, second, microsecond).datetime.datetime: Represents both date and time.datetime.timedelta: Represents the difference between two dates or times.datetime.timezone: Handles time zones and offsets.
Here’s a simple example of creating a date object:
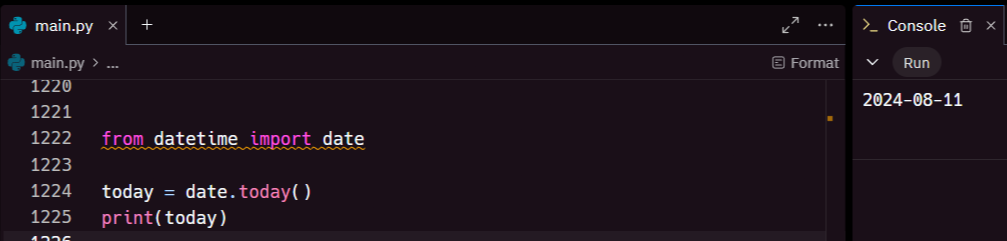
This will output the current date in the format YYYY-MM-DD.
Parsing and Formatting Dates
One of the most common tasks is parsing dates from strings and formatting them for display. The strftime (string format time) and strptime (string parse time) methods are your go-to tools for this:
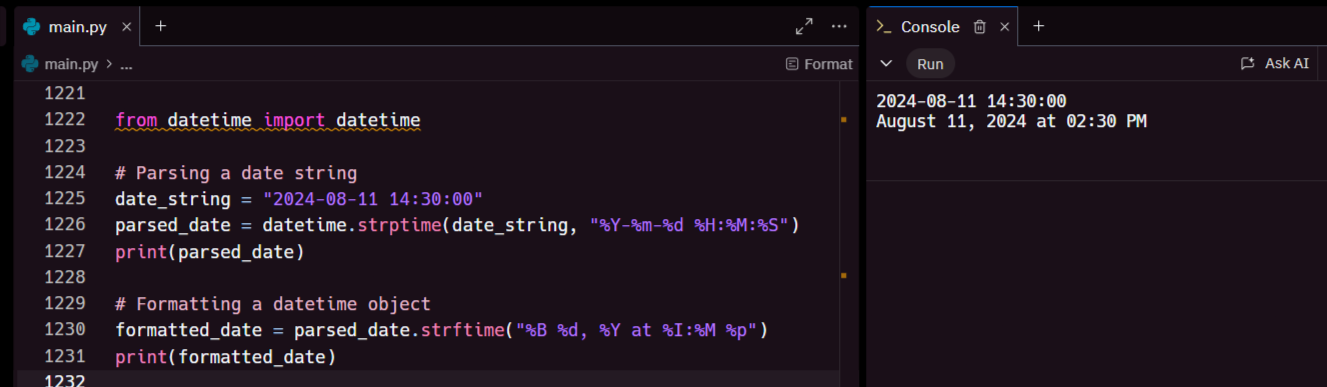
This example converts a string into a datetime object and then formats it into a more readable form like "August 11, 2024 at 02:30 PM".
Working with Time Zones
Handling time zones correctly is crucial in global applications. The datetime module provides the timezone class, which allows you to attach a time zone to a datetime object:
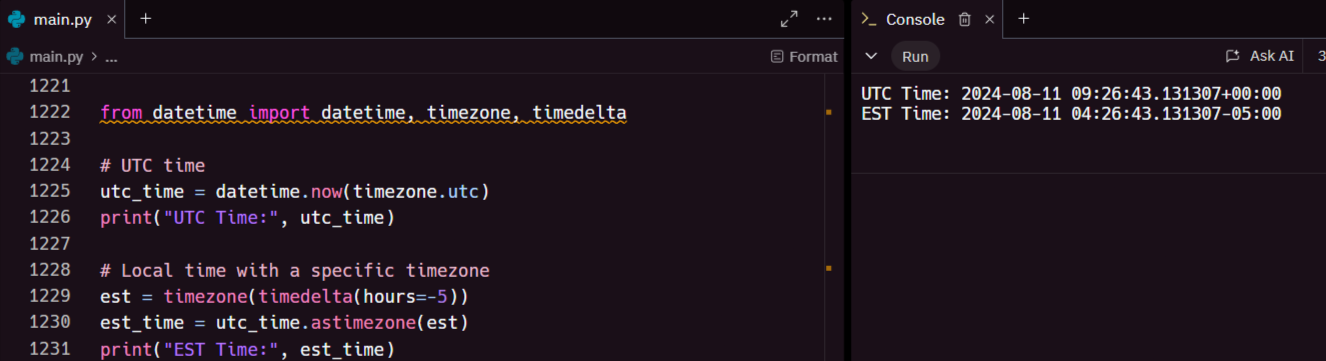
This will output the current time in UTC and then convert it to Eastern Standard Time (EST).
Calculating Time Differences
The timedelta class is used to perform arithmetic with dates and times, making it easy to calculate durations and differences:
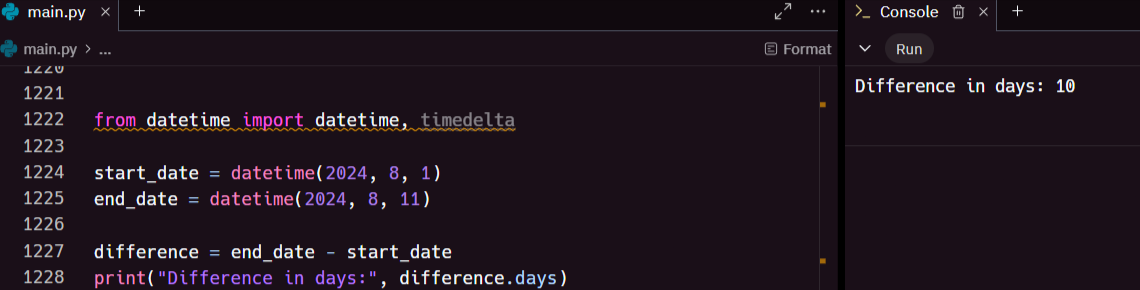
This example calculates the difference between two dates, returning the number of days between them.
Using datetime in Real-World Applications
The datetime module is widely used in various applications:
Logging: Timestamps are often needed for logging events.
Scheduling: Applications like task schedulers rely on accurate date and time calculations.
Data Analysis: Time series data analysis requires precise handling of dates and times.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Shrey Dikshant directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Shrey Dikshant
Shrey Dikshant
Aspiring data scientist with a strong foundation in adaptive quality techniques. Gained valuable experience through internships at YT Views, focusing on operation handling. Proficient in Python and passionate about data visualization, aiming to turn complex data into actionable insights.