Day 16: Advanced Git and GitHub 🚀
 Tanmaya Arora
Tanmaya Arora
1. Git Branching: The Power of Parallel Development 🌳
Branches in Git are like different paths you can take in your project's history. They allow you to work on features, bug fixes, or experiments without affecting the main project. Thus, allowing multiple teams to function together and contribute their expertise to the main project.
What is a Branch?
A branch in Git is simply a movable pointer to a specific commit. The main branch (sometimes called master) is the default branch where all the final code lives. When you create a new branch, you're creating a copy of the project at that point in time.
Creating a Branch
git branch new-feature-branch
OR
git checkout -b new-feature-branch
Here, new-feature-branch is the name of the new branch.
Switching Between Branches
git checkout new-feature-branch
Or, in newer Git versions:
git switch new-feature-branch
This command switches you to the new-feature-branch, allowing you to work independently of the main branch.
Branching Example 🛤️
Imagine you're working on a website, and you want to add a new feature—a contact form. You create a branch called contact-form:
git branch contact-form
git checkout contact-form
Now, you can work on the contact form without affecting the main website.
Flowchart: Git Branching Workflow 🗺️

2. Git Revert and Reset: Undoing Changes with Confidence ⏪
Sometimes, mistakes happen. You might commit something by accident, or you realize a change wasn’t necessary. Git offers two powerful tools to undo changes: git revert and git reset.
Git Revert
git revert creates a new commit (each time) that undoes the changes made in a previous commit. It’s a safe way to undo changes because it doesn’t alter the commit history.
git revert <commit-hash> #Commit hash is a kind of ID associated with each commit.
Git Reset
git reset moves the branch pointer to a previous commit. It can be a little tricky because it changes the commit history, especially when using the --hard option. Generally it is advisable not to use git reset.
Reset Types:
1) Soft: All changes remains staged which means history from Git gets deleted but the files remain in our file system. So basically commit needs to be done here to let the changes reflect.
git reset --soft <commit-hash>
2) Hard: All changes remains untracked which means files remain in our file system but are not tracked by Git. So basically add and commit functions of git, both needs to be done here to let the changes reflect.
git reset --hard <commit-hash>
Example:
If you want to undo your last commit:
git reset --hard HEAD~1
Revert vs. Reset 🔄
Revert is safer, as it doesn’t alter the commit history.
Reset can be more powerful, but it rewrites history, which can be dangerous in shared repositories.
Flowchart: Git Revert and Reset Workflow 🗺️

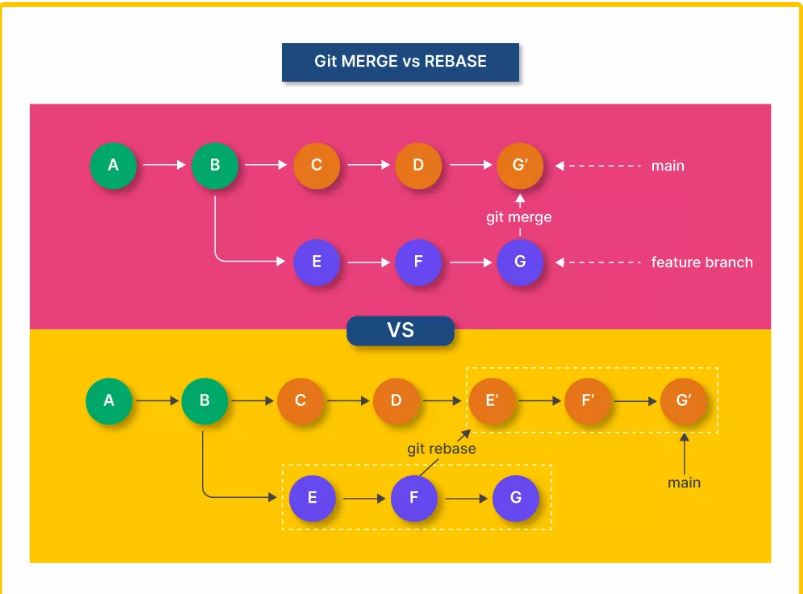
3. Git Merge and Rebase: Keeping Your History Clean 🌟
When your work on a branch is complete, you'll want to incorporate those changes into the main branch. Git offers two methods to do this: git merge and git rebase.
Git Merge
Merging takes the changes from one branch and applies them to another. It creates a new commit that brings both branches together.
Note: We perform the command "git merge <branch_name>" after switching to the branch in which we want the changes to be merged.
git checkout main #Here we first go to main branch as we want changes to be
#merged in main
git merge new-feature-branch #Since we are in main branch so all changes will be
#merged to main branch
Git Rebase
Rebasing, on the other hand, moves or combines a sequence of commits to a new base commit. It’s often used to clean up commit history.
git checkout feature-branch
git rebase main
Example:
If your new-feature-branch has diverged from main, you can rebase it onto main to replay your changes on top of the latest main branch:
git checkout feature-branch
git rebase main
Merge vs. Rebase ⚖️
Merge preserves the history of how branches came together.
Rebase rewrites commit history to make it linear and clean.
Flowchart: Git Merge and Rebase Workflow 🗺️
4. Cherry Picking in Git🍒
Cherry-picking in Git is a powerful feature that allows you to apply a specific commit from one branch to another without merging the entire branch. It is particularly useful in scenarios where you want to incorporate individual changes or fixes from a different branch without including all of that branch's changes.
git cherry-pick <commit/hash id>
Use Case:
Imagine you're working on a dev branch and you find a critical bug that needs to be fixed in production immediately (which is known as a Hotfix situation). You've already made the fix on the dev branch but don't want to merge all the other in-progress work into main or production.
5. Stash and Squash in Git
Stash is a command in Git which is useful when we are working on a feature and wants to keep it on hold for sometime such that we can not commit it right now but also do not want it to get lost in our filesystem (untracked), then we generally do stash.
Squashing in Git combines multiple commits into a single commit, simplifying the commit history. It's often used during a merge or rebase to clean up a branch before integrating it into the main branch.
Conclusion: Empower Your Development with Git and GitHub 🚀
Understanding Git’s branching, revert/reset, and merge/rebase strategies will empower you to manage your code effectively. Whether you’re collaborating with a team or managing your own projects, these tools are invaluable for maintaining a clean and functional codebase.
Happy coding! 💻✨
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Tanmaya Arora directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Tanmaya Arora
Tanmaya Arora
Hey there! 👋 🌟 Welcome to my DevOps journey! 🌟 I'm Tanmaya Arora, an enthusiastic DevOps Engineer. Currently, on a learning adventure, I'm here to share my journey and Blogs about DevOps. I believe in fostering a culture of resilience, transparency, and shared responsibility. Embracing agility and flexibility, in this adventure let's grow together in this vibrant DevOps space. Join me in transforming software delivery through collaboration, innovation, and excellence! 🚀🔧💡 🌐 Connect with me for friendly chats, group discussions, shared experiences and learning moments.