MongoDB Mastery
 Narottam sharma
Narottam sharmaTable of contents
🌟 Introduction to MongoDB 🌟
Imagine a library with endless books 📚—each one representing a piece of data. Traditional databases are like librarians who organize these books in a strict, structured order, which can make finding specific information a bit of a challenge. But MongoDB? It's like a super-smart librarian 🤓 who uses a flexible system to store and retrieve books (data) quickly and efficiently!
So, what exactly is MongoDB?
MongoDB is a modern, special kind of database that stores information in documents 📝—similar to JSON files. This approach makes it incredibly easy for developers to manage data and build fast, scalable applications 🚀.
🌟 Why Choose MongoDB? 🌟
Flexible Data Storage 📈
Adapt your data structure as your application grows.Fast and Scalable ⚡️
Handle large amounts of data and high traffic with ease.User-Friendly 📚
Simple to learn and use, even for beginners.Perfect for Modern Applications 📱
Ideal for today’s dynamic, data-driven world.
In this article, we'll explore MongoDB in an easy-to-understand way, perfect for anyone new to databases 🙌. So, let’s dive in and uncover the power of MongoDB together! 💻
Types of Databases
Depending on the way we organize data they are different types of databases.
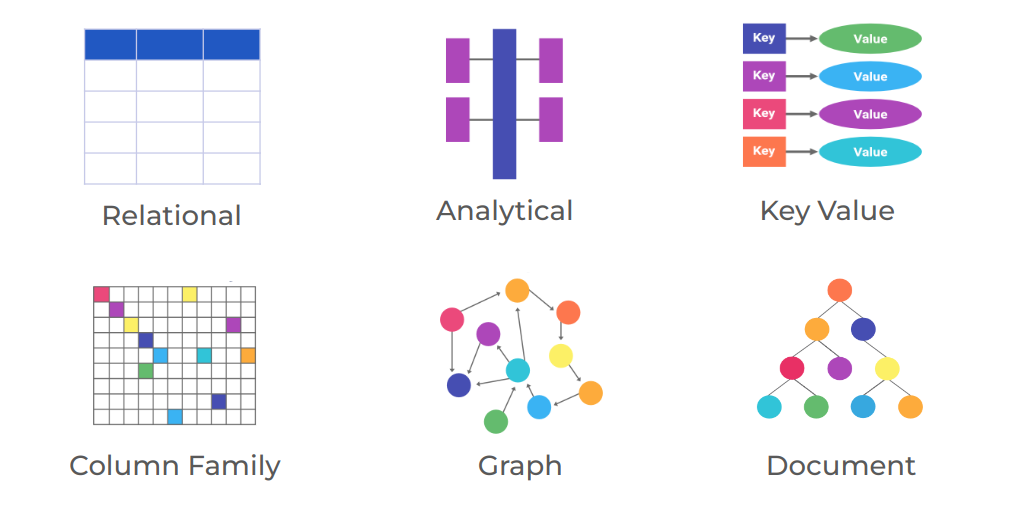
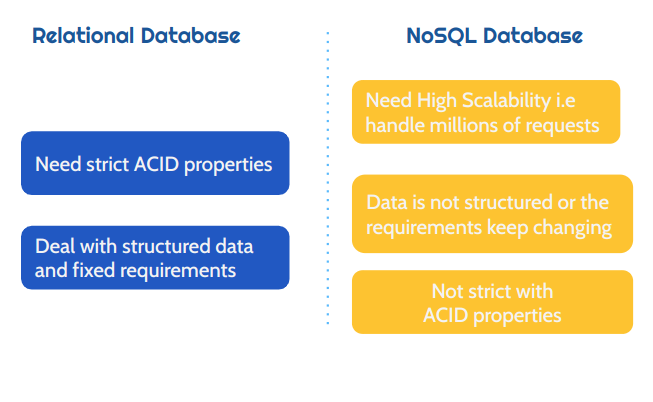
Non-Relational Databases (NoSQL)
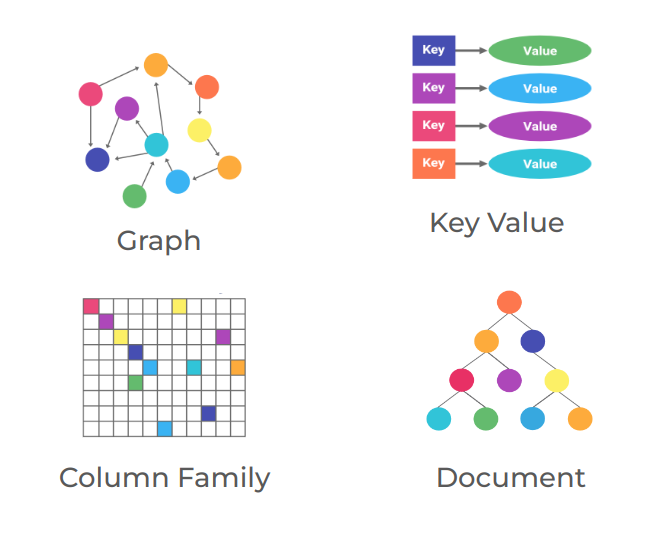
🌟 Why NoSQL? 🌟
NoSQL, short for "Not Only SQL," offers a fresh approach to managing data that goes beyond traditional relational databases.
The two key advantages of NoSQL databases are:
🌟 Flexibility
Adapt and evolve your data structure with ease as your application grows and changes.🚀 High Scalability
Effortlessly scale your database to handle large volumes of data and high traffic, perfect for modern, dynamic applications.
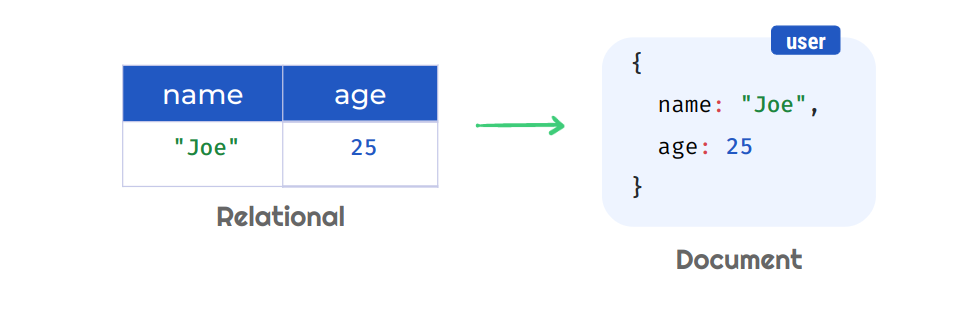
Let's take a Document Database as an example:
Instead of using rigid tables and rows like in a relational database, data is stored as JSON-like objects, giving you more flexibility and speed.
But there's more! MongoDB—a popular NoSQL database—actually stores data in BSON format, which stands for Binary JSON. This format allows data to be traversed and accessed even faster than with regular JSON, making MongoDB a powerful choice for handling large-scale, complex data.
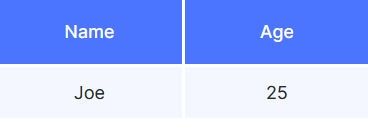
{
"name": "Joe",
"age": 25
}
Relational Database
Flexibility
For example, we are storing user details of an e-commerce application in a Document database.
First storing the subscription expiry date of a prime user, we can add new keys to documents as and when required.
We need not redesign tables(collections in MongoDB) & reorganize data for every change.
Non-Prime user
{
"name": "Joe",
"age": 25
}
Prime user
{
"name": "Sam",
"age": 25,
"expiry_date": "01-01-2022"
}
Unlike relational databases, We can store related data in a single document.
This makes querying simpler & faster as it doesn’t involve any join operations.
Relational Databases:
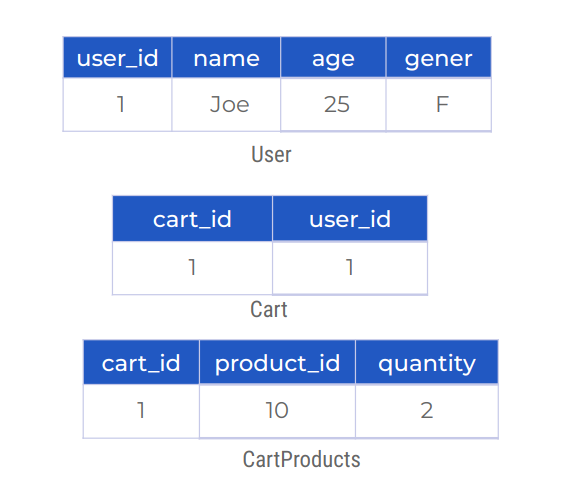
{
"user_id": 1,
"name": "Joe",
"age": 25,
"gender": "F",
"cart": [
{
"product_id": 10,
"quantity": 2
}
...
]
}
High Scalability
On a sale day like the Big Billion Day, the number of requests related to various purchases and products increases enormously.
Ideally, we would like to have our database serve the additional load without any issue
Scalability
The ability to serve the increasing number of incoming requests/data if necessary resources are given.
Built for Scale
NoSQL databases are designed to address scalability and performance issues that traditional relational databases encounter.
Various strategies which are followed are:
Support Horizontal Scaling
Sharding
Relaxation on ACID properties etc.
Advantages:
NoSQL databases are highly adopted in the industry
Document database is one of the most commonly used NoSQL databases
MongoDB
MongoDB is one of the most popular document databases and is used in popular stacks like MERN & MEAN, and it is a NoSQL document database.
Use cases:
Real-time Analytics
Gaming
Mobile Application Development
Internet of Things
Used By: MongoDB is used in the below companies

Collection
The group of documents is called as Collection
RDBMS vs MongoDB
Comparing the terminology and concepts used in Relational Database Management Systems (RDBMS) with those used in MongoDB.
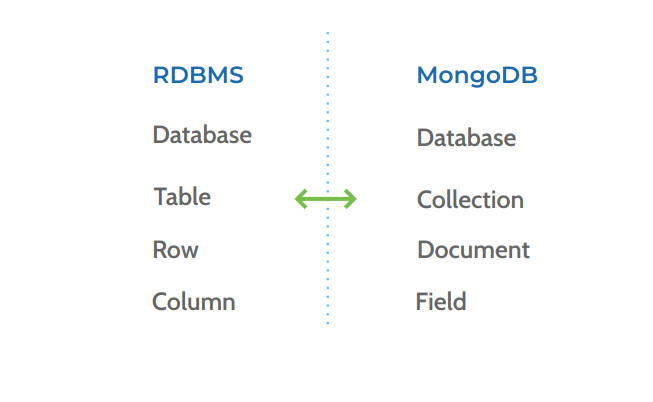
Table vs Collection:
In RDBMS, data is stored in Tables, which are structured with fixed schemas - each table has a defined set of columns and each row in the table is a record.
In MongoDB, the equivalent structure is called a Collection. Unlike tables, collections do not require a fixed schema, meaning that the documents (records) within a collection can have different fields.
In MongoDB, a field is a term that refers to a name-value pair in a document. Documents are composed of these fields, which are similar to columns in a relational database. Each field in a MongoDB document is a piece of data or an element with a name (also known as a "key") and a value.
Choosing a Database
Relational and non-relational databases solve different problems so when picking a DBMS choose the one that best solves the problem.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Narottam sharma directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
