Cyber Resilience
 วีระชัย แย้มวจี
วีระชัย แย้มวจี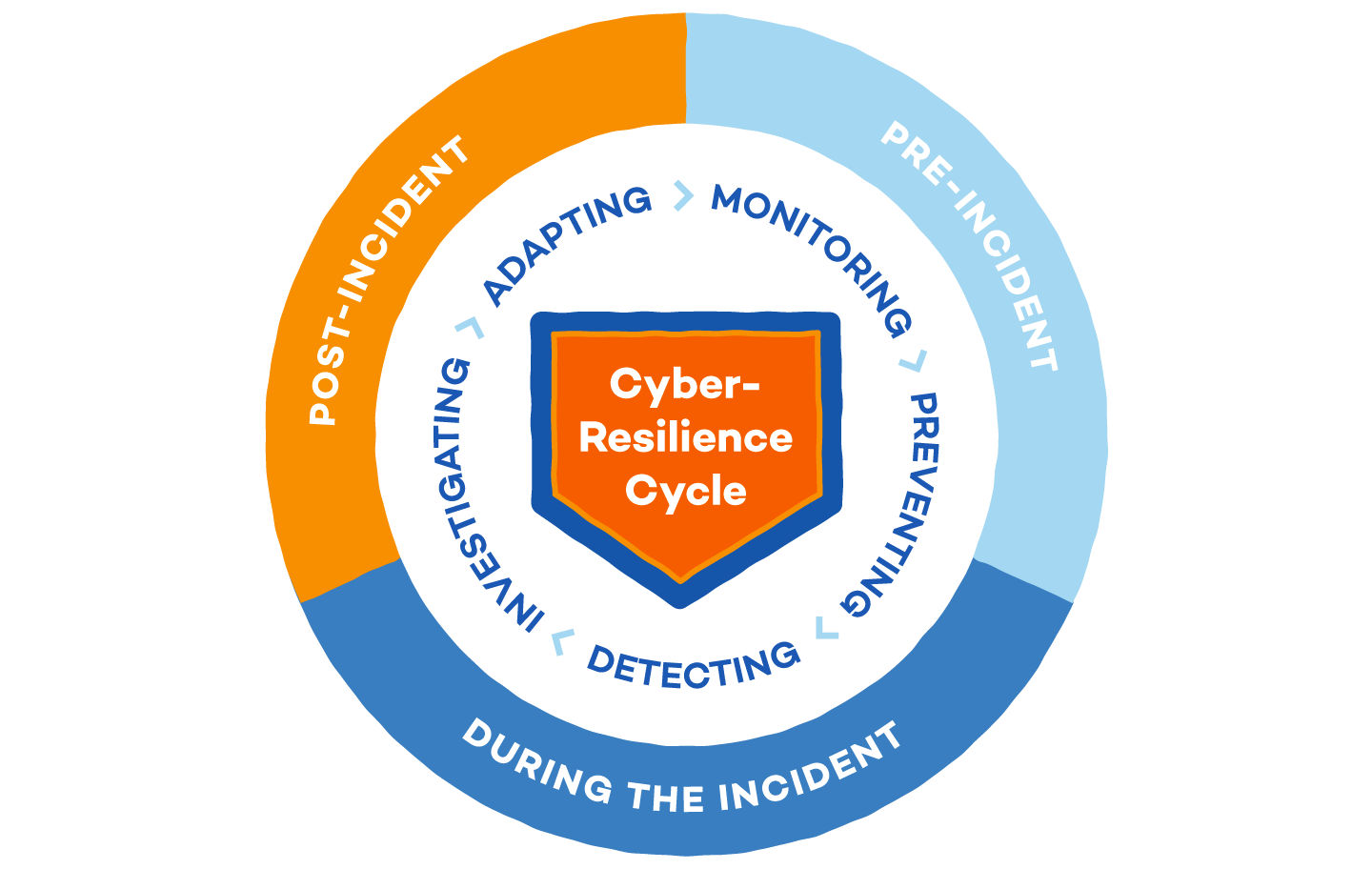
Cyber Resilience refers to an organization’s ability to continuously deliver the intended outcome despite adverse cyber events. It encompasses not just protecting against and responding to cyber threats, but also ensuring recovery and maintaining operations even when incidents occur. Here's a breakdown of key aspects related to cyber resilience:
Key Aspects of Cyber Resilience
Prevention:
Security Measures: Implementing robust security controls to prevent cyber attacks, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and secure coding practices.
Risk Assessment: Regularly identifying and evaluating potential vulnerabilities and threats.
Detection:
Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of systems and networks to detect unusual activity or breaches.
Incident Detection: Using tools and techniques to identify and respond to threats in real-time.
Response:
Incident Response Plan: Developing and maintaining a plan to respond to cybersecurity incidents effectively.
Communication: Ensuring clear communication with stakeholders during and after an incident.
Recovery:
Data Backup: Regularly backing up data and systems to ensure recovery in the event of an attack.
Business Continuity Planning: Creating plans to maintain essential functions and services during and after an incident.
Adaptation:
Learning and Improvement: Analyzing incidents and near-misses to improve defenses and response strategies.
Updating Policies: Regularly reviewing and updating cybersecurity policies and procedures based on lessons learned.
Benefits of Cyber Resilience
Continuity of Operations: Ensures that critical business functions continue even in the face of cyber threats.
Reduced Downtime: Minimizes the impact and duration of disruptions caused by cyber incidents.
Enhanced Trust: Builds confidence among customers, partners, and stakeholders in the organization's ability to manage and recover from cyber threats.
Challenges
Complexity: Managing and integrating various aspects of cybersecurity and resilience can be complex and resource-intensive.
Evolving Threats: Adapting to new and emerging threats requires continuous vigilance and updating of strategies.
Resource Allocation: Balancing investment in preventive measures with the need for response and recovery capabilities.
Example Strategies
Regular Testing: Conducting regular drills and exercises to test incident response and recovery plans.
Integrated Approach: Combining cybersecurity with business continuity and disaster recovery planning.
Collaboration: Working with external partners and experts to enhance resilience and share threat intelligence.
Summary
Cyber resilience goes beyond traditional cybersecurity by focusing not just on preventing and detecting threats but also on ensuring that an organization can continue to operate and recover effectively in the face of cyber incidents. It involves a holistic approach that integrates prevention, detection, response, recovery, and adaptation strategies.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from วีระชัย แย้มวจี directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

วีระชัย แย้มวจี
วีระชัย แย้มวจี
P@Ge2mE