SDLC - Software Development Life Cycle
 Mohammad Ali
Mohammad Ali
What is Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)?
SDLC is a structured process used by software organizations to build, maintain, replace, and enhance software. It consists of a detailed plan that outlines how to develop, maintain, replace, and enhance specific software. The life cycle aims to improve the quality of software and the overall development process.
Stages of the Software Development Life Cycle SDLC
It specifies the task(s) to be performed at various stages by a software engineer or developer. It ensures that the end product is able to meet the customer’s expectations and fits within the overall budget. Hence, it’s vital for a software developer to have prior knowledge of this software development process.
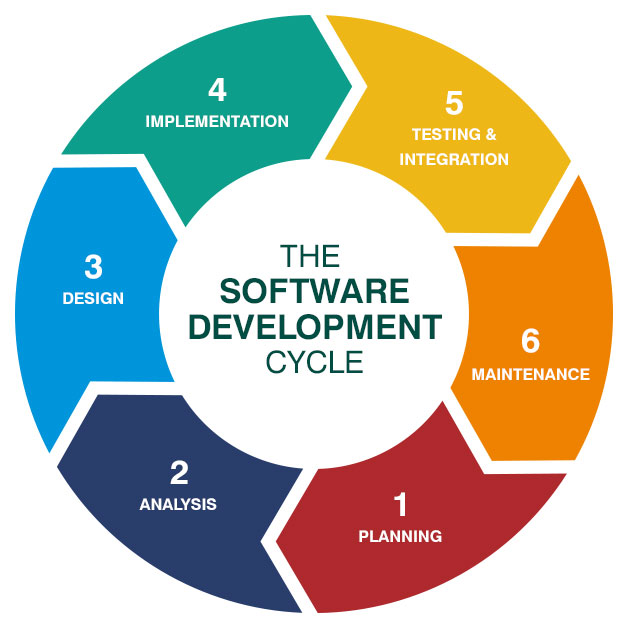
The SDLC model involves six phases or stages while developing any software. SDLC is a collection of these six stages, and the stages of SDLC are as follows:
Stage-1: Planning and Requirement Analysis
Planning is a crucial step in everything, just as in software development. In this same stage, requirement analysis is also performed by the developers of the organization. This is attained from customer inputs, and sales department/market surveys.
The information from this analysis forms the building blocks of a basic project. The quality of the project is a result of planning. Thus, in this stage, the basic project is designed with all the available information.
Planning Define
Project Scope
Set Objectives and Goals
Resource Planning
Stage-2: Defining Requirements
In this stage, all the requirements for the target software are specified. These requirements get approval from customers, market analysts, and stakeholders.
This is fulfilled by utilizing SRS (Software Requirement Specification). This is a sort of document that specifies all those things that need to be defined and created during the entire project cycle.
Defining
Functional Requirement
Technical Requirement
Requirement Reviews & Approved
Stage-3: Designing Architecture
SRS is a reference for software designers to come up with the best architecture for the software. Hence, with the requirements defined in SRS, multiple designs for the product architecture are present in the Design Document Specification (DDS).
This DDS is assessed by market analysts and stakeholders. After evaluating all the possible factors, the most practical and logical design is chosen for development.
Design Low
Level Design
High Level Design
Stage-4: Developing Product
At this stage, the fundamental development of the product starts. For this, developers use a specific programming code as per the design in the DDS. Hence, it is important for the coders to follow the protocols set by the association. Conventional programming tools like compilers, interpreters, debuggers, etc. are also put into use at this stage. Some popular languages like C/C++, Python, Java, etc. are put into use as per the software regulations.
Development
Coding Standard
Scalable Code
Version Control
Code Review
Stage-5: Product Testing and Integration
After the development of the product, testing of the software is necessary to ensure its smooth execution. Although, minimal testing is conducted at every stage of SDLC. Therefore, at this stage, all the probable flaws are tracked, fixed, and retested. This ensures that the product confronts the quality requirements of SRS.
Documentation, Training, and Support: Software documentation is an essential part of the software development life cycle. A well-written document acts as a tool and means to information repository necessary to know about software processes, functions, and maintenance. Documentation also provides information about how to use the product. Training in an attempt to improve the current or future employee performance by increasing an employee’s ability to work through learning, usually by changing his attitude and developing his skills and understanding.
System Testing
Manual Testing
Automated Testing
Stage-6: Deployment and Maintenance of Products
After detailed testing, the conclusive product is released in phases as per the organization’s strategy. Then it is tested in a real industrial environment. It is important to ensure its smooth performance. If it performs well, the organization sends out the product as a whole. After retrieving beneficial feedback, the company releases it as it is or with auxiliary improvements to make it further helpful for the customers. However, this alone is not enough. Therefore, along with the deployment, the product’s supervision.
Deployment and Maintenance
Release Planning
Deployment Automation
Maintenance
Feedback
Software Development Life Cycle Models
To this day, we have more than 50 recognized SDLC models in use. But None of them is perfect, and each brings its favourable aspects and disadvantages for a specific software development project or a team.
Top five most popular SDLC models below:
Waterfall Model: It is the fundamental model of the software development life cycle. This is a very simple model. The waterfall model is not in practice anymore, but it is the basis for all other SDLC models. Because of its simple structure, the waterfall model is easier to use and provides a tangible output. In the waterfall model, once a phase seems to be completed, it cannot be changed, and due to this less flexible nature, the waterfall model is not in practice anymore.
Agile Model: The agile model in SDLC was mainly designed to adapt to changing requests quickly. The main goal of the Agile model is to facilitate quick project completion. The agile model refers to a group of development processes. These processes have some similar characteristics but also possess certain subtle differences among themselves.
Iterative Model: In the Iterative model in SDLC, each cycle results in a semi-developed but deployable version; with each cycle, some requirements are added to the software, and the final cycle results in the software with the complete requirement specification.
Spiral Model: The spiral model in SDLC is one of the most crucial SDLC models that provides support for risk handling. It has various spirals in its diagrammatic representation; the number of spirals depends upon the type of project.
V-Shaped Model: The V-shaped model in SDLC is executed in a sequential manner in V-shape. Each stage or phase of this model is integrated with a testing phase. After every development phase, a testing phase is associated with it, and the next phase will start once the previous phase is completed, i.e., development & testing. It is also known as the verification or validation model.
Big Bang Model: The Big Bang model in SDLC is a term used to describe an informal and unstructured approach to software development, where there is no specific planning, documentation, or well-defined phases.
What is the need for SDLC?
SDLC is a method, approach, or process that is followed by a software development organization while developing any software. SDLC models were introduced to follow a disciplined and systematic method while designing software. With the software development life cycle, the process of software design is divided into small parts, which makes the problem more understandable and easier to solve. SDLC comprises a detailed description or step-by-step plan for designing, developing, testing, and maintaining the software.
Conclusion
The Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a structured process used by software organizations to build, maintain, and enhance software effectively. It involves six key stages: Planning and Requirement Analysis, Defining Requirements, Designing Architecture, Developing Product, Product Testing and Integration, and Deployment and Maintenance. Various models like Waterfall, Agile, Iterative, Spiral, V-Shaped, and Big Bang offer different approaches to these stages. SDLC ensures a high-quality development process, meeting customer expectations and staying within budget, crucial for achieving software development goals efficiently.
All the above content, I read from GeeksForGeeks and seen some YouTube tutorial: Intro to SDLC.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Mohammad Ali directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
