Day 7 #KubeWeek : Mastering kubectl Commands, Analyzing Logs, and Debugging Container Images
 Gunjan Bhadade
Gunjan Bhadade
Welcome to the final day of #KubeWeek! Today, we'll focus on some of the most essential skills for any Kubernetes practitioner: mastering kubectl commands, analyzing logs, and debugging container images. These skills are crucial for managing and troubleshooting Kubernetes clusters effectively. Let's dive in! 🚀
Mastering kubectl Commands
kubectl is the command-line tool for interacting with your Kubernetes cluster. Here are some essential commands and their uses:
Basic Commands
Cluster Information
kubectl cluster-info
Provides information about the cluster.
Get Resources
kubectl get pods kubectl get services kubectl get deployments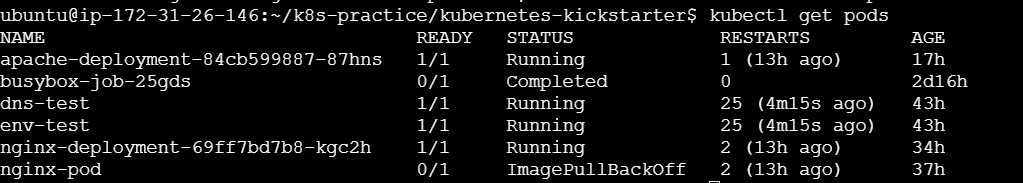


Lists various resources within the cluster.
Describe Resources
kubectl describe pod <pod-name> kubectl describe service <service-name> kubectl describe deployment <deployment-name>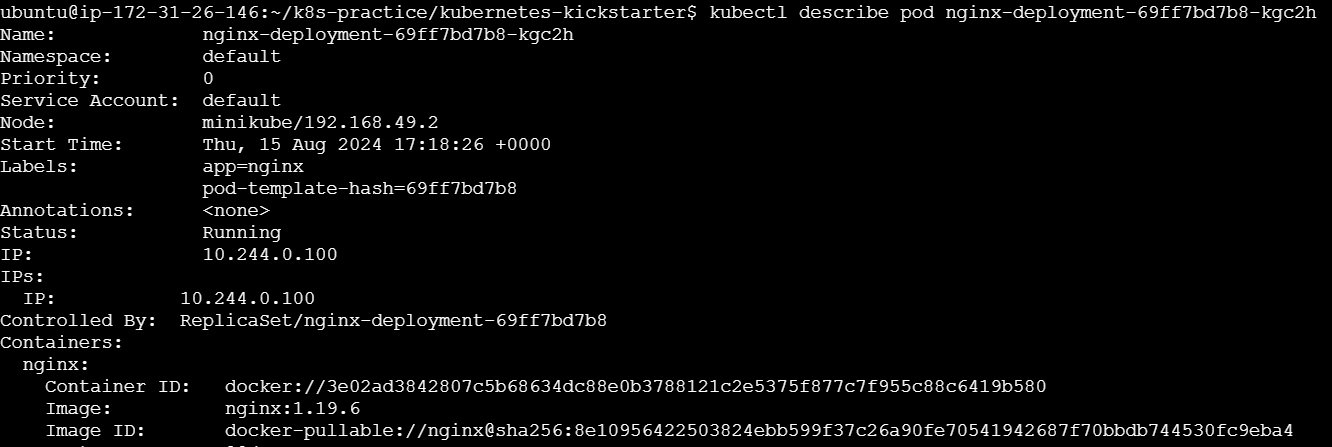
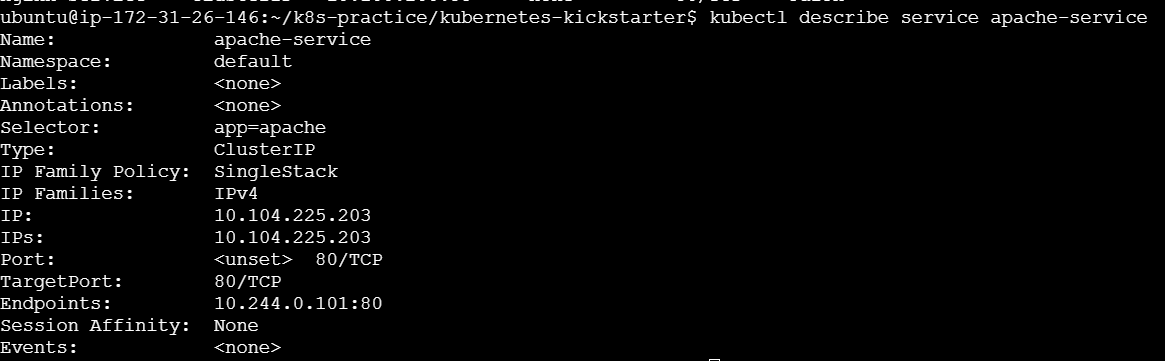
Provides detailed information about a specific resource.
Create, Apply, and Delete Resources
kubectl create -f <file.yaml> kubectl apply -f <file.yaml> kubectl delete -f <file.yaml>Creates, updates, or deletes resources defined in a YAML file.
Advanced Commands
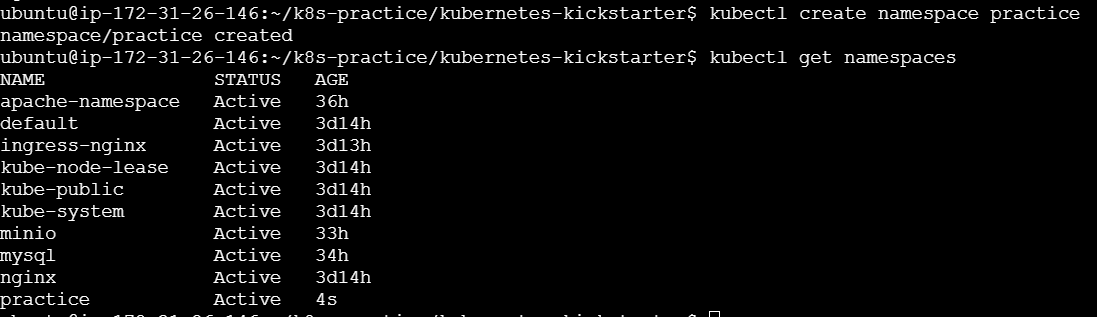
Namespace Management
kubectl get namespaces kubectl create namespace <namespace-name> kubectl delete namespace <namespace-name>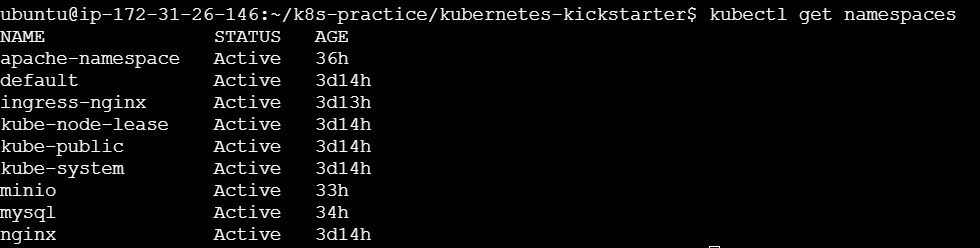

Scaling Deployments
kubectl scale deployment <deployment-name> --replicas=<number>Port Forwarding
kubectl port-forward pod/<pod-name> <local-port>:<pod-port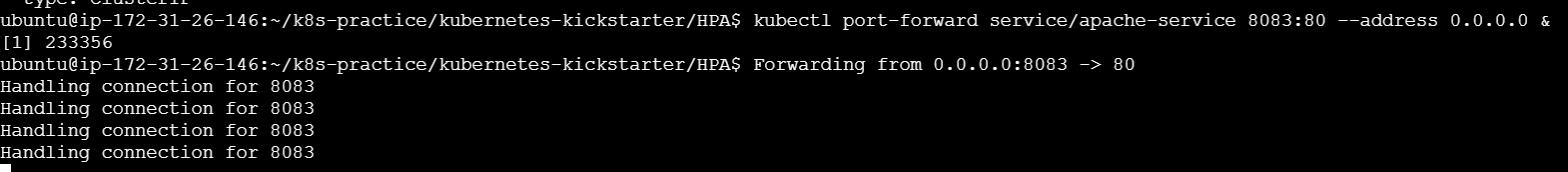
Forwards traffic from a local port to a port on a pod.
Execute Commands in a Pod
kubectl exec -it <pod-name> -- /bin/bashOpens an interactive shell inside a pod.
View Resource Usage
kubectl top nodes kubectl top pods
Analyzing Logs
Logs are crucial for debugging and understanding what's happening inside your applications and pods. Here are some key commands:
View Pod Logs
kubectl logs <pod-name>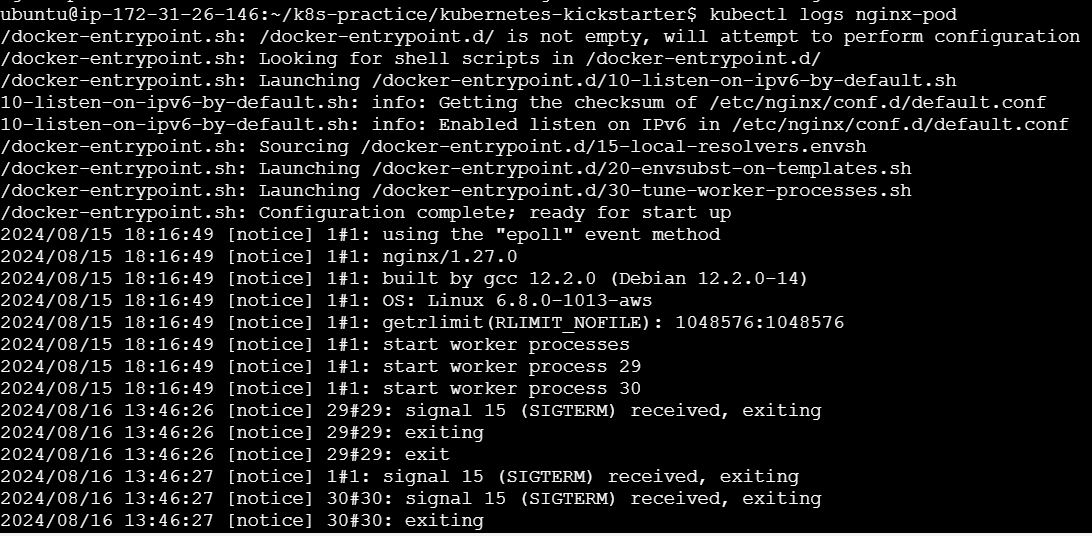
View Logs for a Specific Container in a Pod
kubectl logs <pod-name> -c <container-name>Stream Logs in Real-Time
kubectl logs -f <pod-name>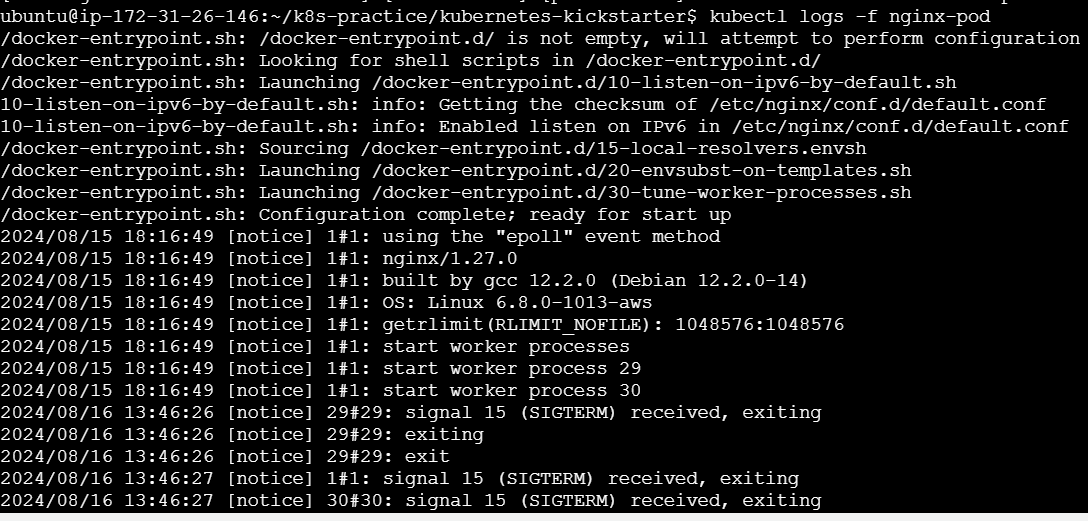
View Logs for All Pods in a Deployment
kubectl logs deployment/<deployment-name>View Previous Logs
kubectl logs <pod-name> --previous
Debugging Container Images
Debugging container images involves inspecting the state of running containers and troubleshooting issues. Here are some techniques:
Inspecting Pod Status
kubectl get pods kubectl describe pod <pod-name>Accessing a Container Shell
kubectl exec -it <pod-name> -- /bin/bash
Debugging Init Containers
kubectl describe pod <pod-name>Look for the status of init containers in the pod description.
Debugging CrashLoopBackOff Errors
Check the pod events and logs:
kubectl describe pod <pod-name> kubectl logs <pod-name>
Using Ephemeral Debug Containers Kubernetes 1.18 introduced ephemeral containers for debugging:
kubectl debug -it <pod-name> --image=<debug-image> --target=<container-name>Debugging Network Issues Use tools like
curl,ping, andnslookupwithin the pod:kubectl exec -it <pod-name> -- /bin/bash curl <service-url> ping <service-url> nslookup <service-url>
Conclusion
On this final day of #KubeWeek, we've covered some of the most critical skills for managing and troubleshooting Kubernetes clusters. Mastering kubectl commands, analyzing logs, and debugging container images are essential for maintaining a healthy and efficient Kubernetes environment. By leveraging these tools and techniques, you'll be well-equipped to handle any challenges that arise in your Kubernetes journey.
Thank you for joining us on this #KubeWeek adventure. Keep learning, keep experimenting, and happy clustering! 🚀
Feel free to reach out with any questions or thoughts in the comments below. Happy DevOps-ing! 🚀
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Gunjan Bhadade directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
