Kubernetes end-to-end project with deployment of Django notes application
 Rajat Chauhan
Rajat Chauhan
This project extends the deployment of a Django Notes application, initially containerized and pushed to DockerHub, by deploying and managing it on a Kubernetes cluster using Minikube. The application will be deployed using the chauhanrajat/note-app-jenkins:latest Docker image within a dedicated Kubernetes namespace, notes-app, ensuring a robust, scalable, and secure environment.
Minikube Cluster Installation
Before proceeding, ensure that Minikube is installed on your system. For detailed steps, refer to the Minikube Installation Guide.
Step 1: Namespace Creation
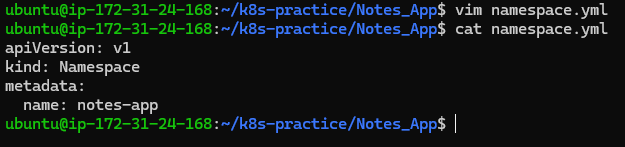
To organize Kubernetes resources, create a dedicated namespace named notes-app.
namespace.yml:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: notes-app
Apply the namespace configuration:
kubectl apply -f namespace.yml

Step 2: Deployment Creation
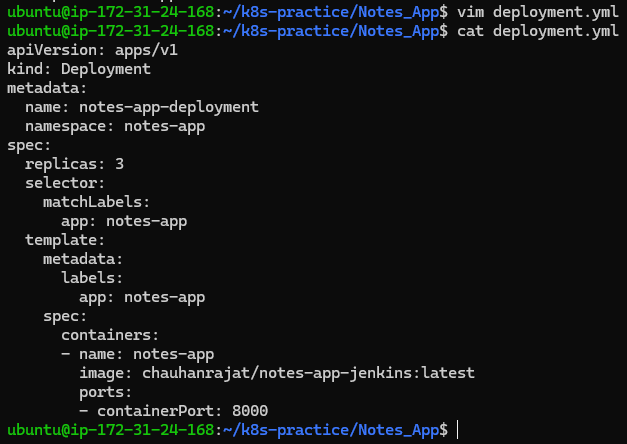
Deploy the notes-app using a Deployment resource to manage replicas and application updates.
deployment.yml:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: notes-app-deployment
namespace: notes-app
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: notes-app
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: notes-app
spec:
containers:
- name: notes-app
image: chauhanrajat/note-app-jenkins:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 8000
Apply the deployment configuration:
kubectl apply -f deployment.yml

Step 3: Service Creation
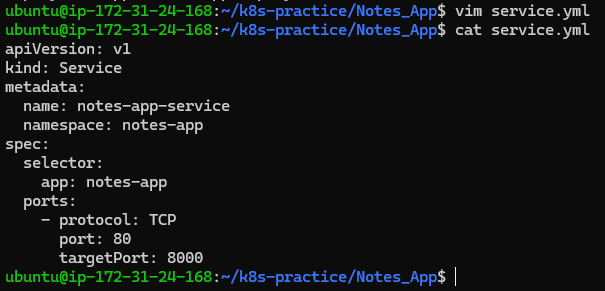
Expose the notes-app deployment using a Kubernetes Service to enable external access.
service.yml:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: notes-app-service
namespace: notes-app
spec:
selector:
app: notes-app
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 8000
Apply the service configuration:
kubectl apply -f service.yml

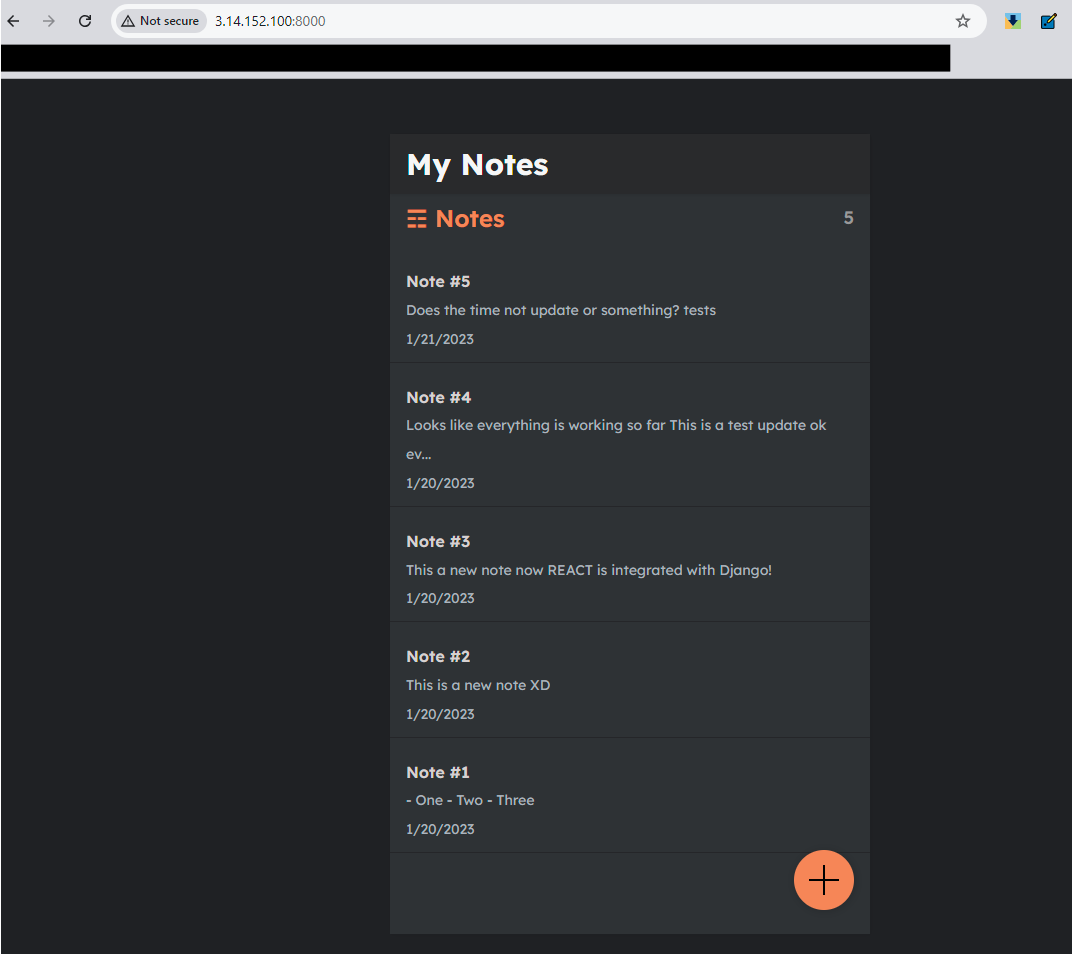
For testing, use port forwarding to access the application:
kubectl port-forward service/notes-app-service 8000:80 --address=0.0.0.0 -n notes-app
- For testing, port forwarding of traffic.

- Copy the Public IP of the instance with port 8000 and access the application on the browser.
Step 4: Persistent Volumes and Claims
Set up Persistent Volumes (PV) and Persistent Volume Claims (PVC) to handle persistent storage for the application.
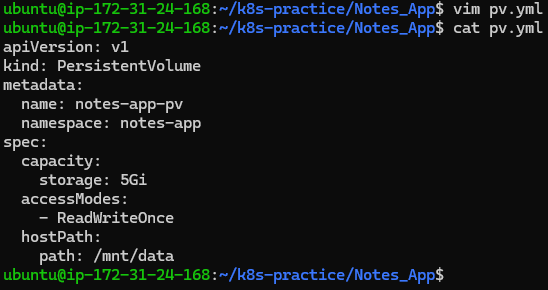
pv.yml:
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: notes-app-pv
namespace: notes-app
spec:
capacity:
storage: 5Gi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
hostPath:
path: /mnt/data
Apply the PersistentVolume configuration:
kubectl apply -f pv.yml

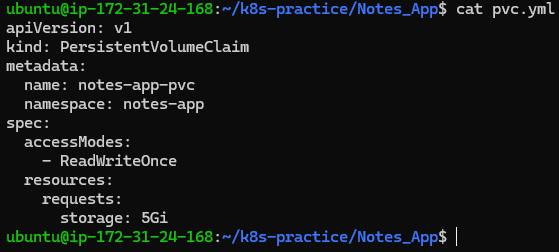
pvc.yml:
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: notes-app-pvc
namespace: notes-app
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 5Gi
Apply the PersistentVolumeClaim configuration:
kubectl apply -f pvc.yml

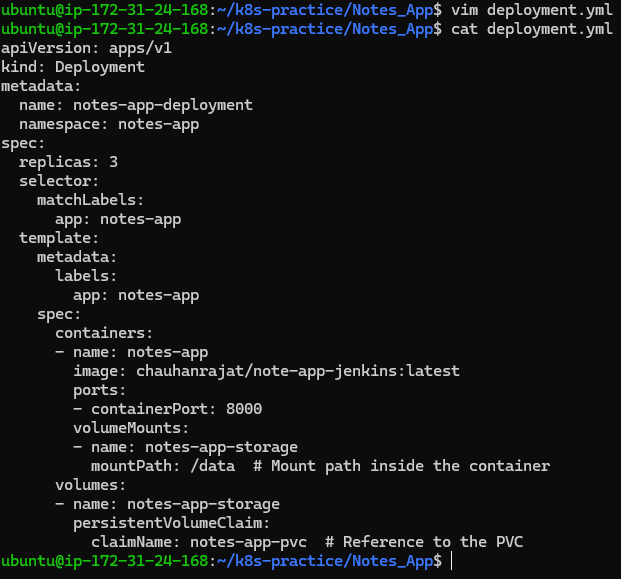
Update the deployment to attach the persistent storage:
iapiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: notes-app-deployment
namespace: notes-app
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: notes-app
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: notes-app
spec:
containers:
- name: notes-app
image: chauhanrajat/note-app-jenkins:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 8000
volumeMounts:
- name: notes-app-storage
mountPath: /data # Mount path inside the container
volumes:
- name: notes-app-storage
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: notes-app-pvc # Reference to the PVC
Apply the deployment configuration:
kubectl apply -f deployment.yml
Step 5: Ingress Controller
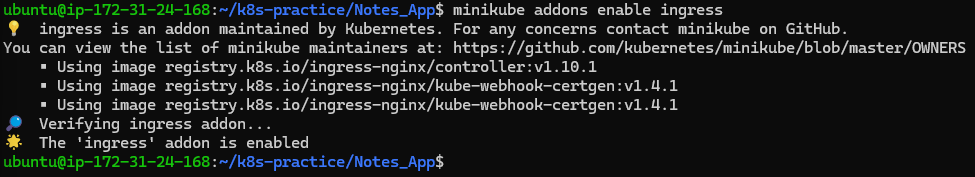
Enable the Ingress addon in Minikube for path-based routing:
minikube addons enable ingress
Set up an Ingress resource for the application:
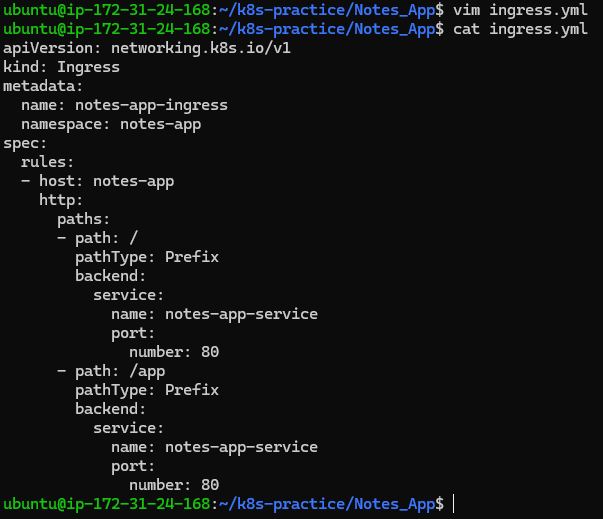
ingress.yml:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: notes-app-ingress
namespace: notes-app
spec:
rules:
- host: notes-app
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: notes-app-service
port:
number: 80
- path: /app
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: notes-app-service
port:
number: 80
Apply the Ingress configuration:
kubectl apply -f ingress.yml

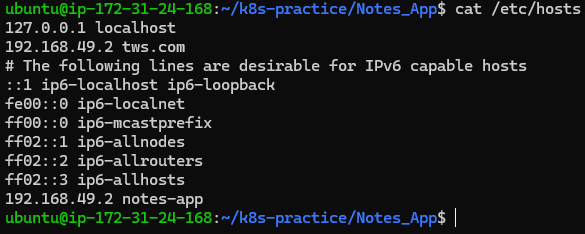
Add a domain entry in /etc/hosts:
sudo nano /etc/hosts
Test the application by sending a query to the URL:
curl notes-app
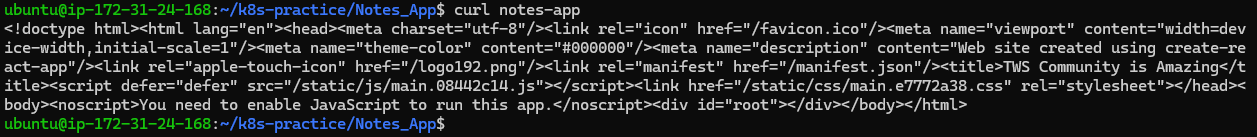
- This is what we called it as path-based routing using the Ingress controller.
Step 6: Network Policies and CNI
Define Network Policies to control the network traffic between pods.
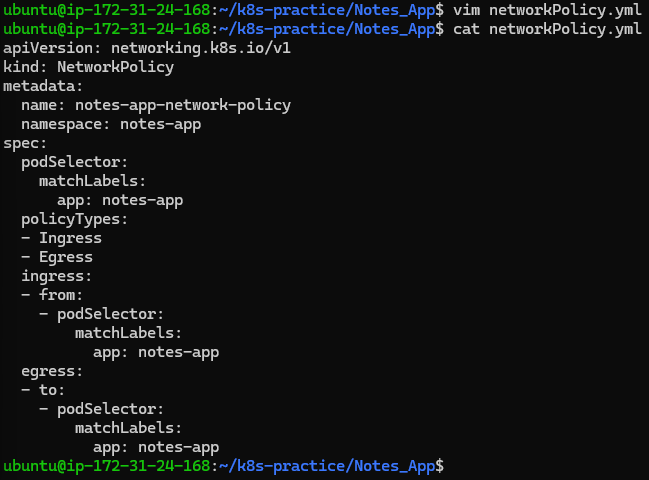
networkPolicy.yml:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: NetworkPolicy
metadata:
name: notes-app-network-policy
namespace: notes-app
spec:
podSelector:
matchLabels:
app: notes-app
policyTypes:
- Ingress
- Egress
ingress:
- from:
- podSelector:
matchLabels:
app: notes-app
egress:
- to:
- podSelector:
matchLabels:
app: notes-app
Apply the NetworkPolicy configuration:
kubectl apply -f networkPolicy.yml

Step 7: Job and CronJob
Define a Job for one-time tasks and a CronJob for scheduled tasks.
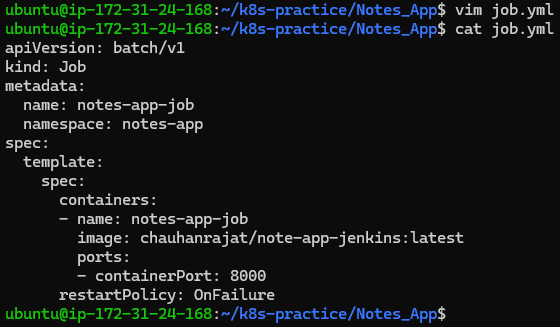
job.yml:
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: notes-app-job
namespace: notes-app
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: notes-app-job
image: chauhanrajat/note-app-jenkins:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 8000
restartPolicy: OnFailure
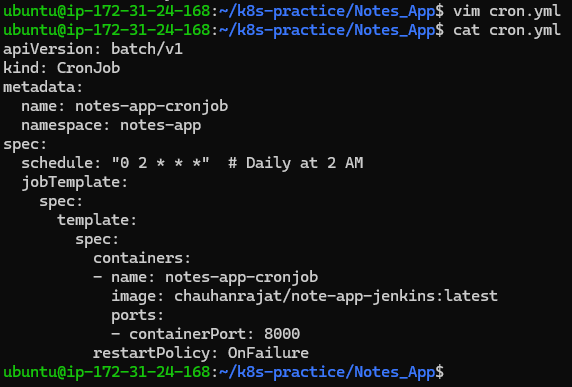
cron.yml:
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: CronJob
metadata:
name: notes-app-cronjob
namespace: notes-app
spec:
schedule: "0 2 * * *" # Daily at 2 AM
jobTemplate:
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: notes-app-cronjob
image: chauhanrajat/note-app-jenkins:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 8000
restartPolicy: OnFailure
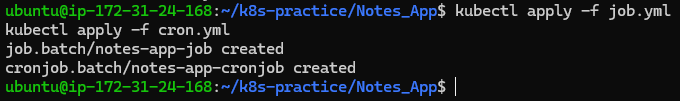
Apply the configurations:
kubectl apply -f job.yml
kubectl apply -f cron.yml
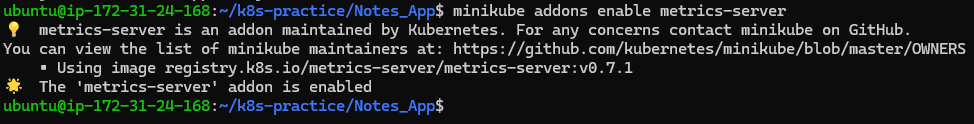
Step 8: Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA)
Enable the metrics-server addon in Minikube for HPA:
minikube addons enable metrics-server
Modify the deployment to include resource limits:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: notes-app-deployment
namespace: notes-app
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: notes-app
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: notes-app
spec:
containers:
- name: notes-app
image: chauhanrajat/note-app-jenkins:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 8000
resources:
requests:
cpu: "100m"
limits:
cpu: "200m"
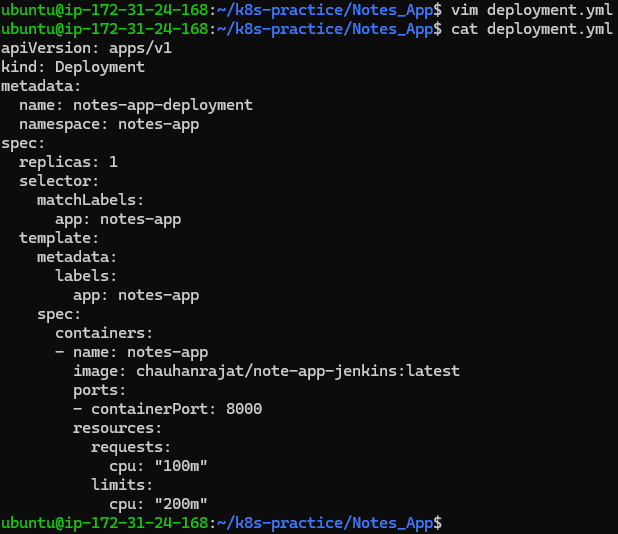
Implement HPA:
hpa.yml:
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: notes-app-hpa
namespace: notes-app
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: notes-app-deployment
minReplicas: 1
maxReplicas: 5
metrics:
- type: Resource
resource:
name: cpu
target:
type: Utilization
averageUtilization: 15
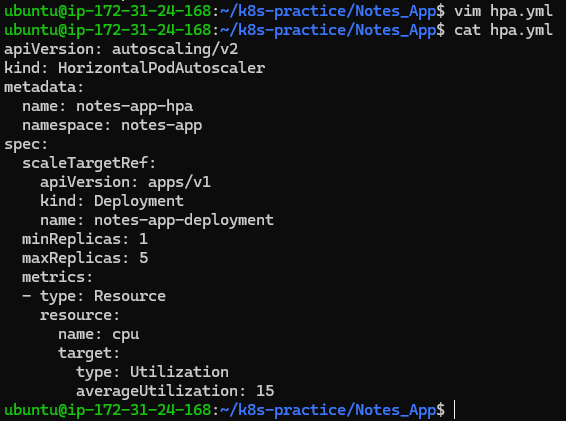
Apply the HPA configuration:
kubectl apply -f hpa.yml

Monitor CPU utilization and autoscaling:
watch kubectl get hpa -n notes-app

Step 9: Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Create a service account:
kubectl create serviceaccount k8s-user

Define a Role and RoleBinding for RBAC:
role.yml:
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: notes-app-role
namespace: notes-app
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
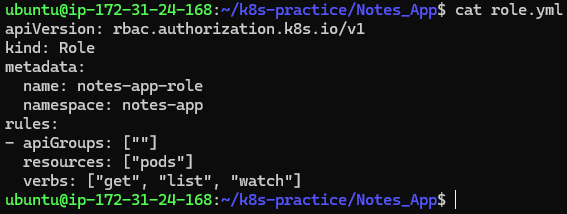
roleBinding.yml:
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: notes-app-rolebinding
namespace: notes-app
subjects:
- kind: User
name: k8s-user # Replace with your Kubernetes user
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: notes-app-role
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
Role defines permissions, and RoleBinding assigns those permissions to a user or set of users.
Testing of RBAC configurations,
Run commands using --as=user flag (Where
useris the name of the user you wish to impersonate.)As
k8s-userhas to get permission,
Step 10: Testing application on the browser
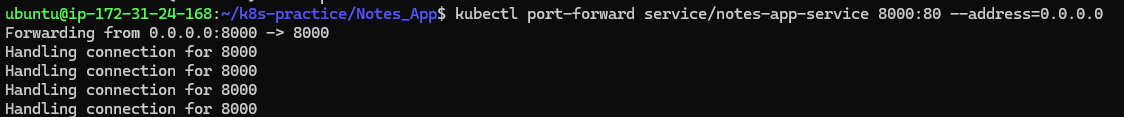
- Forward port on containerPort from the local port and try to access the application,
kubectl port-forward service/notes-app-service 8000:80 --address=0.0.0.0 -n notes-app

Thank you for taking the time to read! 💚
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Rajat Chauhan directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Rajat Chauhan
Rajat Chauhan
Rajat Chauhan is a skilled Devops Engineer, having experience in automating, configuring, deploying releasing and monitoring the applications on cloud environment. • Good experience in areas of DevOps, CI/CD Pipeline, Build and Release management, Hashicorp Terraform, Containerization, AWS, and Linux/Unix Administration. • As a DevOps Engineer, my objective is to strengthen the company’s applications and system features, configure servers and maintain networks to reinforce the company’s technical performance. • Ensure that environment is performing at its optimum level, manage system backups and provide infrastructure support. • Experience working on various DevOps technologies/ tools like GIT, GitHub Actions, Gitlab, Terraform, Ansible, Docker, Kubernetes, Helm, Jenkins, Prometheus and Grafana, and AWS EKS, DevOps, Jenkins. • Positive attitude, strong work ethic, and ability to work in a highly collaborative team environment. • Self-starter, Fast learner, and a Team player with strong interpersonal skills • Developed shell scripts (Bash) for automating day-to-day maintenance tasks on top of that have good python scripting skills. • Proficient in communication and project management with good experience in resolving issues.