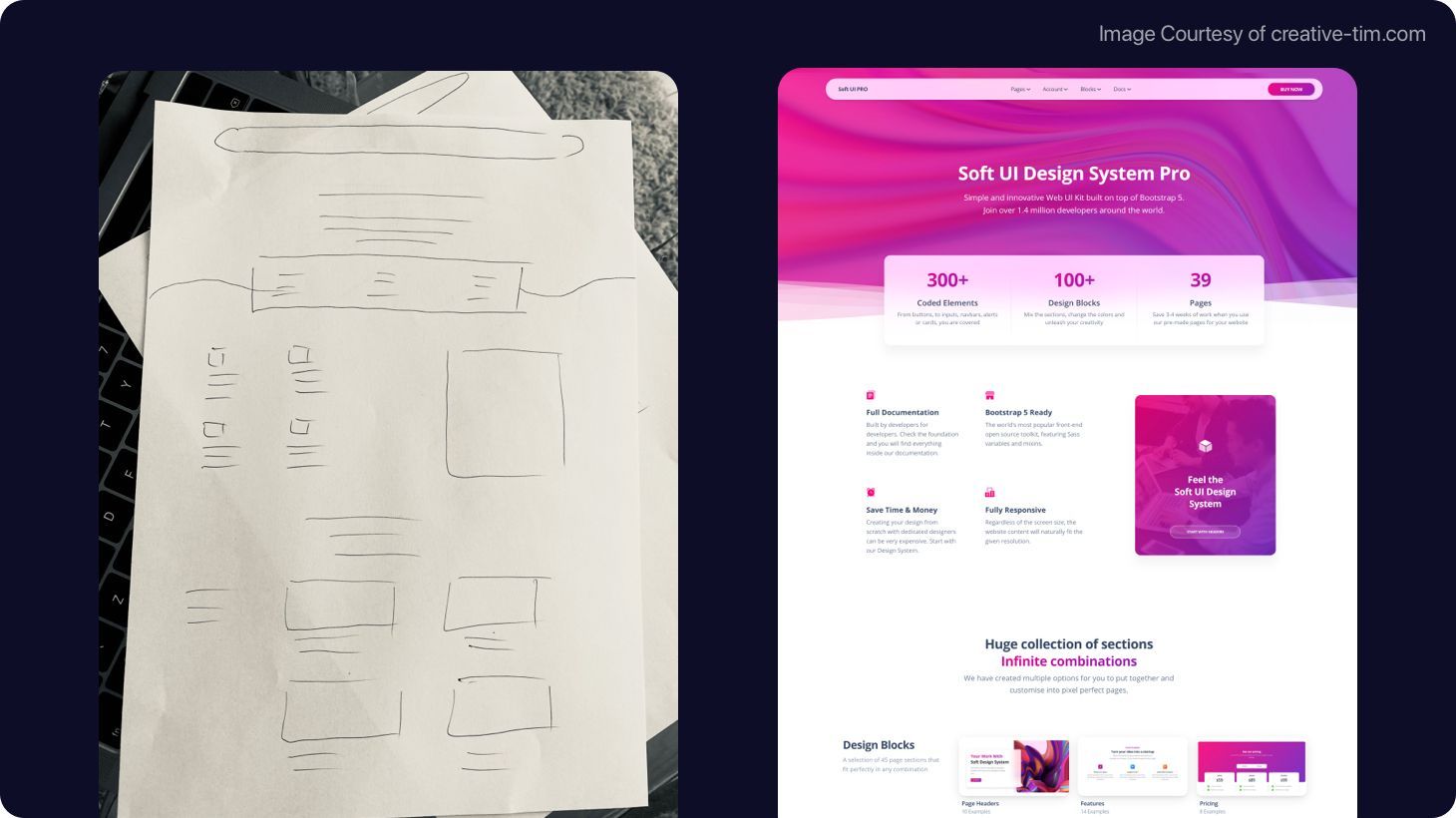
UI/UX Design Guide: What Are UI Designers, and How Are They Different Than UX Designers?
 Alexandru Paduraru
Alexandru Paduraru
Have you noticed how User Interface and User Experience design are considered different topics nowadays?
You're not the only one.
We live in a beautiful era of design, with new techniques and trends coming and going. Frontend development is also gaining increased momentum, with more and more developers getting involved in UI/UX design.
While both UI and UX design are often placed on the same pedestal, they are fundamentally different, and beginners should understand the difference between the two.
Knowing this, my team from Creative Tim and I have done a lot of research and created a comprehensive guide on the most important parts of these two huge domains:
- UI Design — How Things Look
- UX Design — How Things Work
- What Are the Key Differences Between UI and UX Design?
- What Do UI/UX Designers Do?
- What Are the Disadvantages of a Combined UI/UX Role?
- How Do UI/UX Designers Work Together?
- What Are the Salaries of UI and UX Designers?
- How Do You Become a UI or UX Expert? What Kind of Design Courses/Tutorials Should You Take?
- Which Should You Specialize In? UI or UX Design?
UI Design — How Things Look

A UI (User Interface) deals with the application's graphical layout, which includes buttons, screen layout, animations, transitions, micro-interactions, and so on. In short, UI is all about how things look.
UI design includes the following formats:
- Graphical User Interface (GUI): GUI design involves how users interact with the visuals and digital control panels of a system. The computer's desktop is an example of a GUI.
- Voice-controlled Interface (VUI): VUI design deals with the interaction between a user and a system using voice. Smart assistants like Bixby for Samsung mobile devices and Siri for iPhones are examples of VUIs.
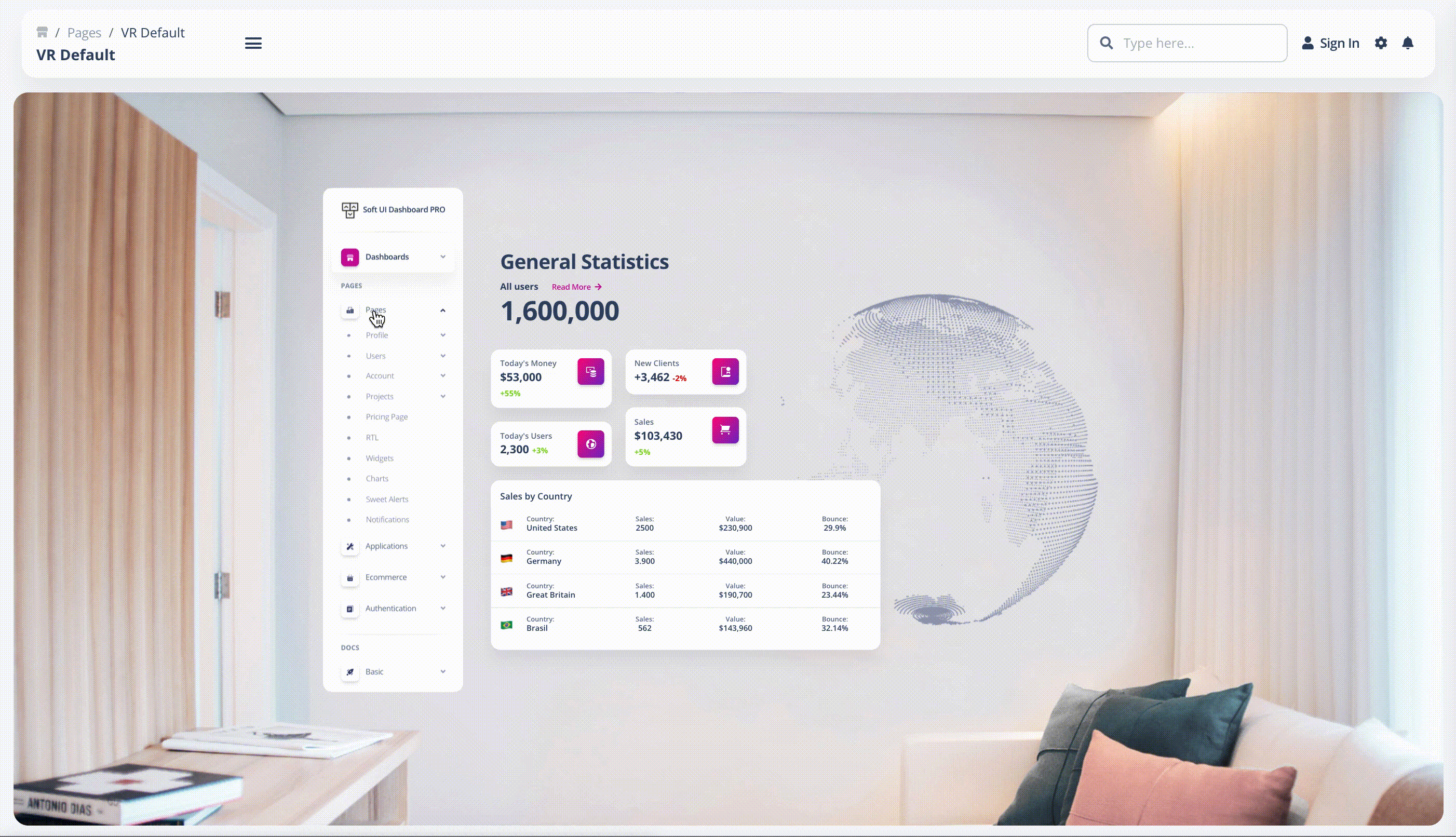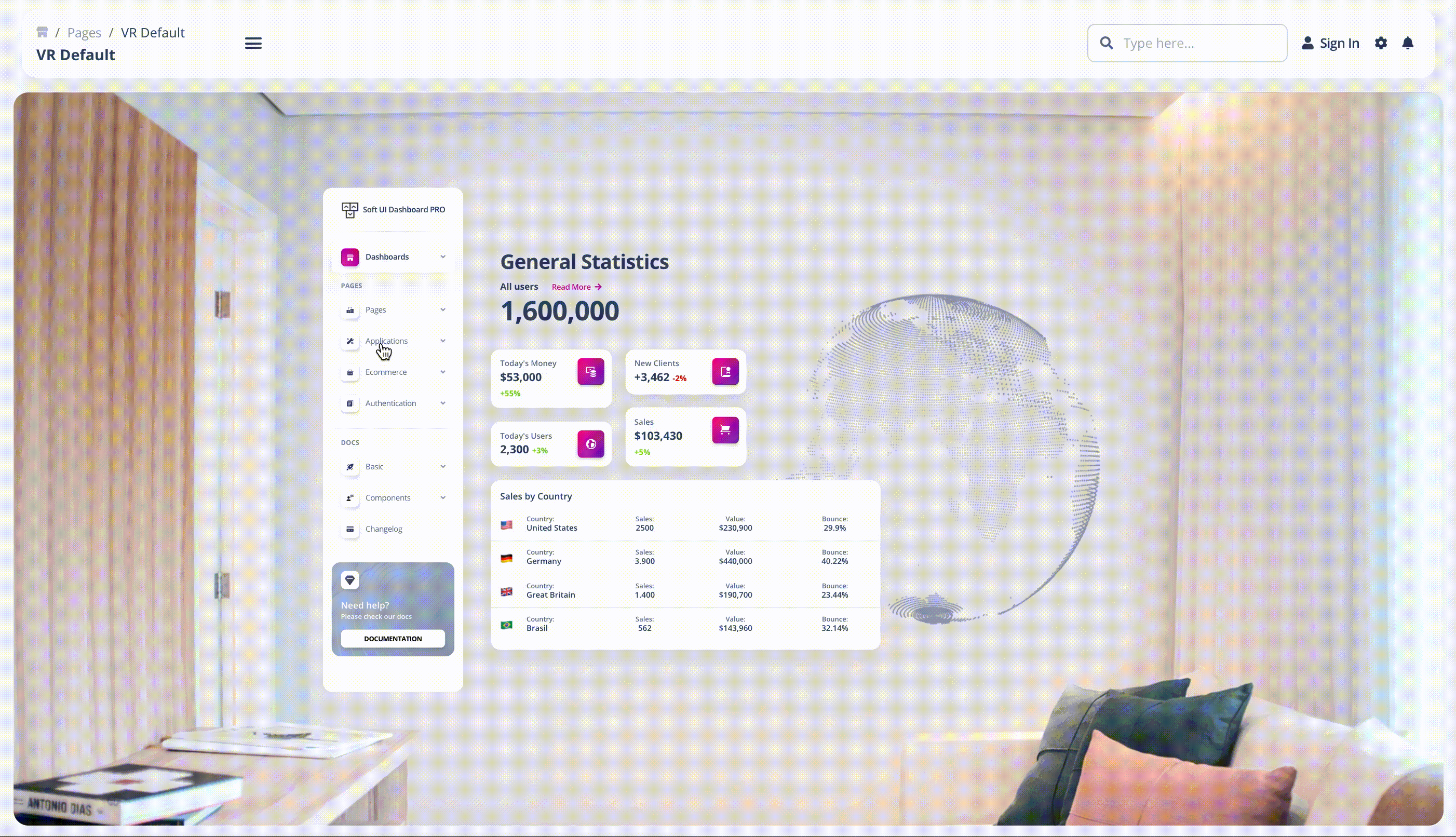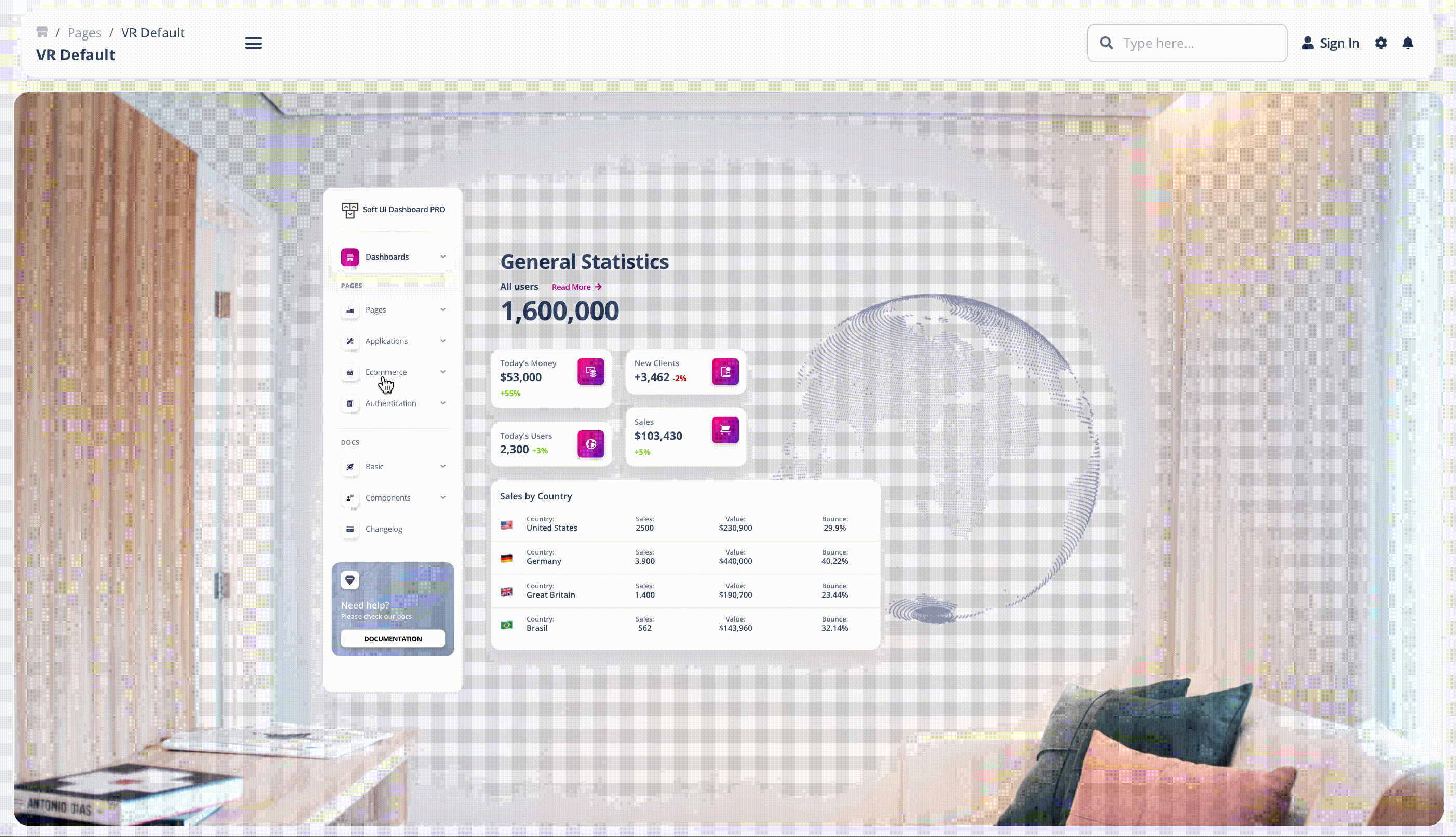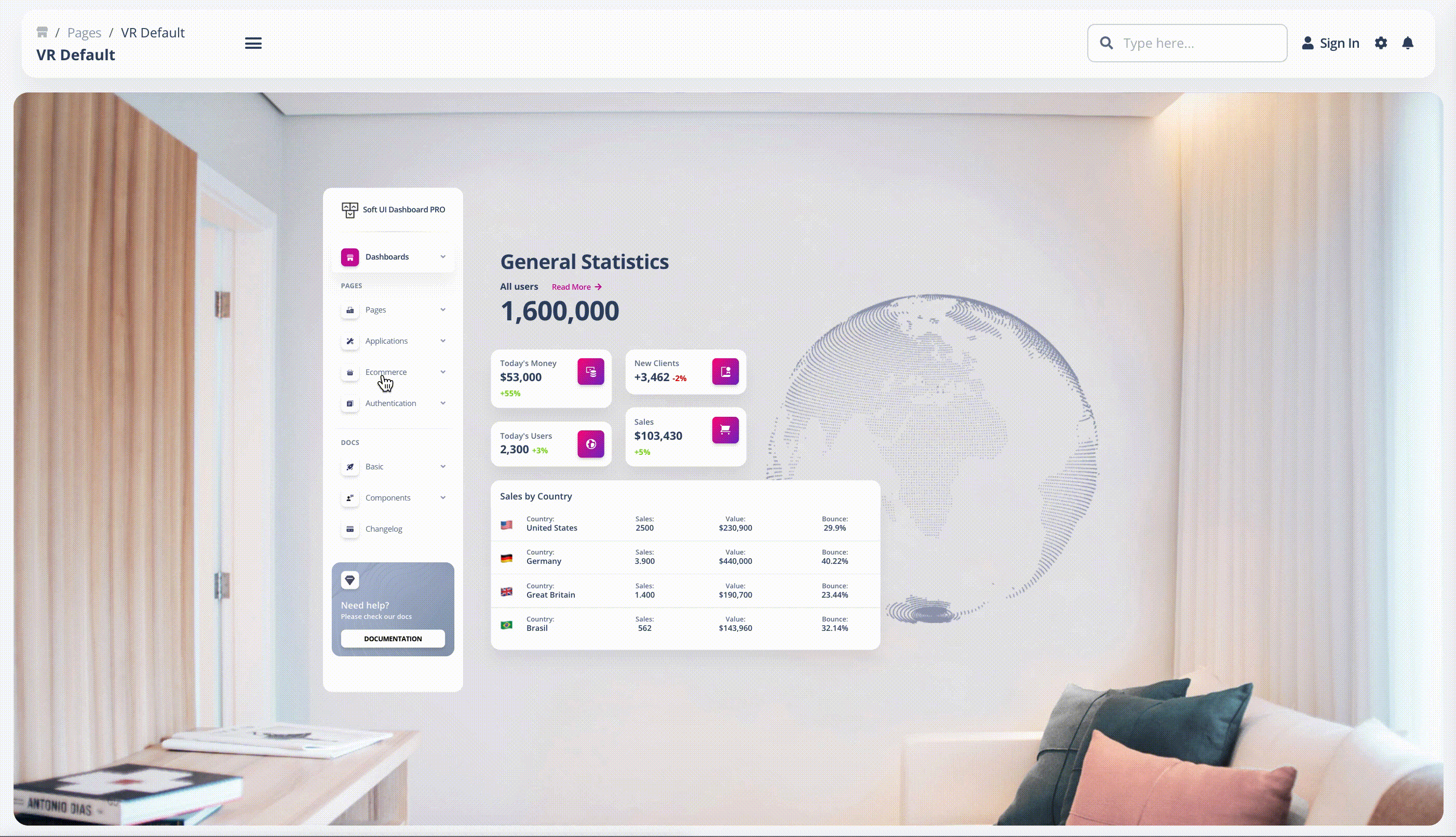
- Gesture-based Interface: This is mostly used in virtual reality (VR) and other gesture-based design scenarios, which deal with the engagement of users within 3D spaces. Here is an example of our fully coded simulation of the Soft UI Admin Dashboard in VR:
For good UI design, you should take these characteristics into consideration:
- The design should be focused on helping users complete tasks quickly with minimum effort. Completing tasks should be a seamless experience.
- It should be enjoyable, satisfactory, and free from frustration.
- The UI design should communicate the brand value of the company/organization.

UX Design — How Things Work
UX (User Experience) design deals with how users interact with the system. Logical navigation and how smooth and intuitive the experience is all fall under UX design. In short, this type of design helps users have a positive experience.
To get a feeling of the UX process, here are the main steps:
- Interaction Design deals with how users can complete their tasks effortlessly by using the interactive components of a system (page transitions, animations, buttons, and so on).
- User Research involves conducting extensive research, collecting feedback and ideas from new or existing customers, understanding end user needs, and making design decisions based on these parameters.
- Information Architecture involves the organization of information and content that users need to do their tasks. This requires a UX designer to understand the relationship between different sets of content and present them in the most understandable way possible.
For good UX design, you should follow these practices:
- The product should be easily usable, logical, and self-explanatory.
- The product should solve users's problems.
- The product should be accessible and usable to a wide range of people.
- The product should create a positive experience for the user, allowing them to complete tasks without frustration.
Cognitive Biases
Great UX designers must be aware of the cognitive biases that we all have, as this can affect the interaction between the user and interfaces. Many marketing strategies are based on these biases:

What Are the Key Differences Between UI and UX Design?

UI and UX design have often been used as interchangeable terms.
While the end product requires consideral input from both design methodologies, the process of designing UI and UX is very different.
UX design mostly deals with the user’s entire journey to solve a problem.
On the other hand, UI design is focused on how the product looks and feels when the problem is being solved.
Here are the main differences between UI and UX design:
- Main focus: The main focus of UI designers is to deal with the quality and visuals of the end product, and use hi-fi models as prototypes. UX designers focus more on the purpose and functionality of the end product, and care more about logic. Additionally, UI designers deal with the technicalities of the product design, while UX designers focus more on project management and analysis of the project.
- Use of color: UI designers design prototypes in full color while UX designers do so in black, white, or grey.
- Tools: UI designers use tools like Sketch, Flinto, Principle, and InVision for collaborative image designing. UX designers use wireframe-based prototyping tools like Mockplus.
- Artistic Component: UI designers have to include an artistic component in their design since it is related to what the end user sees, hears, and feels. UX design has more of a social component, as it needs to understand what a user wants to experience in the end product.
Here is an example of UX and UI prototypes for the same end product:
What Do UI/UX Designers Do?

If you want to become a greate UI designer, you should develop the following skills/responsibilities:
- Working in agile teams.
- Creating user flows, wireframes, prototypes and so on.
- Visualization tools such as InVision, Sketch, Photoshop, Figma, etc. For more details about which tool to choose, check out our research in this article: InVision vs Sketch vs Figma vs Photoshop
- Frontend programming languages such as HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScript.
- Executing visual design stages from inception to final hand-off.
- Collaborating with UX designers, developers, QA, and product managers to design and implement innovative visual ideas for products.
- Communicating the branding and style of the company to users through design.
- Creating the look and feel of the product using customer analysis and research.
- Managing the responsiveness, interactivity, and animation of a product and making it adaptive to all device screen sizes.
If you want to become a great UX designer, you should develop these skills/responsibilities:
- Working in agile teams.
- A strong understanding of the UX process.
- Prototyping tools like Adobe Creative Suite, Sketch, InVision, Axure, etc.
- Problem solving skills and curiosity about everything related to design, people, life and technology.
- Stakeholder management and client interaction.
- Creating process flows, wireframes, sitemaps, prototypes, and UX deliverables.
- Collaborating closely with developers, product managers, UI designers, external stakeholders, and QA Engineers to iterate designs based on market dynamics, user feedback, and tech constraints.
- Analyzing customer needs, competitors, product structure, and strategies for designing the experience of a product.
- Creating seamless design and interaction strategies for mobile, web, desktop, and other hardware endpoints.
What Are the Disadvantages of a Combined UI/UX Role?

Having a combined UI/UX role is almost like wearing two different hats at the same time.
While most organizations advertize a UI/UX role as a single, combined role, a UI and UX designers have different skill sets. Their main focus, way of thinking, and method of prototyping a product differ greatly.
A combined UI/UX role requires constant switching between conceptualization and visualization, which is often difficult and can reduce the amount of attention that each discipline requires.
How Do UI/UX Designers Work Together?

While UI design and UX design require very different skill sets, they are both important components that must work in harmony to give the best experience to end users.
A UI design might be beautiful, but it can be clunky and confusing to navigate without a good UX design. On the other hand, the user experience of a product can be flawless, but it is nothing without a good looking user interface.
Any frontend development and design process should start with understanding the needs of the user. UX and UI designers should work in collaboration with other developers, managers, and product owners to understand what the end product should be able to do, how it should feel, and what it should look like.

UX designers are generally involved in the earlier phases of a product design since they need to design the flow of activities that take place when a user needs to solve a problem. This involves analytic and project management activities.
Later, a UI designer builds on the aesthetics and interactions based on the models provided by the UX designer.
Given this, it is safe to state that UX and UI go hand in hand. And while there are instances when the same person does both, one design principle cannot exist without the other.
What Are the Salaries of UI and UX Designers?
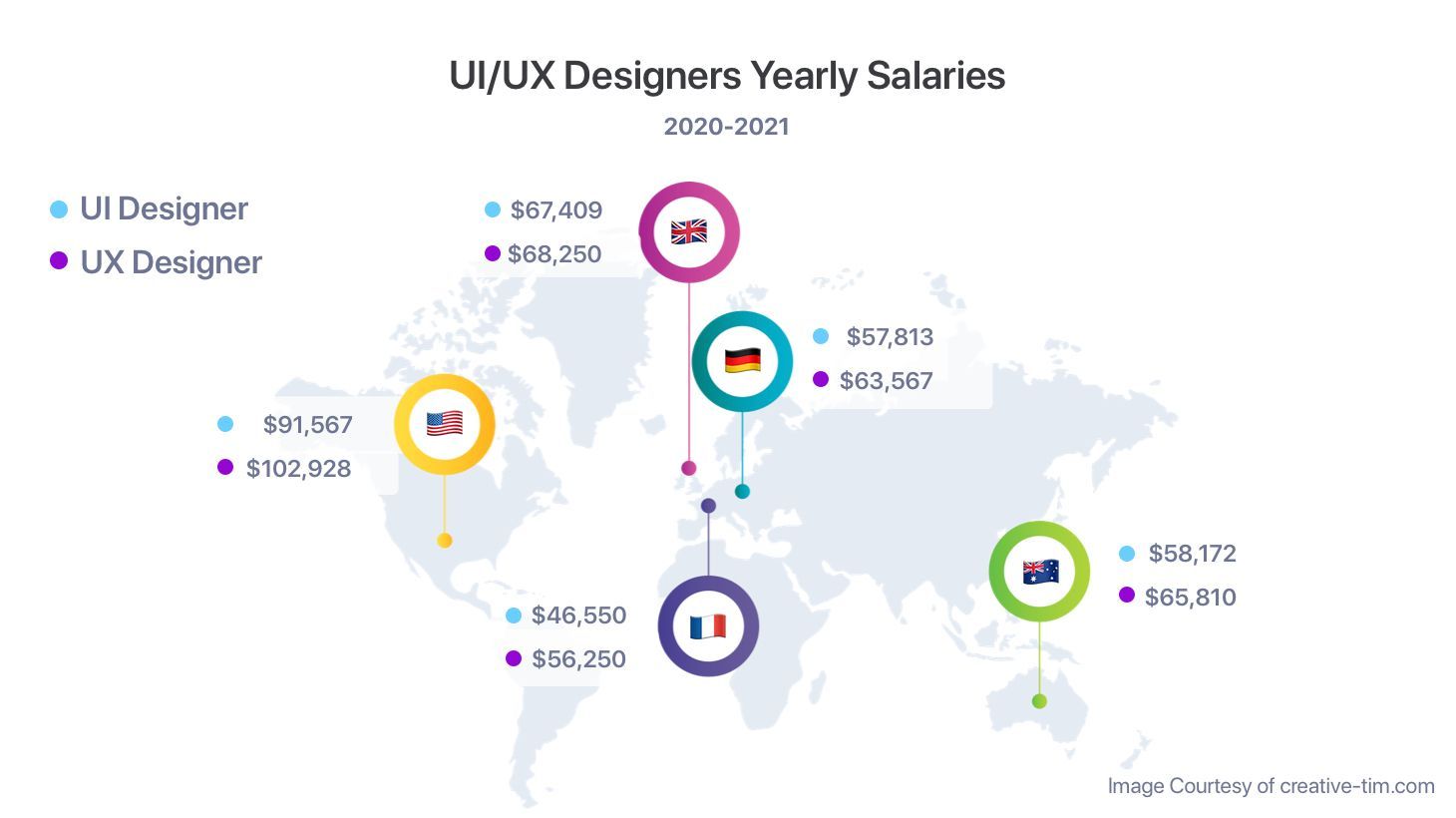
UI designers earn an average of 50k worldwide, with the average salary in the USA being 91k, Germany being 57k, France being 47k, and 67k in the UK.
UX designers earn slightly more, with an average of 52k worldwide. UX designers in the US earn 102k on average, with Germany paying 53k, 49k in France, and 68k in the UK. (Source: Glassdoor)
Note: All the salaries listed above are an average for the area, and are in USD.
How Do You Become a UI or UX Expert? What Kind of Design Courses/Tutorials Should You Take?
Becoming a UI or UX expert starts with being genuinely interested in UI/UX design. Once you know you're interested, you should find resources and take design courses that help prepare you for the job market.
There are online courses like the UI Design Program and Learning UI Design that can help you kickstart your journey towards becoming a UI designer.
For UX design, you can study online, paid courses, or courses from online universities. You can also look at the best online course websites to learn UI/UX so you can see which websites offer courses for free and the user feedback on these websites.
For UX design, there are a number of paid courses, of courses from online universities. You can also check out a list of the best online courses to learn UI/UX design so you can see which websites offer courses for free, and read user feedback.
Suppose you already have some of the required skills to be a UI/UX designer. In that case, you can also take a look at articles like the behavior patterns for UX design, UX methods that you can use, inspirational graphic designs from the world's best designers, and academic research papers that designers should read.
Which Should You Specialize In? UI or UX Design?
Specializing in UI or UX design is a personal preference that depends on your particular skillset.
However, there are a huge number of companies that advertise a combined UI/UX designer role.
While the roles and responsibilities of both these vary differently, there is still a niche market for UI/UX design, making it a good idea to have adequate knowledge about both.
While difficult to implement, a combined UI/UX career can prove fruitful in terms of salary compensation and importance in the company.
However, a combined UI/UX designer role is difficult to perform since it needs constant switching from one mindset to the other. So it is often a better option to specialize in one role instead.
For example, if you are artistic, know effective color combinations, and understand how products can be visually enhanced, UI design is a good choice for you.
On the other hand, if you are good with managing user and stakeholder needs, have excellent analysis skills, and understand how user experiences can be improved, UX design would be more suited to you.

Final Thoughts
User Interface and User Experience design both require an understanding of what users need.
Once you have this understanding, frontend development and design do not have to be a complex affair — there are a lot of ready-made components, tools, and kits that can make design easier and more effective.
Creative Tim offers you a huge number of free and premium, fully coded UI tools like Templates, Dashboards, and Design Systems.
If you want to build your illustrations using hand-drawn sketch components in a scalable manner, look no further than Creative Tim’s product: IRA Design.
And let's keep in touch on Twitter.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Alexandru Paduraru directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by