Understanding Javascript var, let and const
 Martin Mwenda
Martin MwendaUpon the release of ES2015 (ES6), two new ways of variable declaration were introduced to javascript. The two new keywords introduced were, let and const. Earlier the var keyword was only used to declared variables.
In this article we dive deeper and understand
1. Why there was a need for the two new keywords
The differences between var, let and const
The advantages of using let and const over var
To understand each of the 3 ways of declaring a variables, we will first need to understand two important concepts in javascript scope and hoisting.
Scope
In javascript, the scope implies where the variable can be accessed. There are three types of scope, global scope, function scope and block scope
Global Scope
Global scope refers to variables that can be accessed anywhere in the program. Example
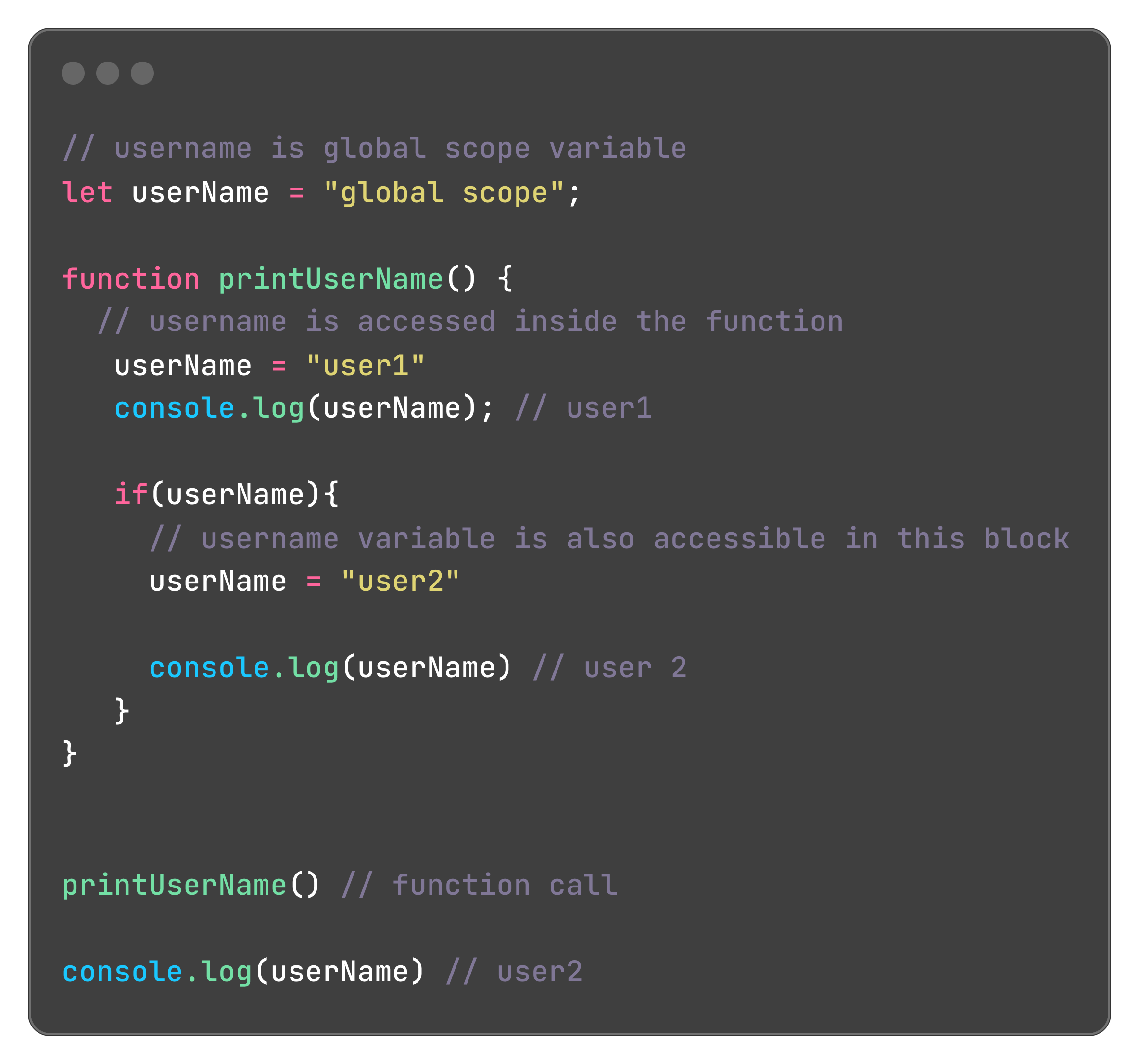
Function Scope
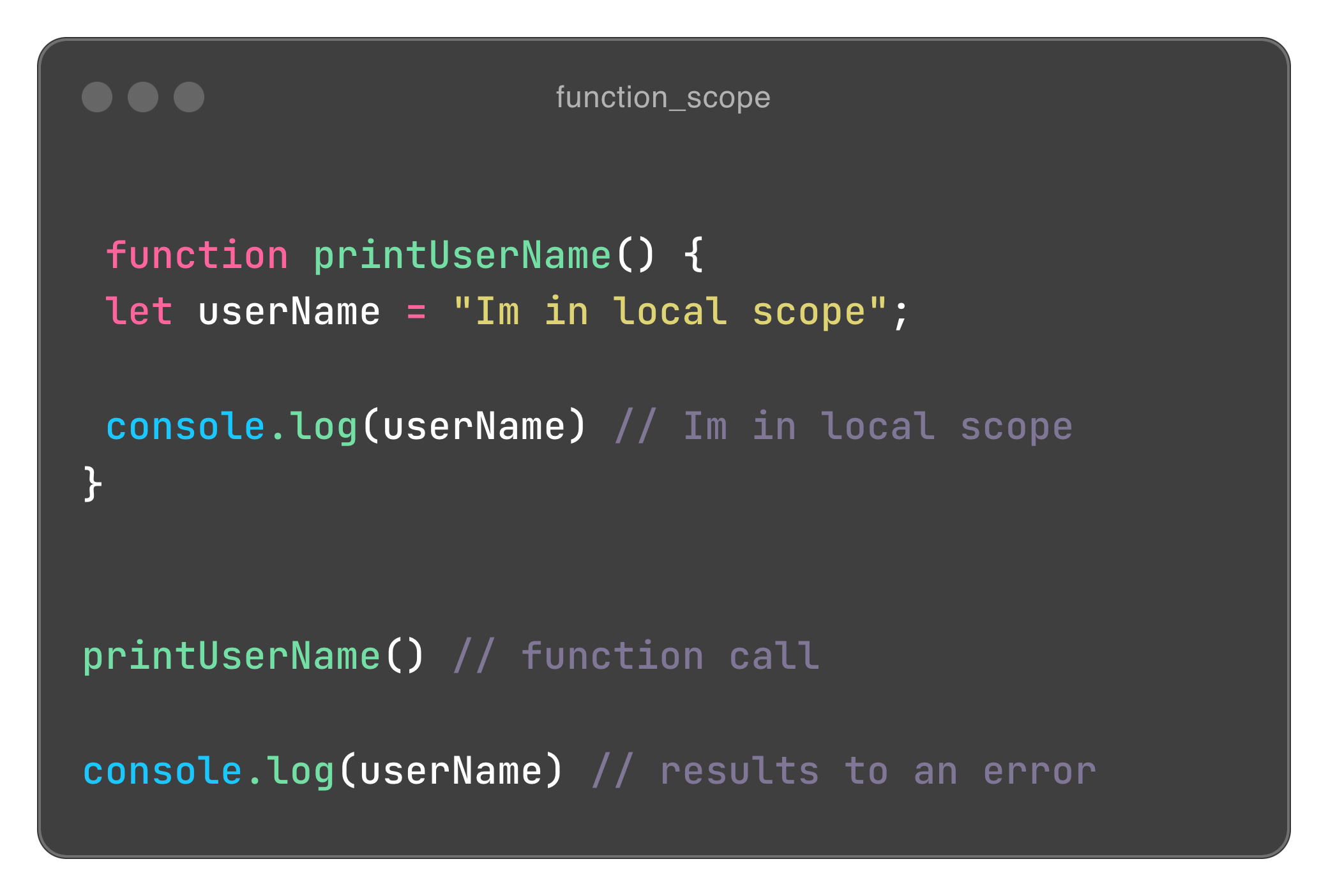
Function scope simply means the variable can only be accessed inside the function but not outside the function's body. In the code below the variable is only accessed within the function and accessing it outside the function will result to an error.
Block Scope
Block scope means the variable can only be accessed in that block of code only and cannot be accessed from outside the block.

Hoisting
Hoisting is a javascript mechanism that allows declarations of variables and functions to be moved at the top of their scope before code execution.
Lets understand hoisting with the help of the following code.

The above code output does not throw an error because of javascript hoisting.
The javascript interpreter separates the declaration from the assignment of variables and hoist the declaration at the top of the scope before execution, The code below explains how javascript interpreters the code.

Var Keyword
Var is a keyword used to declare a variable in JavaScript. Var declared variables
Are function scoped,
Can be re-declared and updated
It gets Hoisted to the top of its scope and initialized to undefined
can be accessed without initialization as its default value is undefined
Problems with the Var Variable
Var variable can be re-declared and re-declaration allows declaring more than one variable with the same name, which can result to overriding the original variable name.
Example
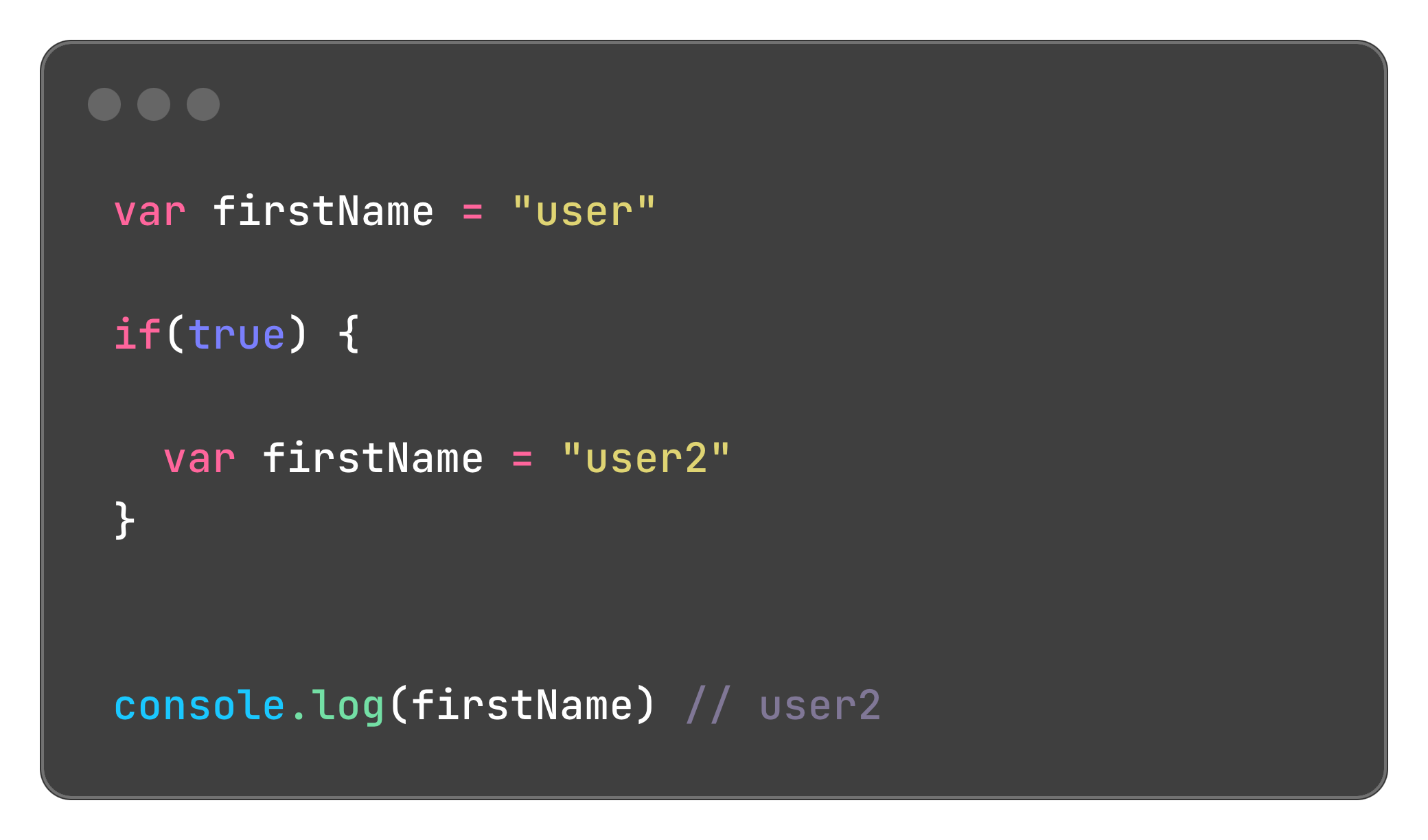
On the code example above we have a firstName variable and an if conditional statement, if the condition is true, the block will override the previously declared firstName variable. Because of this re-declaration behaviour the var variable can lead to unexpected output
- Another problem is the var variable is not able to declare a constant variable that cant be changed once its declared.
Let Keyword
As we have discussed above, the var keyword has some issues associted with it, thats why new keywords were needed.
Let is a keyword introduced with the ES6 version of javascript, it solves the issues we encountered with var. Let declared variables are
Block scoped - meaning the let variable will be accessible only inside the block, if we try to access outside the scope, will result to
Reference Error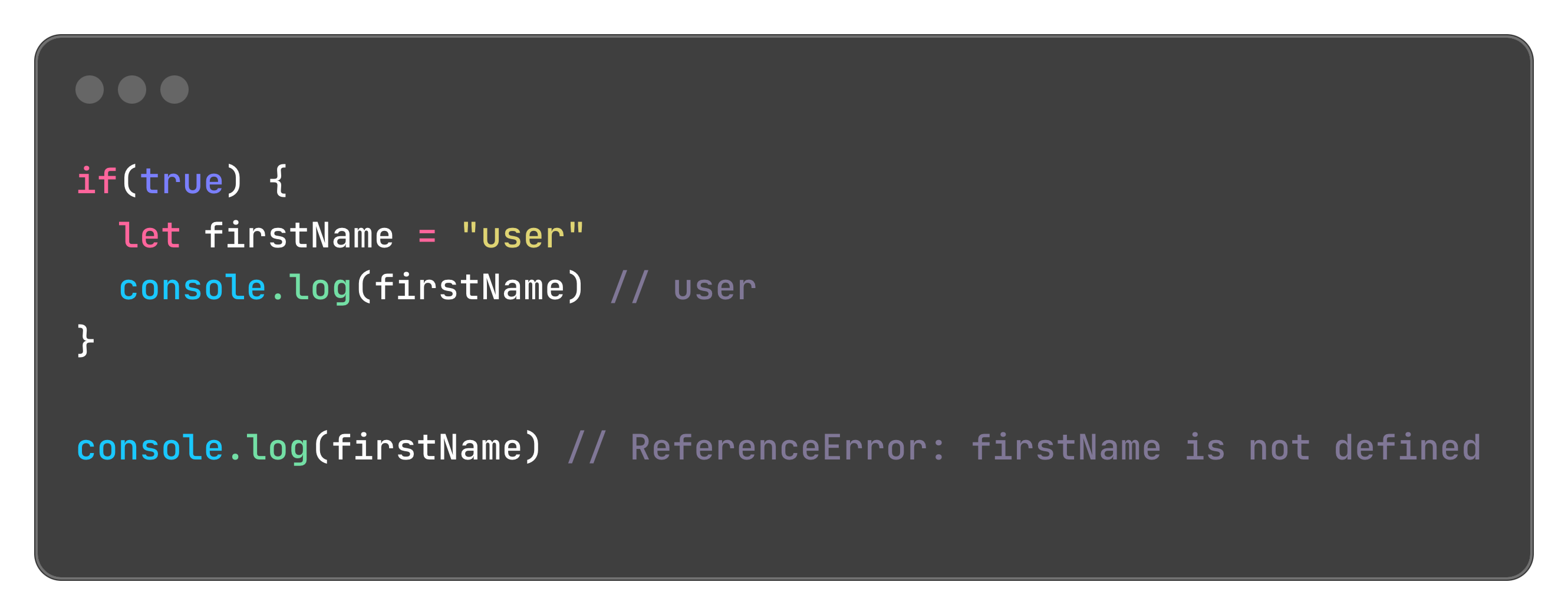
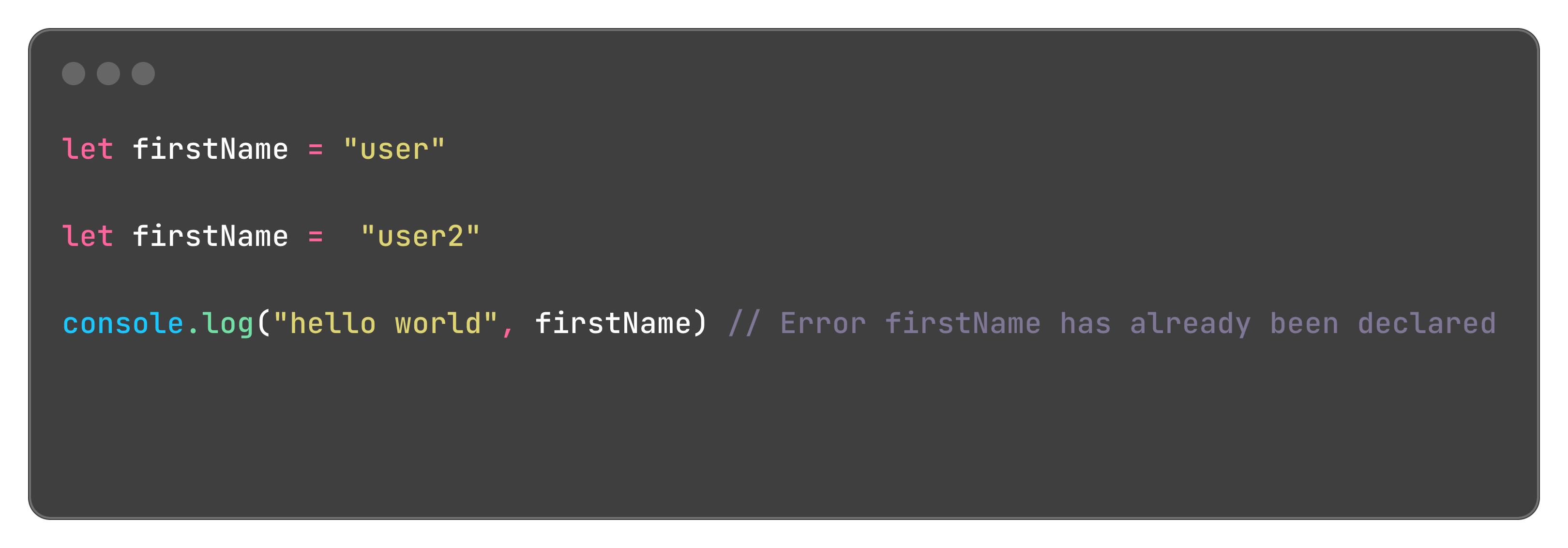
Does not allow re-declaration of the variable but allows to update the variable, re-declaration of the variable was a big problem withe var keyword. Example below
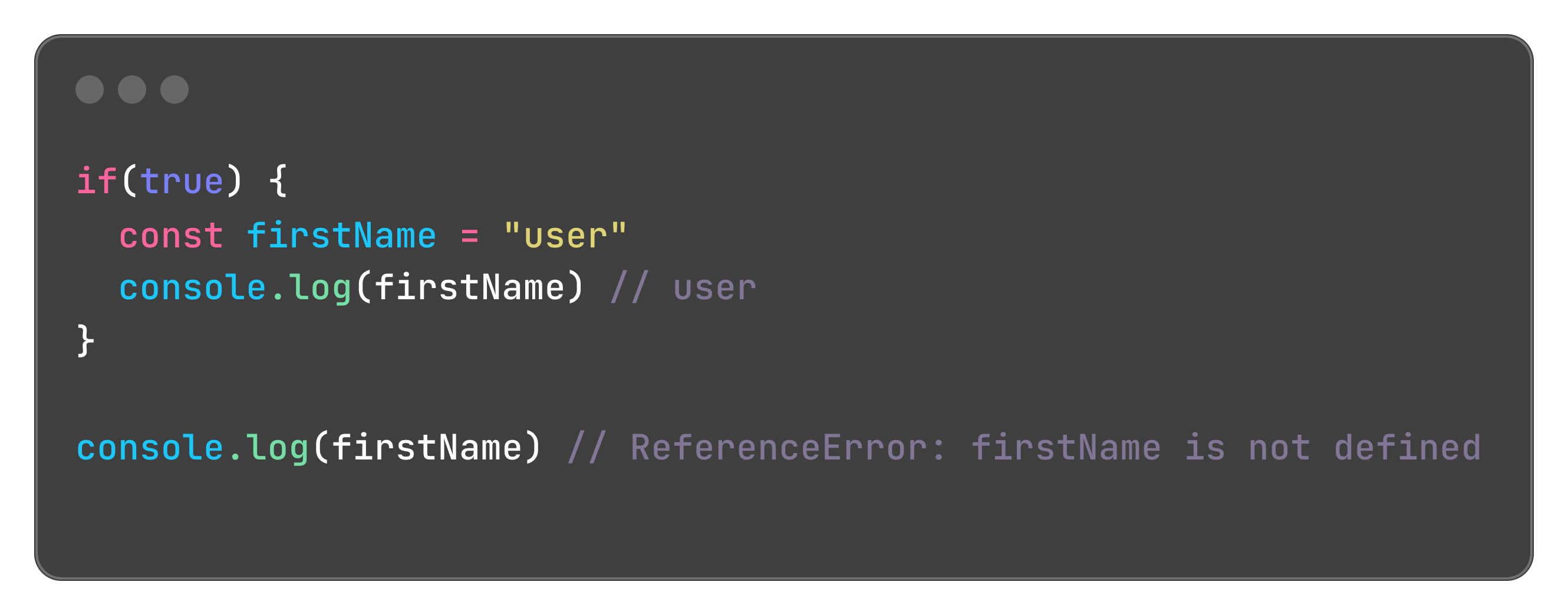
The let variables are also hoisted to the top of the scope, but are not assigned any value, if we try accessing the variable before declaration it will throw an error. Example below
Const Keyword
The Const keyword is used to define constant variables, that can not be changed.
The Const Keyword is
Blocked scoped and cannot be accessed outside the block, if we try to access the variable outside the scope will result to an error
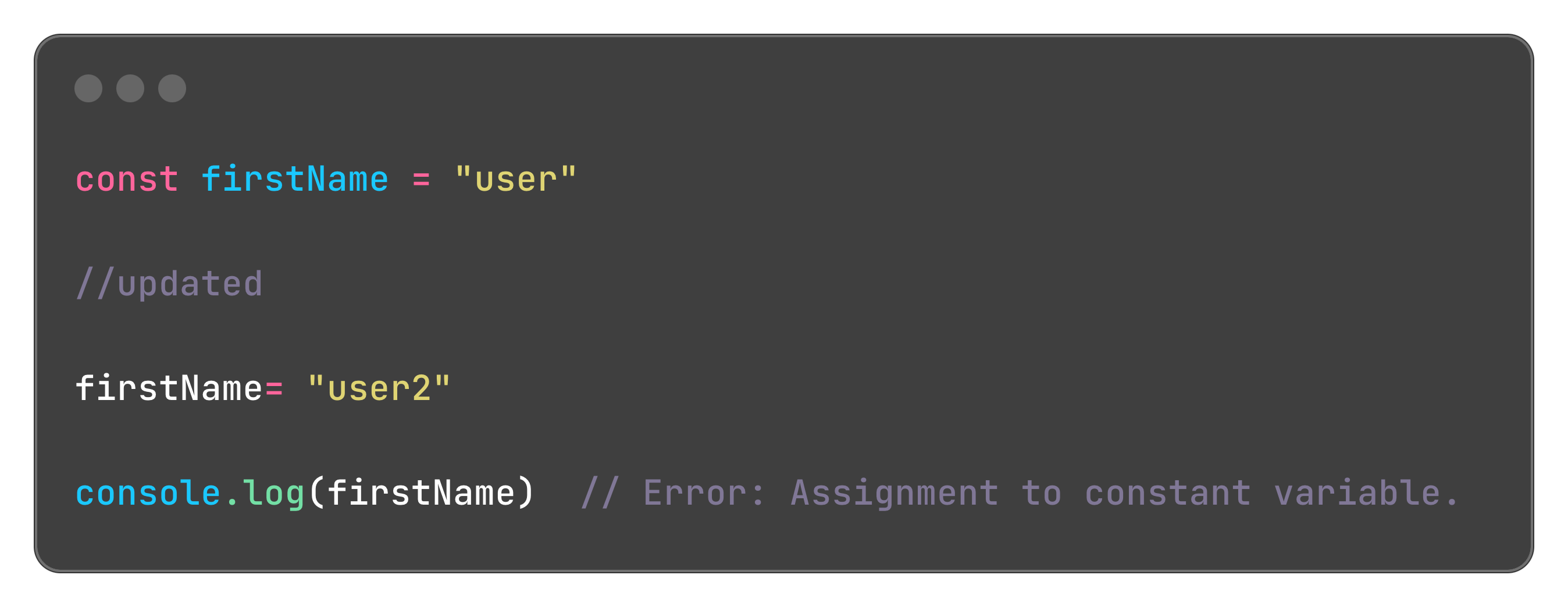
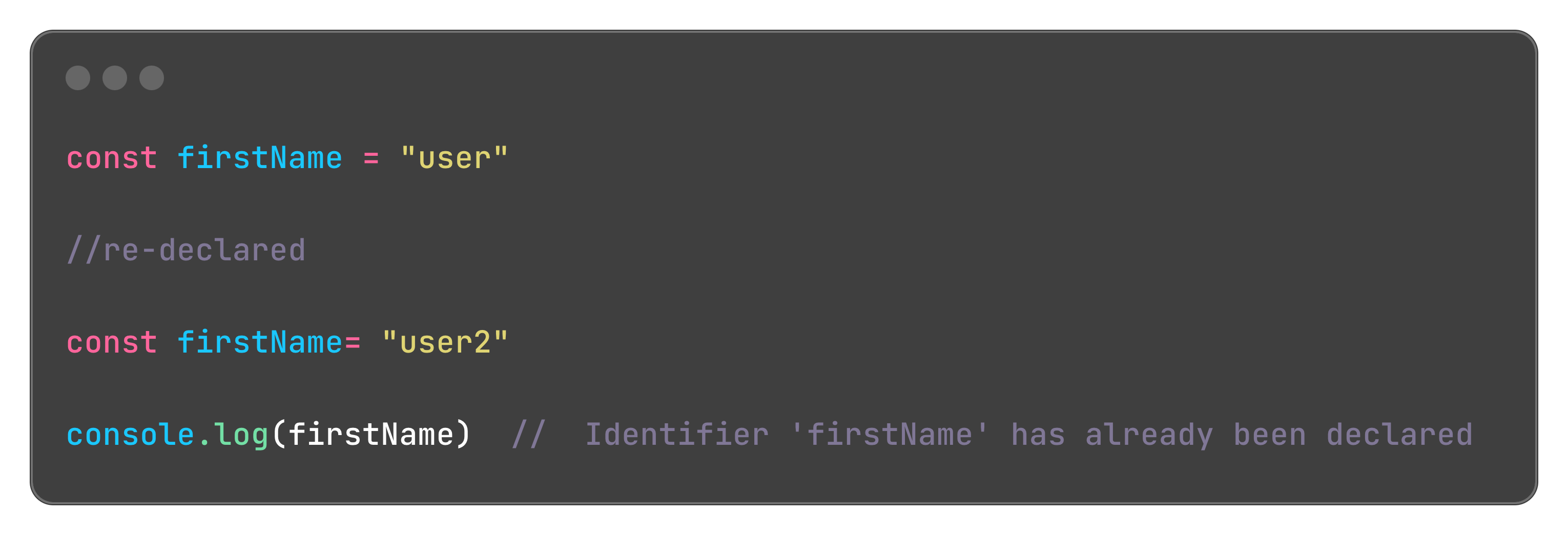
Cannot be re-declared or updated, if redeclared or updated will result to an error
when updated
when re-declared
Its hoisted to the top of their scope but is not initialized with undefined
Summary
In summary, var, let and const are the three different ways to declare variables in javascript. To write better code use let and const to prevent unexpected scope problems. If you need to reassign a variable use let and const when you wish to declare constant variables.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Martin Mwenda directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
