Kubernetes Overview
 KALPESH MOHANTA
KALPESH MOHANTATable of contents
- Problem that Kubernetes solving
- K8s Cluster Architecture
- K8s Namespace
- KOPS (Kubernetes Operations)
- K8s Installation & Commands
- K8s Pods
- K8s Deployment
- K8s Service
- Kubeshark
- K8s Ingress
- K8s RBAC (Role based access control)
- K8s CRD, CR & Custom Controller
- K8s ConfigMaps & Secrets
- K8s Operators & Helm
- K8s Monitoring: PROMETHEUS & GRAFANA

Kubernetes is Orchestration system for automating software deployment, scaling, and management.
Problem that Kubernetes solving
Single Host
K8 work as clusters which has a group of computing nodes, that run containerized applications
Auto Scaling
K8 use
HPA(horizontal pod auto scaling)feature to accommodate the loadAuto Healing
K8 fixes the damaged by creating new container with help of K8 control plane
Enterprise Level
Solve Enterprise level problem like: orchestration, firewall, etc.
K8s Cluster Architecture
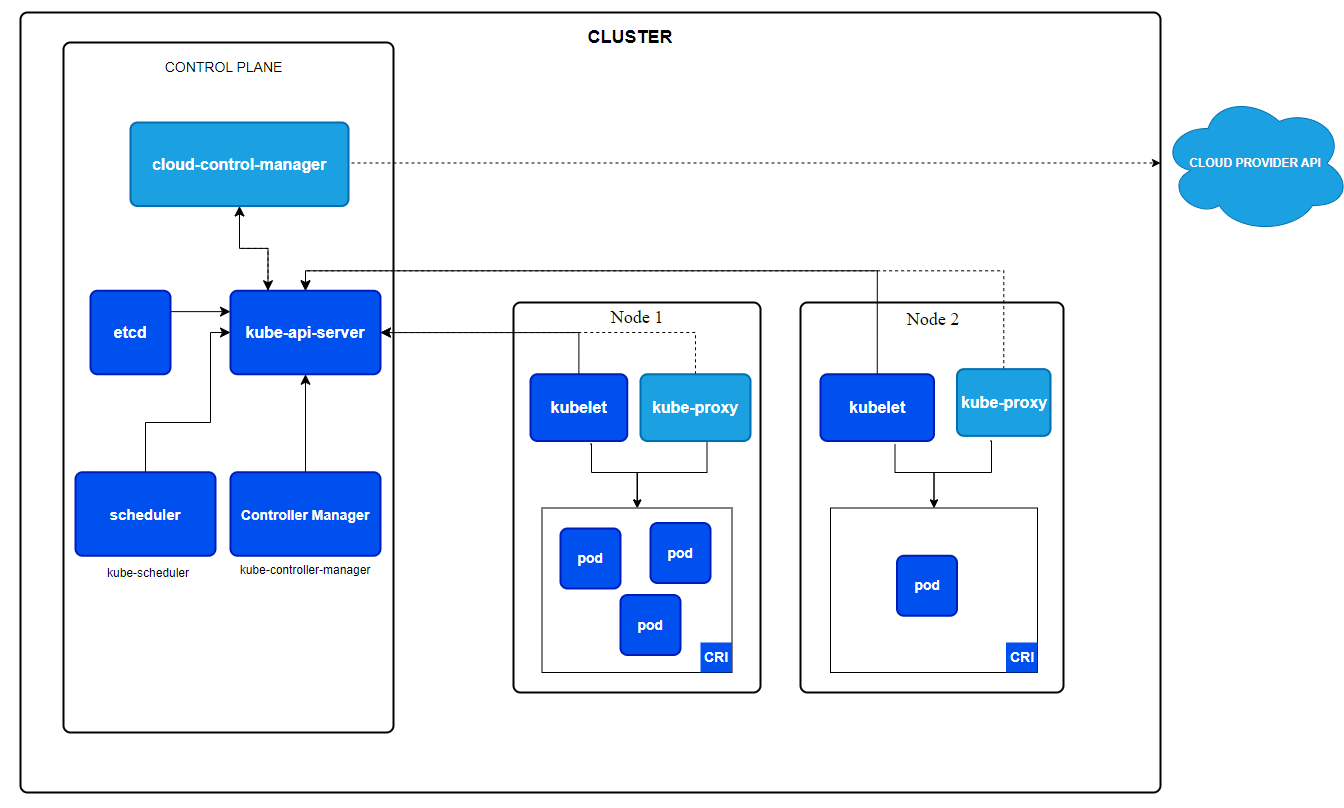
Data Plane (worker nodes)
Container Runtime
In order run container application like docker, we need
container runtime:dockershimcontainerdCRI-O
Pod
Pod is smallest unit in K8s act as
wrapper for containers. It represents asingle instance of a running processin cluster.Provide
declarative way (YAML)Can run
more than 1 containerin a pod
CRI(Container Runtime Interface)
It's a
APIthat allow kubelet to communicate with different container runtimes.kubelet
Responsible for pods monitoring, deletion, creation.
kube-proxy
Responsible for pods networking, IP, load balancing.
Control Plane (master nodes)
kube-api-server
API server act as central management hub of control plane.
It
expose K8s APIto external world, which enables communication b/w different components of the control plane and the worker nodes.scheduler
Responsible for assigning newly created pods to nodes.
Ensuring that workloads are evenly distributed and that pods are placed on nodes that meet their resource and other requirements.
etcd
It's a key-value
data storage. It is responsible for storing all the cluster's state and configuration data. Act asBack-up of K8s clusterController Manager
It responsible for
managing & maintaining desired state of clusterIt runs a
set of controllersthat perform various cluster management tasks.Cloud Controller Manager (CCM)
Responsible for managing cloud-specific resources and interacting with the cloud provider's API.
K8s Namespace
Namespace is logical isolation of resources, n/w, policies, rbac.
KOPS (Kubernetes Operations)
KOPS an open-source tool that simplifies the creation, management, & upgrading of K8s clusters on cloud providers such as AWS, GCE, and Azure.
K8s Installation & Commands
Installation of kubectl
kubectl is command-line for K8s
For further assistance refer: kubectl documentation
- Download the latest release with the command:
curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(curl -L -s https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl"
- Install kubectl
sudo install -o root -g root -m 0755 kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectl
Installation of minikube (local K8s cluster)
For further assistance refer: minikube documentation
- Installation
curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/latest/minikube-linux-amd64
sudo install minikube-linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/minikube && rm minikube-linux-amd64
- Start minikube
# minikube function
# VM -> single node K8s cluster
minikube start
kubectl Commands
get k8s clusters, filter with region
kubectl config get-contexts | grep ap-south-1
selecting k8s cluster
kubectl config use-context <user-name>@< k8scluster name>
checking current k8s cluster
kubectl config current-context
get no. of nodes
kubectl get nodes
create pod
kubectl create -f pod.yml
get no. of pods
kubectl get pods
# More details of pods
kubectl get pods -o wide
delete pods
kubectl delete pod nginx
detail info about pods
kubectl describe pod nginx
debug pods
kubectl logs nginx
K8s Pods
pod.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.14.2
ports:
- containerPort: 80
K8s Deployment
deployment.yml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
replicas: 3 # Replica-set ensure auto-healing by Controller
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx # Label for pods
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.14.2
ports:
- containerPort: 80
K8s Service
A K8s Service provides:
Load balancingService (network) discovery using
labels and selectorsExternal
exposureto world
|---------------------------------------------|
+-------------------+ | +----------------+ +-----------------+ | +-----------+ +-----------+
| Service | --->| | Deployment |---> | ReplicaSet | |--> | Pod | ---> | Container |
| (Load Balancer) | | | | | | | | | | |
+-------------------+ | +----------------+ +-----------------+ | +-----------+ +-----------+
|---------------------------------------------|
Type of service
Types of services:
ClusterIP: Access
within clusternetworkNodePort: Access through
outside cluster: organization, VPC, or nodesLoadBalancer:
Public accessfrom outside
service.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: my-loadbalancer-service
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
selector:
app: my-app
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80 # Service port
targetPort: 8080 # Pod port
Kubeshark
Tool that provides real-time visibility into K8s clusters API traffic
K8s Ingress
K8s Ingress addresses the following enterprise challenges:
Security
Advance Load balancing (various types)
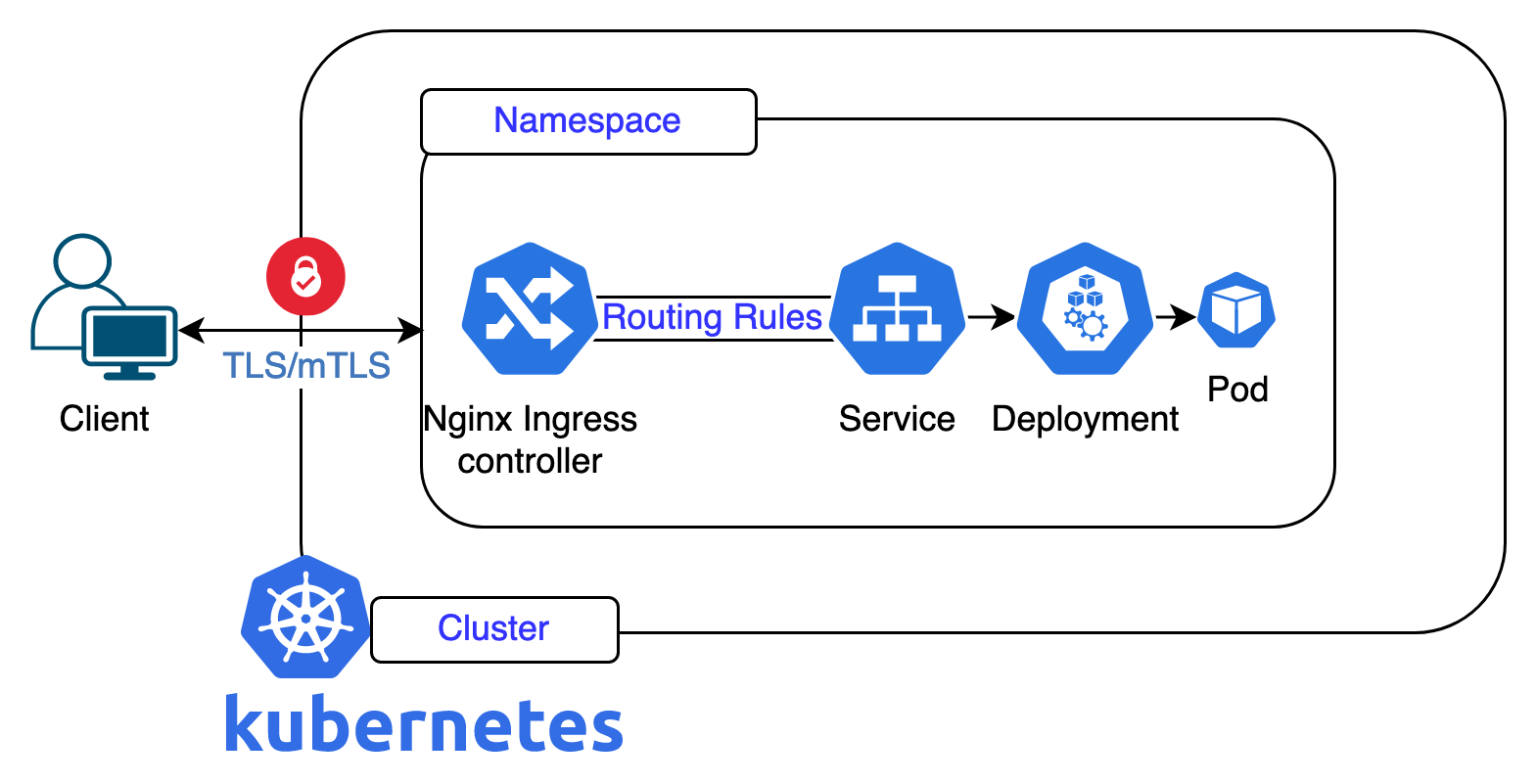
Ingress Controller
Watches for Ingress resources & enforces these rules by updating its underlying load balancer or proxy configuration.
Common Ingress Controller:
NGINX
HAProxy
Ingress Resource
Defines the routing rules
Type of Load Balancing:
Host: Directs traffic based on the hostname.
Paths: Directs traffic based on URL paths.
TLS: HTTPS traffic with SSL certificates.
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: my-ingress
spec:
rules:
- host: myapp.example.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: my-service
port:
number: 80
K8s RBAC (Role based access control)
RBAC is flexible method for managing access control in various systems, OS, databases, and applications, which improve security & ensure compliance
RBAC is general access control manager, unlike AWS IAM which is cloud specific.
Service Account: Provides an
identityfor processes running in a podRole: Defines a
set of permissionsRole Binding:
Associatesrolewithservice account(or user/group)

K8s CRD, CR & Custom Controller

CRD (Custom Resource Definition)
CRD is a way to
extend the Kubernetes APIto create your own custom resources.It allows you to define
new types of resourcesthat Kubernetes can manage, beyond the built-in types like Pods, Services, and Deployments.
CR (Custom Resource)
Custom Resource is an
instance/new type of resourceof a Custom Resource Definition.Once a CRD is defined and applied to the cluster, you can create, read, update, and delete instances of that custom resource.
Custom Controller
A custom controller is a piece of software that
watches for changesto custom resources (or other Kubernetes resources)Reconcile the current state of the cluster with the desired state specified by those resources.
K8s ConfigMaps & Secrets
Solves ENV variable problems:
Decoupling Configuration from Code
Dynamic Updates
Reusability Across Multiple Pods
ConfigMaps
- ConfigMaps are used to
store non-confidential configuration datain key-value pairs.
Secrets
Secrets are used to
store sensitive data, such as passwords, OAuth tokens, and SSH keys &encrypted at restUse RBAC to get least access privilege.
Dynamic Configuration: ConfigMaps/Secrets as Volume
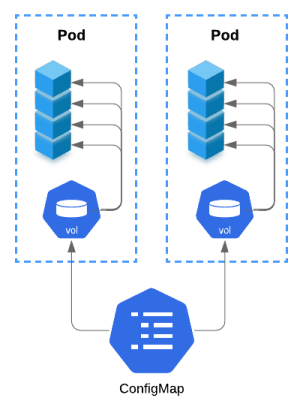
configmap.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: example-config
data:
database_url: "mongodb://localhost:27017"
feature_flag: "true"
deployment.yml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: example-deployment
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: example-app
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: example-app
spec:
containers:
- name: example-container
image: example-image
envFrom:
- configMapRef:
name: example-config
volumeMounts: # Mounting Volume to Deploy -> POD
- name: config-volume
mountPath: /etc/config
volumes: # ConfigMaps as Volume
- name: config-volume
configMap:
name: example-config
K8s Operators & Helm
Both tools that help manage K8s complex (stateful) applications
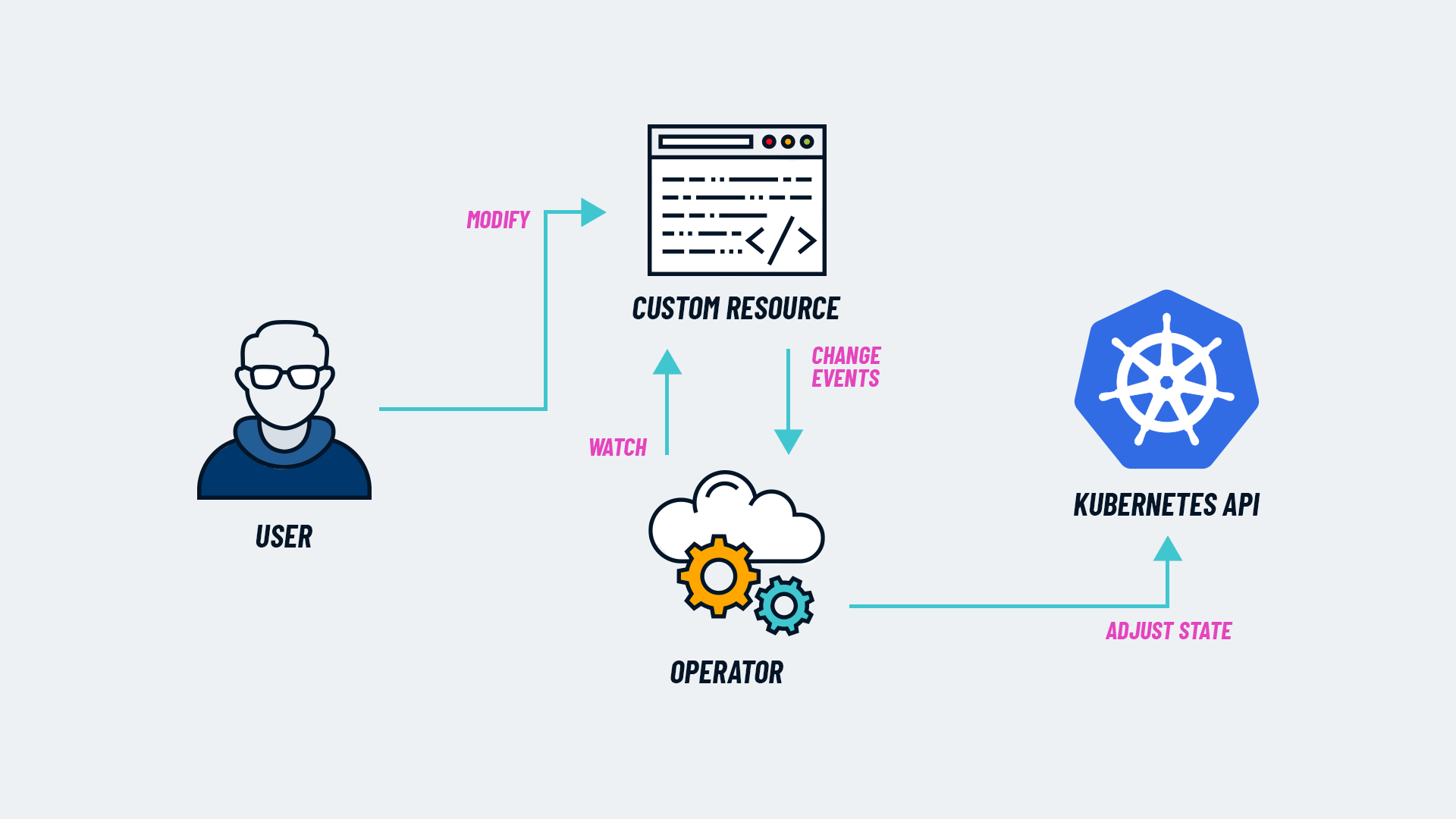
K8s Operator
Manage tasks with
minimal or no restartsAutomate operational tasks:
Upgrades
Backups
Failover
Scaling
Functions as a
controllerthat extends K8s capabilities by usingCustom Resource Definitions
Helm

May trigger
restartsduring deployments/upgradesPackage managerfor Kubernetes that simplifies the deployment process by usingcharts, which arecollections of YAML filesdescribing a set ofK8s resources.Helm help with:
Defining, Installing, and Upgrading Applications: Standardizes and simplifies application lifecycle management.
Customizing Deployments: Enables environment-specific configurations through
value overrides.Release Management: Tracks application releases for rollbacks or updates.
Versioning: Manages versioned manifest files for repeatable deployments.
Sharing Charts: Facilitates reuse and collaboration across teams or organizations.
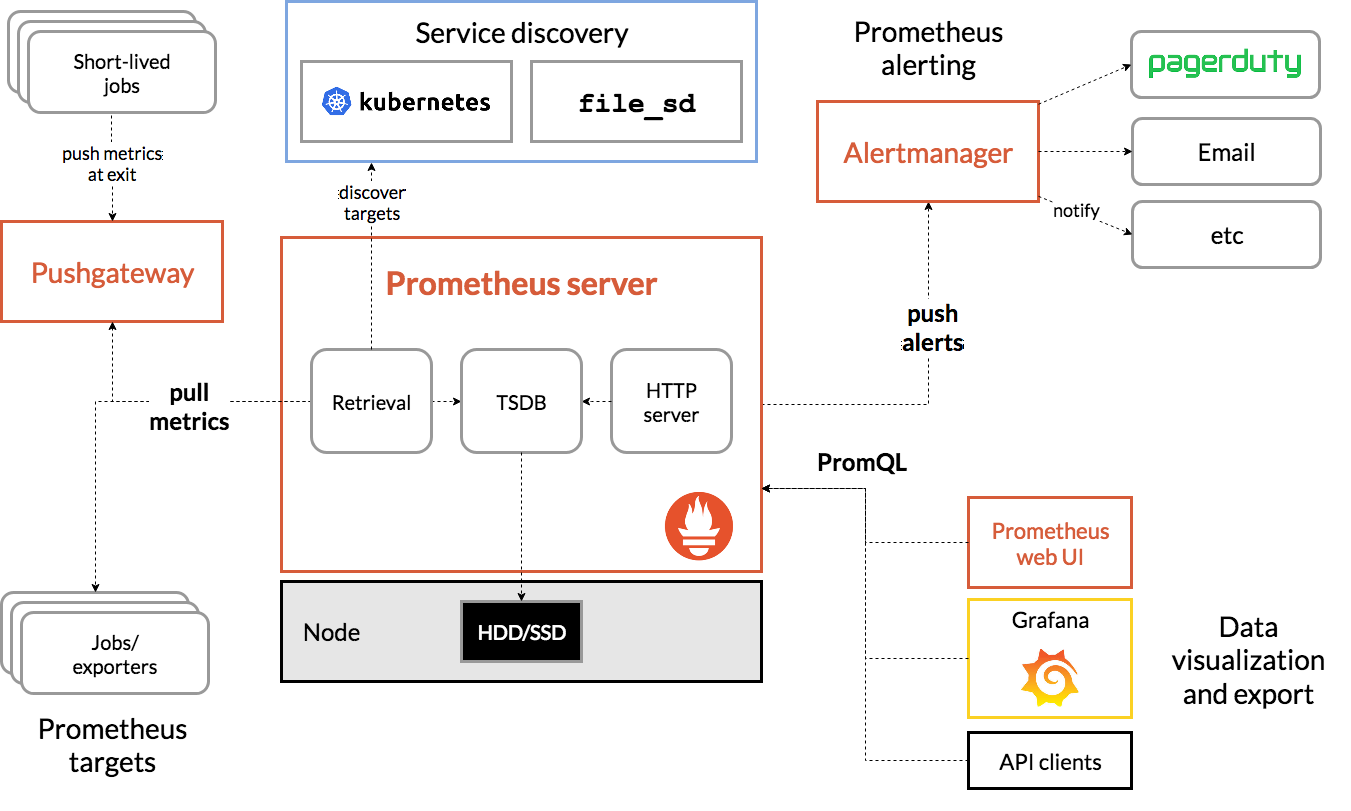
K8s Monitoring: PROMETHEUS & GRAFANA
PROMETHEUS
Monitors and alerts cloud-native environments by collecting metrics from applications and infrastructure
GRAFANA
Allows users to visualize and monitor data through dashboards and charts, using Prometheus.
Feel free to share and spread the knowledge! 🌟😊 Enjoy Learning! 😊
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from KALPESH MOHANTA directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

KALPESH MOHANTA
KALPESH MOHANTA
👋 Hi there! Welcome to my DevOps adventure! 🚀 I'm Kalpesh, a DevOps Engineer, and I'm thrilled to share my journey in the dynamic world of DevOps and Cloud Technologies. 🌐 🔧 Tech Arsenal: CI/CD Automation: Streamlining workflows for seamless deployments. Containers & Orchestration: Docker & Kubernetes. Cloud Platforms: Azure, AWS. Version Control: Git. Configuration Management: YAML, Linux commands. 🚀 My Journey: I've had the privilege to work on diverse projects, including a notable deployment for PepsiCo. My expertise spans CI/CD automation, containerization, cloud services, and scripting to enhance system performance and reliability. 💡 Why Follow Me? Join me as I delve into: Cutting-edge DevOps practices. Automation techniques. Cloud innovations. Tips & tricks for aspiring DevOps professionals. 🤝 Connect & Collaborate: Let's build, learn, and innovate together. Whether you're a fellow tech enthusiast, a professional looking to share insights, or someone eager to learn, let's connect and grow in this vibrant community. 📢 Follow my LinkedIn & Hashnode blog for insights, tutorials, and updates. Together, we'll embrace the ever-evolving DevOps landscape!
