How to Build a Python Command-Line To-Do List App
 ByteScrum Technologies
ByteScrum Technologies
Managing tasks efficiently is crucial for productivity. A command-line To-Do List app in Python is a simple yet powerful tool that allows you to keep track of your tasks directly from your terminal. This project is a great way to practice Python fundamentals, including file operations, user input handling, and list manipulations. Let’s build a command-line To-Do List app that enables users to add, view, complete, and delete tasks easily.
Features of the Command-Line To-Do List App
Add Tasks: Users can add new tasks to their list.
View Tasks: Display all tasks, showing their status (completed or pending).
Mark Tasks as Completed: Users can mark tasks as done.
Delete Tasks: Remove tasks from the list.
Save and Load Tasks: Tasks are saved to a file and loaded when the app starts, ensuring persistence.
Step-by-Step Implementation
Let’s walk through the steps to create this To-Do List app in Python.
Step 1: Setup Your Environment
First, make sure you have Python installed on your machine. No additional libraries are needed for this project, as we’ll use Python’s built-in functionalities.
Step 2: Define the Basic Structure
We’ll use a simple list to store tasks in memory and a text file (tasks.txt) to save tasks persistently. This file allows the app to remember tasks between sessions.
Here’s the basic structure of our Python script:
import os
# File to store tasks
TASK_FILE = "tasks.txt"
def load_tasks():
"""Load tasks from a file."""
tasks = []
if os.path.exists(TASK_FILE):
with open(TASK_FILE, "r") as file:
tasks = [line.strip() for line in file.readlines()]
return tasks
def save_tasks(tasks):
"""Save tasks to a file."""
with open(TASK_FILE, "w") as file:
for task in tasks:
file.write(f"{task}\n")
def add_task(tasks):
"""Add a new task to the list."""
task = input("Enter the task description: ")
tasks.append(task)
print(f"Task '{task}' added.")
def view_tasks(tasks):
"""Display all tasks with their statuses."""
if not tasks:
print("No tasks available.")
else:
for index, task in enumerate(tasks, start=1):
print(f"{index}. {task}")
def mark_task_complete(tasks):
"""Mark a task as completed."""
view_tasks(tasks)
try:
task_number = int(input("Enter the task number to mark as complete: "))
tasks[task_number - 1] = "[Completed] " + tasks[task_number - 1]
print(f"Task {task_number} marked as complete.")
except (ValueError, IndexError):
print("Invalid task number.")
def delete_task(tasks):
"""Delete a task from the list."""
view_tasks(tasks)
try:
task_number = int(input("Enter the task number to delete: "))
task = tasks.pop(task_number - 1)
print(f"Task '{task}' deleted.")
except (ValueError, IndexError):
print("Invalid task number.")
def main():
"""Main function to run the To-Do List app."""
tasks = load_tasks()
while True:
print("\nTo-Do List App")
print("1. View Tasks")
print("2. Add Task")
print("3. Mark Task as Completed")
print("4. Delete Task")
print("5. Exit")
choice = input("Choose an option (1-5): ")
if choice == "1":
view_tasks(tasks)
elif choice == "2":
add_task(tasks)
save_tasks(tasks)
elif choice == "3":
mark_task_complete(tasks)
save_tasks(tasks)
elif choice == "4":
delete_task(tasks)
save_tasks(tasks)
elif choice == "5":
print("Exiting the app. Goodbye!")
break
else:
print("Invalid choice. Please try again.")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Step 3: Implement Core Functions
load_tasks(): Reads tasks from the file and loads them into a list.save_tasks(tasks): Saves the current list of tasks to a file.add_task(tasks): Prompts the user to add a new task and appends it to the list.view_tasks(tasks): Displays all tasks with their status (pending or completed).mark_task_complete(tasks): Allows the user to mark a task as completed.delete_task(tasks): Deletes a selected task from the list.main(): Runs the app, handling user input to manage tasks.
Step 4: Running Your To-Do List App
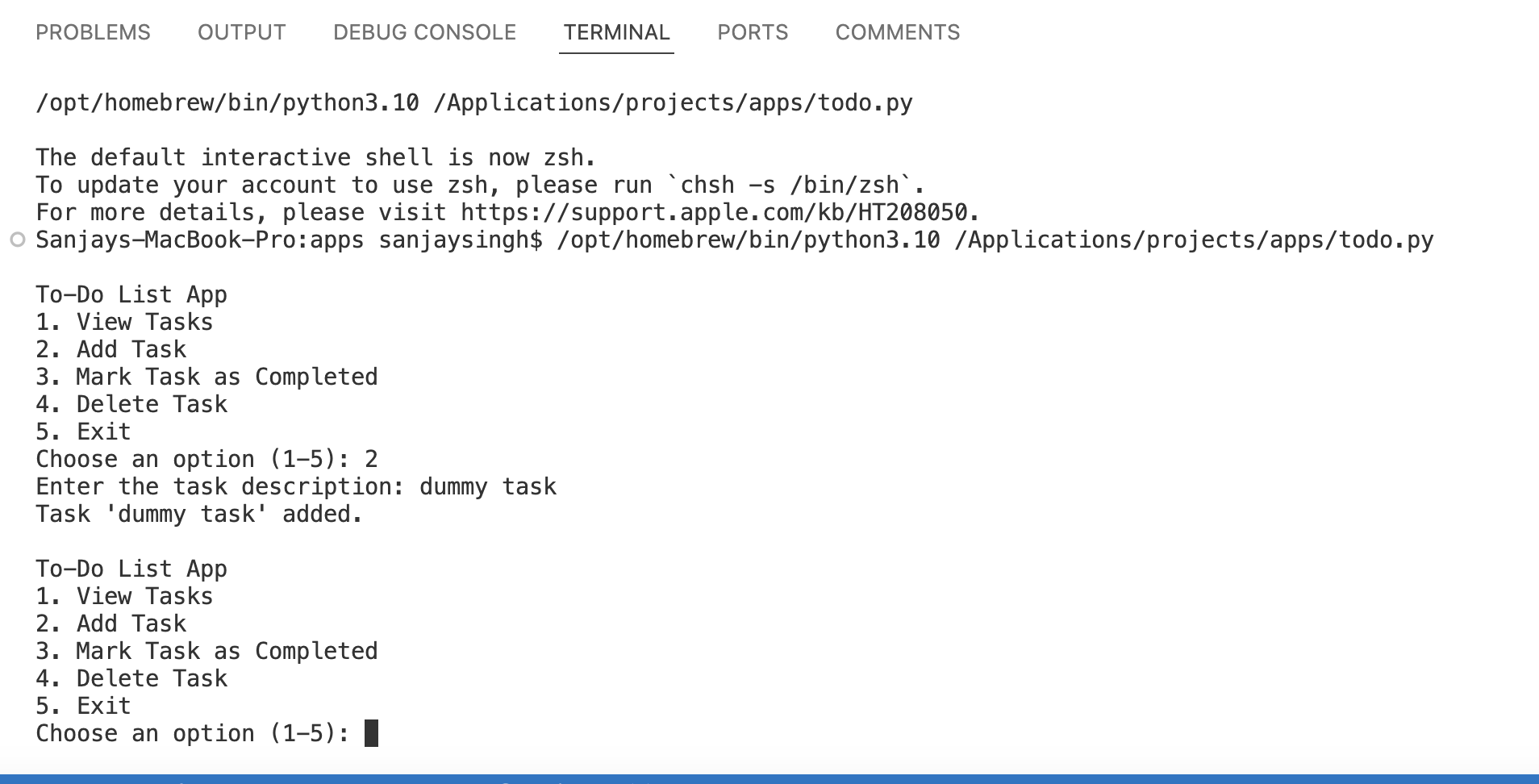
To run your To-Do List app:
Save the script in a file named
todo.py.Open your terminal or command prompt.
Navigate to the directory where
todo.pyis located.Run the script using Python:
python todo.py
You will see a menu allowing you to view, add, complete, or delete tasks. Your tasks will be saved in tasks.txt for future sessions.
Conclusion
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from ByteScrum Technologies directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

ByteScrum Technologies
ByteScrum Technologies
Our company comprises seasoned professionals, each an expert in their field. Customer satisfaction is our top priority, exceeding clients' needs. We ensure competitive pricing and quality in web and mobile development without compromise.