Understanding Blockchain Rollups: A Deep Dive into Scaling Solutions
 Navya Srivastava
Navya Srivastava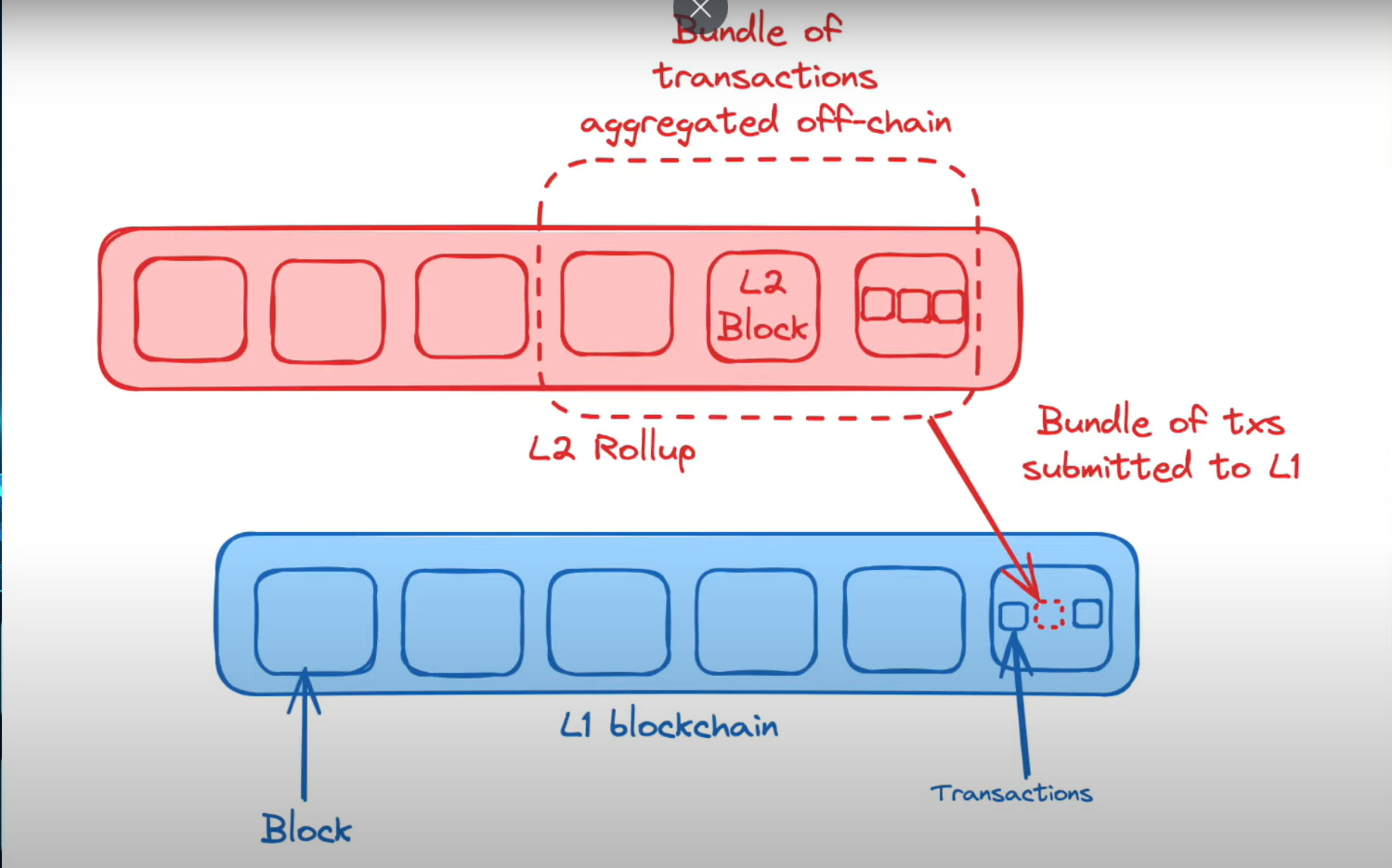
Introduction
As blockchain technology continues to evolve, the need for scalable solutions has become increasingly apparent. One of the most promising approaches to scaling blockchain networks is the use of rollups. Rollups offer a way to significantly increase transaction throughput while maintaining the security and decentralization of the base layer blockchain. In this article, we'll explore what rollups are, how they work, their benefits, and provide detailed examples to illustrate their impact.
What Are Rollups?
Rollups are a type of Layer 2 scaling solution that processes transactions off-chain while still leveraging the security of the main blockchain (Layer 1). They aggregate or "roll up" multiple transactions into a single batch, which is then recorded on the Layer 1 blockchain. This approach helps to reduce congestion and fees on the base layer by handling most of the transaction processing off-chain.
There are two primary types of rollups:
Optimistic Rollups
ZK-Rollups (Zero-Knowledge Rollups)
Optimistic Rollups
Optimistic Rollups assume that transactions are valid by default and only perform extensive computations when a challenge or dispute arises. Here's how they work:
Transaction Aggregation: Multiple transactions are aggregated off-chain into a single rollup block.
Submission: This aggregated rollup block is submitted to the Layer 1 blockchain with a minimal proof.
Challenge Period: A challenge period is provided during which anyone can contest the validity of the rollup block. If no valid challenges are made, the rollup block is finalized, and the transactions are considered valid.
Benefits:
Scalability: Optimistic Rollups can significantly increase transaction throughput as they batch multiple transactions into one.
Lower Fees: By reducing the amount of data that needs to be stored on the Layer 1 blockchain, fees are lower compared to processing each transaction individually.
Drawbacks:
Challenge Period: The challenge period can introduce latency, as transactions are not considered final until the period expires without challenges.
Fraud Proofs: If fraud occurs, the process of challenging and verifying can be complex and resource-intensive.
Example: Optimistic Rollup on Ethereum
One of the prominent implementations of Optimistic Rollups is Optimism on the Ethereum blockchain. Optimism aggregates transactions off-chain and posts them to Ethereum. This allows for a significant increase in transaction throughput and reduction in gas fees compared to directly using Ethereum’s mainnet.
ZK-Rollups (Zero-Knowledge Rollups)
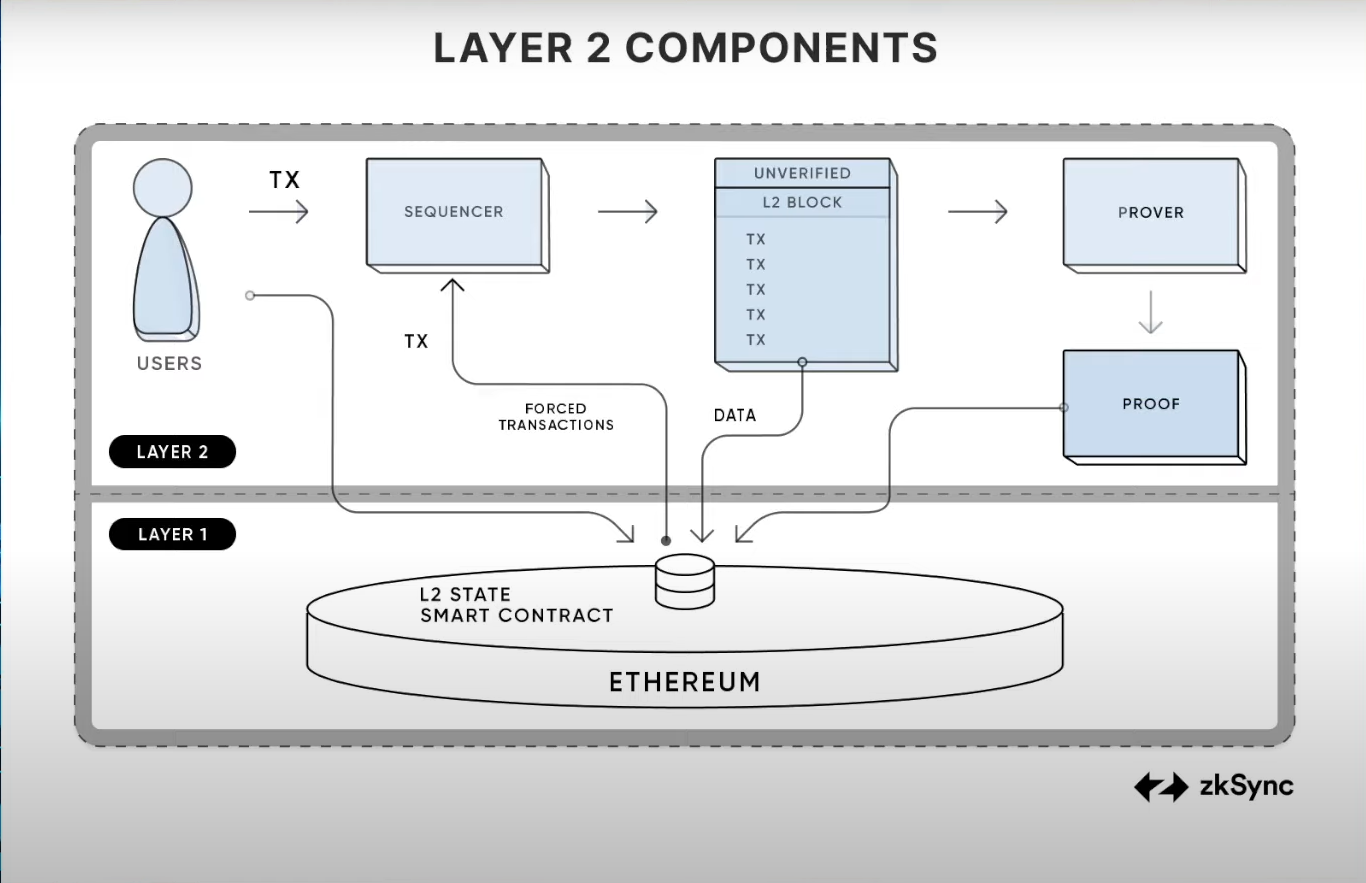
ZK-Rollups use cryptographic proofs to ensure that transactions are valid. Instead of assuming transactions are valid until proven otherwise, ZK-Rollups provide a succinct proof (known as a zero-knowledge proof) that all transactions in a rollup batch are correct.
Here's how ZK-Rollups work:
Transaction Aggregation: Multiple transactions are aggregated off-chain.
Proof Generation: A zero-knowledge proof is generated to verify the correctness of all aggregated transactions.
Submission: The rollup block, along with the proof, is submitted to the Layer 1 blockchain.
Verification: The Layer 1 blockchain verifies the zero-knowledge proof. If valid, the rollup block is finalized and the transactions are considered valid.
Benefits:
Immediate Finality: Transactions are considered final as soon as the zero-knowledge proof is verified.
High Security: ZK-Rollups provide strong cryptographic guarantees, making them highly secure.
Drawbacks:
Complex Proof Generation: Generating zero-knowledge proofs can be computationally intensive and may require advanced cryptographic techniques.
Higher Costs for Proof Generation: The complexity of generating and verifying proofs can lead to higher costs.
Example: ZK-Rollup on Ethereum
zkSync is a notable example of ZK-Rollups on Ethereum. zkSync uses zero-knowledge proofs to validate transactions off-chain, significantly increasing transaction throughput while maintaining high security. Users benefit from lower fees and faster transaction times compared to the Ethereum mainnet.
Comparing Optimistic and ZK-Rollups
Both Optimistic and ZK-Rollups offer distinct advantages and trade-offs:
| Feature | Optimistic Rollups | ZK-Rollups |
| Finality | After challenge period | Immediate |
| Complexity of Proofs | Minimal | High |
| Latency | Higher due to challenge period | Lower due to immediate finality |
| Security | Strong, but relies on fraud proofs | Very strong with cryptographic proofs |
Future of Rollups
The rollup technology is rapidly evolving, with ongoing research and development aimed at improving their efficiency and usability. The integration of rollups with Ethereum and other blockchains is a significant step towards achieving scalable, high-performance blockchain systems.
Key Trends:
Interoperability: Combining different rollup technologies to enhance cross-chain compatibility.
Optimizations: Advancements in cryptographic techniques to reduce proof generation costs and improve performance.
Adoption: Increasing adoption of rollups by major blockchain projects and platforms.
Conclusion
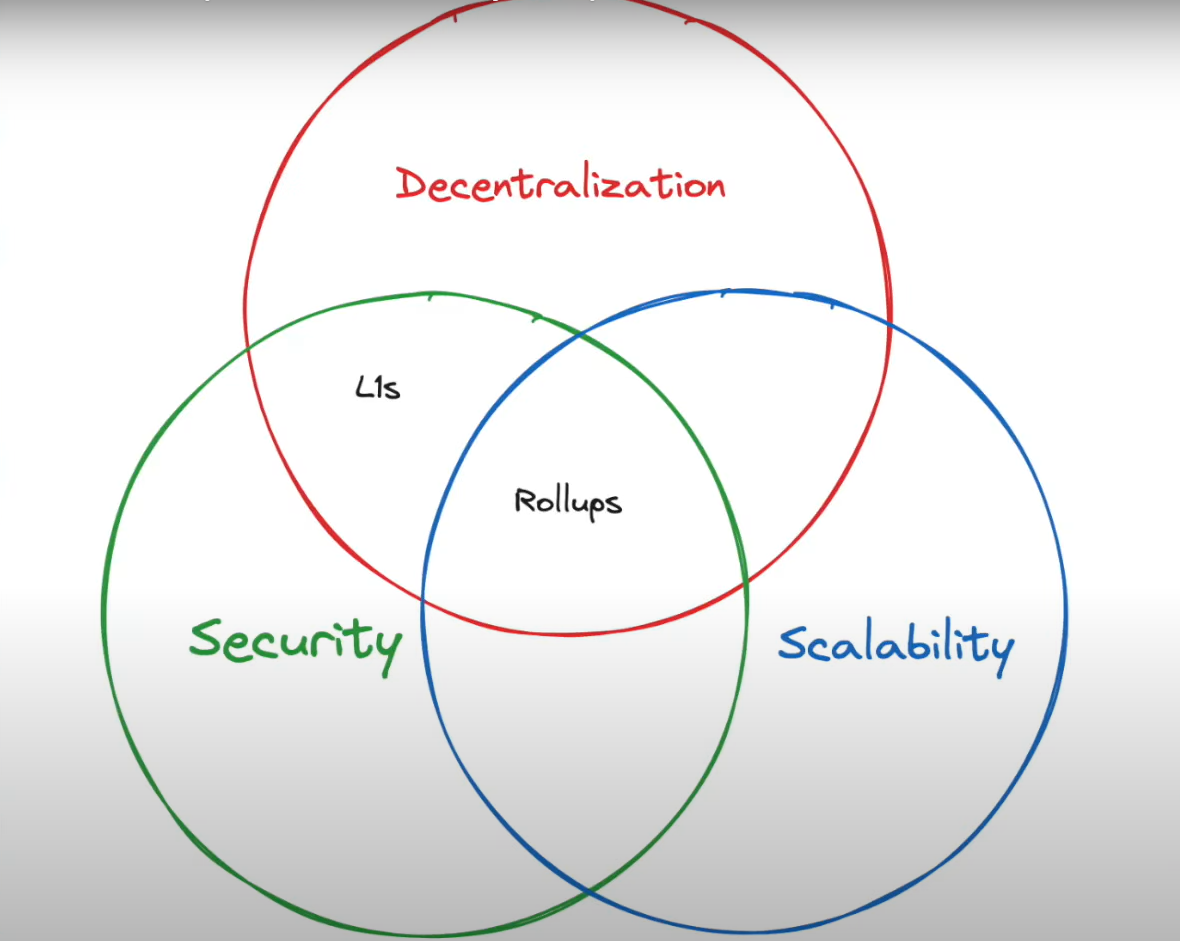
Rollups represent a powerful solution for scaling blockchains, offering a way to handle more transactions with lower fees while maintaining security. Whether through Optimistic Rollups or ZK-Rollups, these technologies are paving the way for a more scalable and efficient blockchain ecosystem.
As rollup technology continues to advance, it will play a crucial role in addressing the challenges of blockchain scalability, enabling more widespread adoption and usage of decentralized applications and services.
Feel free to explore and experiment with rollup implementations to see how they can benefit your projects and contribute to the broader blockchain community.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Navya Srivastava directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Navya Srivastava
Navya Srivastava
Hi! I am Navya, a dedicated coding enthusiast, deeply interested in Web3 technologies and exploring the future of decentralized applications and blockchain innovation.