How to Set Up a Kubernetes Cluster on Linux 8 Using Kubeadm
 Siddhartha Gaurav
Siddhartha Gaurav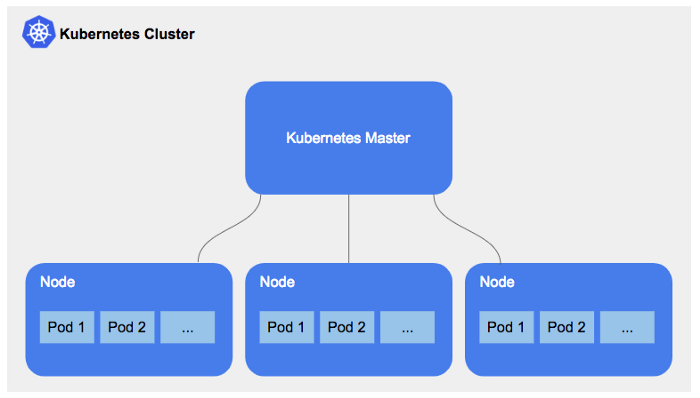
Kubernetes, often abbreviated as K8s, has become the de facto standard for container orchestration, providing a robust platform for deploying, scaling, and managing containerized applications. Whether you're managing a small development environment or a large-scale production cluster, Kubernetes offers the flexibility and power needed to handle diverse workloads.
In this guide, we’ll walk through the process of setting up a Kubernetes cluster using kubeadm, a tool designed to make cluster configuration easy and consistent. We’ll be working with a minimal cluster setup, featuring one master node and two worker nodes, all running on Linux 8 (CentOS 8, RHEL 8, or a similar distribution). This setup is ideal for learning, development, or small-scale production environments.
Why Use Kubeadm?
kubeadm simplifies the process of setting up a Kubernetes cluster. It handles the complex configurations required to get a cluster up and running, allowing you to focus on deploying and managing your applications. With kubeadm, you can quickly set up a production-ready cluster by following a series of straightforward commands.
Cluster Architecture
Our cluster will consist of:
One Master Node: Responsible for managing the cluster, scheduling workloads, and maintaining the desired state of the cluster.
Two Worker Nodes: Where the actual workloads (containers) will run. The worker nodes will communicate with the master node to receive instructions and report back on the status of their workloads.
Prerequisites
Before diving into the setup, let’s cover the prerequisites. Ensuring these are met will help avoid common pitfalls during installation and configuration.
Operating System: We’re using Linux 8 (CentOS 8, RHEL 8, or a similar distribution) for all nodes in the cluster. Ensure all nodes are updated and have the same OS version.
System Requirements:
Master Node: Minimum of 2 CPUs and 2GB RAM (more is recommended for production).
Worker Nodes: Minimum of 1 CPU and 1GB RAM per node.
Network Configuration:
All nodes should be able to communicate with each other over the network.
Assign static IP addresses to each node to ensure consistent connectivity.
Ensure hostnames are unique and resolvable between nodes.
Internet Connectivity: Required for downloading Kubernetes packages and container images. If your environment is air-gapped, you’ll need to manually provide these resources.
User Privileges: You should have
rootorsudoaccess on all nodes to perform the necessary configurations.
Preparing the System
Proper system preparation is key to a smooth Kubernetes installation. This involves configuring the network, setting up necessary kernel modules, adjusting firewall settings, and ensuring the container runtime is correctly installed and running. Here’s what we’ll be doing in this stage:
Disable Swap: Kubernetes requires swap to be disabled to function correctly.
Enable Necessary Kernel Modules: Ensure the system can forward IPv4 traffic and handle bridged network traffic required by Kubernetes.
Adjust Firewall and SELinux Settings: Kubernetes requires specific ports to be open and SELinux to be in permissive mode to avoid conflicts with cluster operations.
Install Container Runtime: We will use
containerd, a lightweight and Kubernetes-supported container runtime.
By following the steps outlined in this guide, you’ll set up a Kubernetes cluster that can scale and adapt to your application’s needs. Let’s get started!
Step 1: System Preparation
Disable Swap: Kubernetes requires that swap be disabled on all nodes.
[root@k8s-master ~]# swapoff -a [root@k8s-master ~]# sed -i '/swap/d' /etc/fstab [root@k8s-master ~]#Load Kernel Modules: Enable the necessary kernel modules for Kubernetes networking. (on all nodes)
[root@k8s-master ~]# cat <<EOF | tee /etc/modules-load.d/k8s.conf > overlay > br_netfilter > EOF overlay br_netfilter [root@k8s-master ~]# modprobe overlay [root@k8s-master ~]# modprobe br_netfilter [root@k8s-master ~]#Apply Sysctl Settings: Adjust sysctl settings to allow Kubernetes networking features. (all nodes)
[root@k8s-master ~]# cat <<EOF | tee /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf > net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1 > net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1 > net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1 > EOF net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1 net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1 net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1 [root@k8s-master ~]# [root@k8s-master ~]# sysctl --system * Applying /usr/lib/sysctl.d/01-unprivileged-bpf.conf ... kernel.unprivileged_bpf_disabled = 1 * Applying /usr/lib/sysctl.d/10-default-yama-scope.conf ... kernel.yama.ptrace_scope = 0 * Applying /usr/lib/sysctl.d/50-coredump.conf ... kernel.core_pattern = |/usr/lib/systemd/systemd-coredump %P %u %g %s %t %c %h %e kernel.core_pipe_limit = 16 * Applying /usr/lib/sysctl.d/50-default.conf ... kernel.sysrq = 16 kernel.core_uses_pid = 1 kernel.kptr_restrict = 1 net.ipv4.conf.all.rp_filter = 1 net.ipv4.conf.all.accept_source_route = 0 net.ipv4.conf.all.promote_secondaries = 1 net.core.default_qdisc = fq_codel fs.protected_hardlinks = 1 fs.protected_symlinks = 1 * Applying /usr/lib/sysctl.d/50-libkcapi-optmem_max.conf ... net.core.optmem_max = 81920 * Applying /etc/sysctl.d/50-libreswan.conf ... net.ipv6.conf.default.accept_redirects = 0 net.ipv6.conf.all.accept_redirects = 0 net.ipv4.conf.default.send_redirects = 0 net.ipv4.conf.default.accept_redirects = 0 net.ipv4.conf.all.send_redirects = 0 net.ipv4.conf.all.accept_redirects = 0 * Applying /usr/lib/sysctl.d/50-pid-max.conf ... kernel.pid_max = 4194304 * Applying /etc/sysctl.d/99-sysctl.conf ... * Applying /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf ... net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1 net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1 net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1 * Applying /etc/sysctl.conf ... [root@k8s-master ~]#Configure SELinux: Set SELinux to permissive mode or disable it to avoid conflicts with Kubernetes. (all nodes)
[root@k8s-master ~]# setenforce 0 setenforce: SELinux is disabled [root@k8s-master ~]# [root@k8s-master ~]# sed -i 's/^SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=permissive/' /etc/selinux/config [root@k8s-master ~]#Open Necessary Firewall Ports: If you are using a firewall, open the following ports on all nodes: (all nodes)
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=6443/tcp firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=2379-2380/tcp firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=10250/tcp firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=10251/tcp firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=10252/tcp firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=10255/tcp firewall-cmd --reloadAlternatively, you can disable the firewall:
systemctl disable --now firewalldInstall Docker-CE on CentOS 8: You will need to add the Docker repository first as it is no longer in the default package list using the following dnf config-manager command. (on all nodes)
[root@k8s-master sssd]# dnf config-manager --add-repo=https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo Adding repo from: https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo [root@k8s-master sssd]# [root@k8s-master ~]# dnf install https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/7/x86_64/stable/Packages/containerd.io-1.2.6-3.3.el7.x86_64.rpm Last metadata expiration check: 0:01:09 ago on Mon 26 Aug 2024 05:02:17 AM EDT. Dependencies resolved. ========================================================================================================================== Package Architecture Version Repository Size ========================================================================================================================== Installing: containerd.io x86_64 1.2.6-3.3.el7 @commandline 26 M replacing runc.x86_64 1:1.1.12-4.module+el8.10.0+90384+a78ffc57 Installing dependencies: crun x86_64 1.14.3-2.module+el8.10.0+90384+a78ffc57 ol8_appstream 257 k Installing weak dependencies: criu-libs x86_64 3.18-5.module+el8.10.0+90384+a78ffc57 ol8_appstream 38 k Transaction Summary ========================================================================================================================== Install 3 Packages Total size: 26 M Total download size: 295 k Is this ok [y/N]: y Downloading Packages: (1/2): criu-libs-3.18-5.module+el8.10.0+90384+a78ffc57.x86_64.rpm 83 kB/s | 38 kB 00:00 (2/2): crun-1.14.3-2.module+el8.10.0+90384+a78ffc57.x86_64.rpm 384 kB/s | 257 kB 00:00 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Total 426 kB/s | 295 kB 00:00 Running transaction check Transaction check succeeded. Running transaction test Transaction test succeeded. Running transaction Preparing : 1/1 Installing : criu-libs-3.18-5.module+el8.10.0+90384+a78ffc57.x86_64 1/4 Installing : crun-1.14.3-2.module+el8.10.0+90384+a78ffc57.x86_64 2/4 Installing : containerd.io-1.2.6-3.3.el7.x86_64 3/4 Running scriptlet: containerd.io-1.2.6-3.3.el7.x86_64 3/4 Obsoleting : runc-1:1.1.12-4.module+el8.10.0+90384+a78ffc57.x86_64 4/4 Running scriptlet: runc-1:1.1.12-4.module+el8.10.0+90384+a78ffc57.x86_64 4/4 Verifying : criu-libs-3.18-5.module+el8.10.0+90384+a78ffc57.x86_64 1/4 Verifying : crun-1.14.3-2.module+el8.10.0+90384+a78ffc57.x86_64 2/4 Verifying : containerd.io-1.2.6-3.3.el7.x86_64 3/4 Verifying : runc-1:1.1.12-4.module+el8.10.0+90384+a78ffc57.x86_64 4/4 Installed: containerd.io-1.2.6-3.3.el7.x86_64 criu-libs-3.18-5.module+el8.10.0+90384+a78ffc57.x86_64 crun-1.14.3-2.module+el8.10.0+90384+a78ffc57.x86_64 Complete! [root@k8s-master ~]#Now install the docker-ce package. We have some conflict and obsoletes package so we will use the best available package.
[root@k8s-master ~]# dnf install docker-ce --allowerasing Last metadata expiration check: 0:01:56 ago on Mon 26 Aug 2024 05:02:17 AM EDT. Dependencies resolved. ========================================================================================================================== Package Arch Version Repository Size ========================================================================================================================== Installing: docker-ce x86_64 3:26.1.3-1.el8 docker-ce-stable 27 M Upgrading: containerd.io x86_64 1.6.32-3.1.el8 docker-ce-stable 35 M Installing dependencies: docker-ce-cli x86_64 1:26.1.3-1.el8 docker-ce-stable 7.8 M libcgroup x86_64 0.41-19.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 70 k Installing weak dependencies: docker-buildx-plugin x86_64 0.14.0-1.el8 docker-ce-stable 14 M docker-ce-rootless-extras x86_64 26.1.3-1.el8 docker-ce-stable 5.0 M docker-compose-plugin x86_64 2.27.0-1.el8 docker-ce-stable 13 M Removing dependent packages: buildah x86_64 2:1.33.8-4.module+el8.10.0+90384+a78ffc57 @ol8_appstream 31 M cockpit-podman noarch 84.1-1.module+el8.10.0+90384+a78ffc57 @ol8_appstream 682 k podman x86_64 4:4.9.4-12.0.2.module+el8.10.0+90384+a78ffc57 @ol8_appstream 52 M podman-catatonit x86_64 4:4.9.4-12.0.2.module+el8.10.0+90384+a78ffc57 @ol8_appstream 794 k Downgrading: containers-common x86_64 1:1.2.2-10.0.1.module+el8.4.0+20195+0a4a4953 ol8_appstream 100 k Transaction Summary ========================================================================================================================== Install 6 Packages Upgrade 1 Package Remove 4 Packages Downgrade 1 Package Total download size: 103 M Is this ok [y/N]: y Downloading Packages: (1/8): docker-ce-26.1.3-1.el8.x86_64.rpm 6.1 MB/s | 27 MB 00:04 (2/8): containers-common-1.2.2-10.0.1.module+el8.4.0+20195+0a4a4953.x86_64.rpm 22 kB/s | 100 kB 00:04 (3/8): docker-ce-cli-26.1.3-1.el8.x86_64.rpm 5.7 MB/s | 7.8 MB 00:01 (4/8): docker-compose-plugin-2.27.0-1.el8.x86_64.rpm 6.9 MB/s | 13 MB 00:01 (5/8): libcgroup-0.41-19.el8.x86_64.rpm 117 kB/s | 70 kB 00:00 (6/8): containerd.io-1.6.32-3.1.el8.x86_64.rpm 7.4 MB/s | 35 MB 00:04 (7/8): docker-ce-rootless-extras-26.1.3-1.el8.x86_64.rpm 129 kB/s | 5.0 MB 00:39 (8/8): docker-buildx-plugin-0.14.0-1.el8.x86_64.rpm 109 kB/s | 14 MB 02:08 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Total 820 kB/s | 103 MB 02:08 Docker CE Stable - x86_64 4.5 kB/s | 1.6 kB 00:00 Importing GPG key 0x621E9F35: Userid : "Docker Release (CE rpm) <docker@docker.com>" Fingerprint: 060A 61C5 1B55 8A7F 742B 77AA C52F EB6B 621E 9F35 From : https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/gpg Is this ok [y/N]: y Key imported successfully Running transaction check Transaction check succeeded. Running transaction test Transaction test succeeded. Running transaction Preparing : 1/1 Running scriptlet: docker-compose-plugin-2.27.0-1.el8.x86_64 1/1 Installing : docker-compose-plugin-2.27.0-1.el8.x86_64 1/14 Running scriptlet: docker-compose-plugin-2.27.0-1.el8.x86_64 1/14 Upgrading : containerd.io-1.6.32-3.1.el8.x86_64 2/14 Running scriptlet: containerd.io-1.6.32-3.1.el8.x86_64 2/14 Running scriptlet: libcgroup-0.41-19.el8.x86_64 3/14 Installing : libcgroup-0.41-19.el8.x86_64 3/14 Running scriptlet: libcgroup-0.41-19.el8.x86_64 3/14 Installing : docker-buildx-plugin-0.14.0-1.el8.x86_64 4/14 Running scriptlet: docker-buildx-plugin-0.14.0-1.el8.x86_64 4/14 Installing : docker-ce-cli-1:26.1.3-1.el8.x86_64 5/14 Running scriptlet: docker-ce-cli-1:26.1.3-1.el8.x86_64 5/14 Installing : docker-ce-rootless-extras-26.1.3-1.el8.x86_64 6/14 Running scriptlet: docker-ce-rootless-extras-26.1.3-1.el8.x86_64 6/14 Installing : docker-ce-3:26.1.3-1.el8.x86_64 7/14 Running scriptlet: docker-ce-3:26.1.3-1.el8.x86_64 7/14 Downgrading : containers-common-1:1.2.2-10.0.1.module+el8.4.0+20195+0a4a4953.x86_64 8/14 Erasing : buildah-2:1.33.8-4.module+el8.10.0+90384+a78ffc57.x86_64 9/14 Erasing : cockpit-podman-84.1-1.module+el8.10.0+90384+a78ffc57.noarch 10/14 Running scriptlet: podman-4:4.9.4-12.0.2.module+el8.10.0+90384+a78ffc57.x86_64 11/14 Erasing : podman-4:4.9.4-12.0.2.module+el8.10.0+90384+a78ffc57.x86_64 11/14 Running scriptlet: podman-4:4.9.4-12.0.2.module+el8.10.0+90384+a78ffc57.x86_64 11/14 Cleanup : containers-common-2:1-82.0.1.module+el8.10.0+90384+a78ffc57.x86_64 12/14 Running scriptlet: containerd.io-1.2.6-3.3.el7.x86_64 13/14 Cleanup : containerd.io-1.2.6-3.3.el7.x86_64 13/14 Running scriptlet: containerd.io-1.2.6-3.3.el7.x86_64 13/14 Erasing : podman-catatonit-4:4.9.4-12.0.2.module+el8.10.0+90384+a78ffc57.x86_64 14/14 Running scriptlet: podman-catatonit-4:4.9.4-12.0.2.module+el8.10.0+90384+a78ffc57.x86_64 14/14 Verifying : containers-common-1:1.2.2-10.0.1.module+el8.4.0+20195+0a4a4953.x86_64 1/14 Verifying : containers-common-2:1-82.0.1.module+el8.10.0+90384+a78ffc57.x86_64 2/14 Verifying : docker-buildx-plugin-0.14.0-1.el8.x86_64 3/14 Verifying : docker-ce-3:26.1.3-1.el8.x86_64 4/14 Verifying : docker-ce-cli-1:26.1.3-1.el8.x86_64 5/14 Verifying : docker-ce-rootless-extras-26.1.3-1.el8.x86_64 6/14 Verifying : docker-compose-plugin-2.27.0-1.el8.x86_64 7/14 Verifying : libcgroup-0.41-19.el8.x86_64 8/14 Verifying : containerd.io-1.6.32-3.1.el8.x86_64 9/14 Verifying : containerd.io-1.2.6-3.3.el7.x86_64 10/14 Verifying : buildah-2:1.33.8-4.module+el8.10.0+90384+a78ffc57.x86_64 11/14 Verifying : cockpit-podman-84.1-1.module+el8.10.0+90384+a78ffc57.noarch 12/14 Verifying : podman-4:4.9.4-12.0.2.module+el8.10.0+90384+a78ffc57.x86_64 13/14 Verifying : podman-catatonit-4:4.9.4-12.0.2.module+el8.10.0+90384+a78ffc57.x86_64 14/14 Upgraded: containerd.io-1.6.32-3.1.el8.x86_64 Downgraded: containers-common-1:1.2.2-10.0.1.module+el8.4.0+20195+0a4a4953.x86_64 Installed: docker-buildx-plugin-0.14.0-1.el8.x86_64 docker-ce-3:26.1.3-1.el8.x86_64 docker-ce-cli-1:26.1.3-1.el8.x86_64 docker-ce-rootless-extras-26.1.3-1.el8.x86_64 docker-compose-plugin-2.27.0-1.el8.x86_64 libcgroup-0.41-19.el8.x86_64 Removed: buildah-2:1.33.8-4.module+el8.10.0+90384+a78ffc57.x86_64 cockpit-podman-84.1-1.module+el8.10.0+90384+a78ffc57.noarch podman-4:4.9.4-12.0.2.module+el8.10.0+90384+a78ffc57.x86_64 podman-catatonit-4:4.9.4-12.0.2.module+el8.10.0+90384+a78ffc57.x86_64 Complete! [root@k8s-master ~]#Now enable and start the docker service.
[root@k8s-master ~]# systemctl enable docker Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/docker.service → /usr/lib/systemd/system/docker.service. [root@k8s-master ~]# systemctl start docker [root@k8s-master ~]#
Step 2: Install Kubernetes Components
Run these steps on all nodes:
Add the Kubernetes Repository:
cat <<EOF | tee /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo [kubernetes] name=Kubernetes baseurl=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64 enabled=1 gpgcheck=1 repo_gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg EOFInstall Kubernetes Tools: Install
kubeadm,kubelet, andkubectlon all nodes.[root@k8s-master ~]# dnf install kubeadm -y Kubernetes 357 B/s | 454 B 00:01 Kubernetes 2.7 kB/s | 2.6 kB 00:00 Importing GPG key 0x13EDEF05: Userid : "Rapture Automatic Signing Key (cloud-rapture-signing-key-2022-03-07-08_01_01.pub)" Fingerprint: A362 B822 F6DE DC65 2817 EA46 B53D C80D 13ED EF05 From : https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg Importing GPG key 0xDC6315A3: Userid : "Artifact Registry Repository Signer <artifact-registry-repository-signer@google.com>" Fingerprint: 35BA A0B3 3E9E B396 F59C A838 C0BA 5CE6 DC63 15A3 From : https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg Kubernetes 784 B/s | 975 B 00:01 Importing GPG key 0x3E1BA8D5: Userid : "Google Cloud Packages RPM Signing Key <gc-team@google.com>" Fingerprint: 3749 E1BA 95A8 6CE0 5454 6ED2 F09C 394C 3E1B A8D5 From : https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg Kubernetes 75 kB/s | 182 kB 00:02 Dependencies resolved. ========================================================================================================================== Package Architecture Version Repository Size ========================================================================================================================== Installing: kubeadm x86_64 1.28.2-0 kubernetes 11 M Installing dependencies: conntrack-tools x86_64 1.4.4-11.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 204 k cri-tools x86_64 1.26.0-0 kubernetes 8.6 M kubectl x86_64 1.28.2-0 kubernetes 11 M kubelet x86_64 1.28.2-0 kubernetes 21 M kubernetes-cni x86_64 1.2.0-0 kubernetes 17 M libnetfilter_cthelper x86_64 1.0.0-15.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 24 k libnetfilter_cttimeout x86_64 1.0.0-11.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 24 k libnetfilter_queue x86_64 1.0.4-3.el8 ol8_baseos_latest 31 k socat x86_64 1.7.4.1-1.el8 ol8_appstream 323 k Transaction Summary ========================================================================================================================== Install 10 Packages Total download size: 69 M Installed size: 292 M Downloading Packages: (1/10): cee73f8035d734e86f722f77f1bf4e7d643e78d36646fd000148deb8af98b61c-kubeadm-1.28.2-0 297 kB/s | 11 MB 00:37 (2/10): 3f5ba2b53701ac9102ea7c7ab2ca6616a8cd5966591a77577585fde1c434ef74-cri-tools-1.26.0 144 kB/s | 8.6 MB 01:01 (3/10): a24e42254b5a14b67b58c4633d29c27370c28ed6796a80c455a65acc813ff374-kubectl-1.28.2-0 141 kB/s | 11 MB 01:20 (4/10): conntrack-tools-1.4.4-11.el8.x86_64.rpm 273 kB/s | 204 kB 00:00 (5/10): libnetfilter_cthelper-1.0.0-15.el8.x86_64.rpm 280 kB/s | 24 kB 00:00 (6/10): libnetfilter_cttimeout-1.0.0-11.el8.x86_64.rpm 261 kB/s | 24 kB 00:00 (7/10): libnetfilter_queue-1.0.4-3.el8.x86_64.rpm 364 kB/s | 31 kB 00:00 (8/10): socat-1.7.4.1-1.el8.x86_64.rpm 1.8 MB/s | 323 kB 00:00 (9/10): e1cae938e231bffa3618f5934a096bd85372ee9b1293081f5682a22fe873add8-kubelet-1.28.2-0 298 kB/s | 21 MB 01:11 (10/10): 0f2a2afd740d476ad77c508847bad1f559afc2425816c1f2ce4432a62dfe0b9d-kubernetes-cni- 138 kB/s | 17 MB 02:04 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Total 378 kB/s | 69 MB 03:06 Kubernetes 1.8 kB/s | 2.6 kB 00:01 Importing GPG key 0x13EDEF05: Userid : "Rapture Automatic Signing Key (cloud-rapture-signing-key-2022-03-07-08_01_01.pub)" Fingerprint: A362 B822 F6DE DC65 2817 EA46 B53D C80D 13ED EF05 From : https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg Key imported successfully Importing GPG key 0xDC6315A3: Userid : "Artifact Registry Repository Signer <artifact-registry-repository-signer@google.com>" Fingerprint: 35BA A0B3 3E9E B396 F59C A838 C0BA 5CE6 DC63 15A3 From : https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg Key imported successfully Kubernetes 887 B/s | 975 B 00:01 Importing GPG key 0x3E1BA8D5: Userid : "Google Cloud Packages RPM Signing Key <gc-team@google.com>" Fingerprint: 3749 E1BA 95A8 6CE0 5454 6ED2 F09C 394C 3E1B A8D5 From : https://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg Key imported successfully Running transaction check Transaction check succeeded. Running transaction test Transaction test succeeded. Running transaction Preparing : 1/1 Installing : socat-1.7.4.1-1.el8.x86_64 1/10 Installing : libnetfilter_queue-1.0.4-3.el8.x86_64 2/10 Running scriptlet: libnetfilter_queue-1.0.4-3.el8.x86_64 2/10 Installing : libnetfilter_cttimeout-1.0.0-11.el8.x86_64 3/10 Running scriptlet: libnetfilter_cttimeout-1.0.0-11.el8.x86_64 3/10 Installing : libnetfilter_cthelper-1.0.0-15.el8.x86_64 4/10 Running scriptlet: libnetfilter_cthelper-1.0.0-15.el8.x86_64 4/10 Installing : conntrack-tools-1.4.4-11.el8.x86_64 5/10 Running scriptlet: conntrack-tools-1.4.4-11.el8.x86_64 5/10 Installing : kubernetes-cni-1.2.0-0.x86_64 6/10 Installing : kubelet-1.28.2-0.x86_64 7/10 Installing : kubectl-1.28.2-0.x86_64 8/10 Installing : cri-tools-1.26.0-0.x86_64 9/10 Installing : kubeadm-1.28.2-0.x86_64 10/10 Running scriptlet: kubeadm-1.28.2-0.x86_64 10/10 Verifying : cri-tools-1.26.0-0.x86_64 1/10 Verifying : kubeadm-1.28.2-0.x86_64 2/10 Verifying : kubectl-1.28.2-0.x86_64 3/10 Verifying : kubelet-1.28.2-0.x86_64 4/10 Verifying : kubernetes-cni-1.2.0-0.x86_64 5/10 Verifying : conntrack-tools-1.4.4-11.el8.x86_64 6/10 Verifying : libnetfilter_cthelper-1.0.0-15.el8.x86_64 7/10 Verifying : libnetfilter_cttimeout-1.0.0-11.el8.x86_64 8/10 Verifying : libnetfilter_queue-1.0.4-3.el8.x86_64 9/10 Verifying : socat-1.7.4.1-1.el8.x86_64 10/10 Installed: conntrack-tools-1.4.4-11.el8.x86_64 cri-tools-1.26.0-0.x86_64 kubeadm-1.28.2-0.x86_64 kubectl-1.28.2-0.x86_64 kubelet-1.28.2-0.x86_64 kubernetes-cni-1.2.0-0.x86_64 libnetfilter_cthelper-1.0.0-15.el8.x86_64 libnetfilter_cttimeout-1.0.0-11.el8.x86_64 libnetfilter_queue-1.0.4-3.el8.x86_64 socat-1.7.4.1-1.el8.x86_64 Complete! [root@k8s-master ~]#
Enable and start the kubelet service on the master node.
[root@k8s-master ~]# systemctl enable kubelet
Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/kubelet.service → /usr/lib/systemd/system/kubelet.service.
[root@k8s-master ~]# systemctl start kubelet
[root@k8s-master ~]#
Step 3: Initialize the Master Node
Run the following commands only on the master node:
Initialize the Cluster:
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubeadm init I0826 05:14:29.358589 7237 version.go:256] remote version is much newer: v1.31.0; falling back to: stable-1.28 [init] Using Kubernetes version: v1.28.13 [preflight] Running pre-flight checks [WARNING FileExisting-tc]: tc not found in system path error execution phase preflight: [preflight] Some fatal errors occurred: [ERROR CRI]: container runtime is not running: output: time="2024-08-26T05:14:30-04:00" level=fatal msg="validate service connection: CRI v1 runtime API is not implemented for endpoint \"unix:///var/run/containerd/containerd.sock\": rpc error: code = Unimplemented desc = unknown service runtime.v1.RuntimeService" , error: exit status 1 [preflight] If you know what you are doing, you can make a check non-fatal with `--ignore-preflight-errors=...` To see the stack trace of this error execute with --v=5 or higher [root@k8s-master ~]#We get the above error while initializing the k8s control plane. To resolve this issue, we need to delete this file /etc/containerd/config.toml and restart the containerd service.
[root@k8s-master ~]# rm /etc/containerd/config.toml rm: remove regular file '/etc/containerd/config.toml'? yes [root@k8s-master ~]# [root@k8s-master ~]# systemctl restart containerd [root@k8s-master ~]#Now let's try to initialize the k8s control plane.
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubeadm init I0826 05:19:18.436203 7761 version.go:256] remote version is much newer: v1.31.0; falling back to: stable-1.28 [init] Using Kubernetes version: v1.28.13 [preflight] Running pre-flight checks [WARNING FileExisting-tc]: tc not found in system path [preflight] Pulling images required for setting up a Kubernetes cluster [preflight] This might take a minute or two, depending on the speed of your internet connection [preflight] You can also perform this action in beforehand using 'kubeadm config images pull' W0826 05:23:24.551620 7761 checks.go:835] detected that the sandbox image "registry.k8s.io/pause:3.6" of the container runtime is inconsistent with that used by kubeadm. It is recommended that using "registry.k8s.io/pause:3.9" as the CRI sandbox image. [certs] Using certificateDir folder "/etc/kubernetes/pki" [certs] Generating "ca" certificate and key [certs] Generating "apiserver" certificate and key [certs] apiserver serving cert is signed for DNS names [k8s-master.ha.stalab.ciena.com kubernetes kubernetes.default kubernetes.default.svc kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local] and IPs [10.96.0.1 10.121.230.193] [certs] Generating "apiserver-kubelet-client" certificate and key [certs] Generating "front-proxy-ca" certificate and key [certs] Generating "front-proxy-client" certificate and key [certs] Generating "etcd/ca" certificate and key [certs] Generating "etcd/server" certificate and key [certs] etcd/server serving cert is signed for DNS names [k8s-master.ha.stalab.ciena.com localhost] and IPs [10.121.230.193 127.0.0.1 ::1] [certs] Generating "etcd/peer" certificate and key [certs] etcd/peer serving cert is signed for DNS names [k8s-master.ha.stalab.ciena.com localhost] and IPs [10.121.230.193 127.0.0.1 ::1] [certs] Generating "etcd/healthcheck-client" certificate and key [certs] Generating "apiserver-etcd-client" certificate and key [certs] Generating "sa" key and public key [kubeconfig] Using kubeconfig folder "/etc/kubernetes" [kubeconfig] Writing "admin.conf" kubeconfig file [kubeconfig] Writing "kubelet.conf" kubeconfig file [kubeconfig] Writing "controller-manager.conf" kubeconfig file [kubeconfig] Writing "scheduler.conf" kubeconfig file [etcd] Creating static Pod manifest for local etcd in "/etc/kubernetes/manifests" [control-plane] Using manifest folder "/etc/kubernetes/manifests" [control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-apiserver" [control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-controller-manager" [control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-scheduler" [kubelet-start] Writing kubelet environment file with flags to file "/var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env" [kubelet-start] Writing kubelet configuration to file "/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml" [kubelet-start] Starting the kubelet [wait-control-plane] Waiting for the kubelet to boot up the control plane as static Pods from directory "/etc/kubernetes/manifests". This can take up to 4m0s [apiclient] All control plane components are healthy after 8.001106 seconds [upload-config] Storing the configuration used in ConfigMap "kubeadm-config" in the "kube-system" Namespace [kubelet] Creating a ConfigMap "kubelet-config" in namespace kube-system with the configuration for the kubelets in the cluster [upload-certs] Skipping phase. Please see --upload-certs [mark-control-plane] Marking the node k8s-master.ha.stalab.ciena.com as control-plane by adding the labels: [node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane node.kubernetes.io/exclude-from-external-load-balancers] [mark-control-plane] Marking the node k8s-master.ha.stalab.ciena.com as control-plane by adding the taints [node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane:NoSchedule] [bootstrap-token] Using token: cjg2kt.c40lsm41bwm3l9sa [bootstrap-token] Configuring bootstrap tokens, cluster-info ConfigMap, RBAC Roles [bootstrap-token] Configured RBAC rules to allow Node Bootstrap tokens to get nodes [bootstrap-token] Configured RBAC rules to allow Node Bootstrap tokens to post CSRs in order for nodes to get long term certificate credentials [bootstrap-token] Configured RBAC rules to allow the csrapprover controller automatically approve CSRs from a Node Bootstrap Token [bootstrap-token] Configured RBAC rules to allow certificate rotation for all node client certificates in the cluster [bootstrap-token] Creating the "cluster-info" ConfigMap in the "kube-public" namespace [kubelet-finalize] Updating "/etc/kubernetes/kubelet.conf" to point to a rotatable kubelet client certificate and key [addons] Applied essential addon: CoreDNS [addons] Applied essential addon: kube-proxy Your Kubernetes control-plane has initialized successfully! To start using your cluster, you need to run the following as a regular user: mkdir -p $HOME/.kube sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config Alternatively, if you are the root user, you can run: export KUBECONFIG=/etc/kubernetes/admin.conf You should now deploy a pod network to the cluster. Run "kubectl apply -f [podnetwork].yaml" with one of the options listed at: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/addons/ Then you can join any number of worker nodes by running the following on each as root: kubeadm join 10.121.230.193:6443 --token cjg2kt.c40lsm41bwm3l9sa \ --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:7e2a71cb74c5d024626cf9d2a47c160142d62c15bad84aa6f140bd6b358ab74b [root@k8s-master ~]#This command initializes the Kubernetes control plane and sets up the master node.
Set Up kubeconfig: Configure kubectl to use the admin kubeconfig for cluster management.
[root@k8s-master ~]# mkdir -p $HOME/.kube [root@k8s-master ~]# sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config [root@k8s-master ~]# sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/configDeploy a Pod Network: Apply a pod network add-on, such as Calico, to allow communication between pods across nodes.
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl apply -f https://docs.projectcalico.org/manifests/calico.yaml poddisruptionbudget.policy/calico-kube-controllers created serviceaccount/calico-kube-controllers created serviceaccount/calico-node created configmap/calico-config created customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/bgpconfigurations.crd.projectcalico.org created customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/bgppeers.crd.projectcalico.org created customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/blockaffinities.crd.projectcalico.org created customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/caliconodestatuses.crd.projectcalico.org created customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/clusterinformations.crd.projectcalico.org created customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/felixconfigurations.crd.projectcalico.org created customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/globalnetworkpolicies.crd.projectcalico.org created customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/globalnetworksets.crd.projectcalico.org created customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/hostendpoints.crd.projectcalico.org created customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/ipamblocks.crd.projectcalico.org created customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/ipamconfigs.crd.projectcalico.org created customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/ipamhandles.crd.projectcalico.org created customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/ippools.crd.projectcalico.org created customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/ipreservations.crd.projectcalico.org created customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/kubecontrollersconfigurations.crd.projectcalico.org created customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/networkpolicies.crd.projectcalico.org created customresourcedefinition.apiextensions.k8s.io/networksets.crd.projectcalico.org created clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/calico-kube-controllers created clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/calico-node created clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/calico-kube-controllers created clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/calico-node created daemonset.apps/calico-node created deployment.apps/calico-kube-controllers created [root@k8s-master ~]#Now, let's the master node status in our cluster.
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get nodes NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION k8s-master Ready control-plane 6m1s v1.28.2 [root@k8s-master ~]#
Step 4: Join the Worker Nodes to the Cluster
After setting up the master node, the next step is to join the worker nodes to the cluster. This will allow them to communicate with the master node and run your application workloads.
Join the Worker Nodes:
On each worker node, run the following command to join the cluster. This command uses the IP address of the master node, a token for authentication, and the CA certificate hash for verification.
[root@k8s-worker2 ~]# kubeadm join x.x.x.x:6443 --token cjg2kt.c40lsm41bwm3l9sa --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:7e2a71cb74c5d024626cf9d2a47c160142d62c15bad84aa6f140bd6b358ab74b [preflight] Running pre-flight checks [WARNING FileExisting-tc]: tc not found in system path [preflight] Reading configuration from the cluster... [preflight] FYI: You can look at this config file with 'kubectl -n kube-system get cm kubeadm-config -o yaml' [kubelet-start] Writing kubelet configuration to file "/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml" [kubelet-start] Writing kubelet environment file with flags to file "/var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env" [kubelet-start] Starting the kubelet [kubelet-start] Waiting for the kubelet to perform the TLS Bootstrap... This node has joined the cluster: * Certificate signing request was sent to apiserver and a response was received. * The Kubelet was informed of the new secure connection details. Run 'kubectl get nodes' on the control-plane to see this node join the cluster. [root@k8s-worker2 ~]#Once this command is executed, the worker nodes will connect to the master node and become part of the cluster.
Verify the Cluster Status:
After all worker nodes have joined the cluster, return to the master node to verify that everything is working correctly.
kubectl get nodesThe output should list all the nodes in the cluster (the master node and both worker nodes), showing their status as
Ready.Example output:
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get nodes NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION k8s-master Ready control-plane 30m v1.28.0 k8s-worker1 Ready <none> 10m v1.28.0 k8s-worker2 Ready <none> 10m v1.28.0
As we can see from the above output, k8s-master node has the role of control-plane and k8s-worker1 and k8s-worker2 are the part of this cluster. Let's configure these two nodes as worker nodes.
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl label nodes k8s-worker1 node-role.kubernetes.io/worker=worker
node/k8s-worker1 labeled
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl label nodes k8s-worker2 node-role.kubernetes.io/worker=worker
node/k8s-worker2 labeled
[root@k8s-master ~]#
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
k8s-master Ready control-plane 30m v1.28.0
k8s-worker1 Ready worker 10m v1.28.0
k8s-worker2 Ready worker 10m v1.28.0
Step 5: Deploy a Test Application
To ensure the cluster is functioning properly, you can deploy a simple application across the nodes:
Deploy a Nginx Pod:
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl create deployment nginx --image=nginx deployment.apps/nginx created [root@k8s-master ~]#Expose the Nginx Deployment:
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl expose deployment nginx --port=80 --type=NodePort service/nginx exposed [root@k8s-master ~]#Access the Application: Get the NodePort assigned to the Nginx service:
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get services NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 6h21m nginx NodePort 10.104.37.81 <none> 80:32644/TCP 12s [root@k8s-master ~]#Access the application using the worker node's IP address and the NodePort.
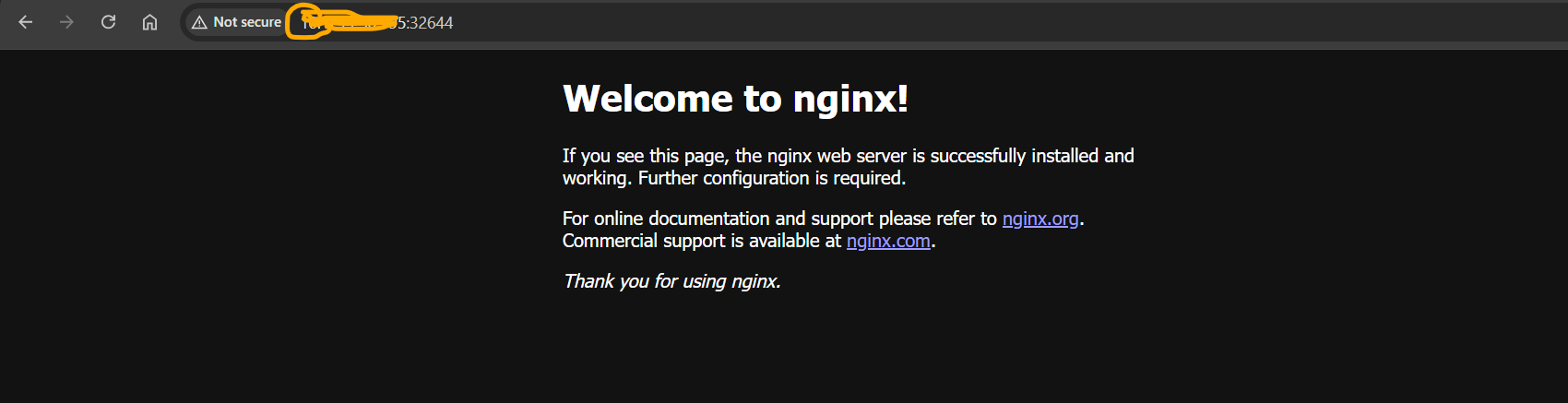
Hurray! our application is running fine and accessible on the browser.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You have successfully set up a Kubernetes cluster on Linux 8 using kubeadm, with one master node and two worker nodes. Your cluster is now ready for deploying and managing containerized applications. This setup is ideal for development, testing, and learning purposes. As you gain more experience, you can expand this cluster to meet production-level needs by adding more nodes, setting up high availability, and configuring more advanced networking and storage solution.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Siddhartha Gaurav directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Siddhartha Gaurav
Siddhartha Gaurav
I'm a passionate DevOps engineer with a knack for streamlining development workflows and ensuring seamless deployment pipelines. With experience in managing cloud infrastructure, implementing DevOps best practices, and leveraging automation tools, I thrive on tackling complex challenges and driving efficiency in software delivery. Let's connect and explore how I can contribute to your projects!