AWS Global Infrastructure
 Jeevan
Jeevan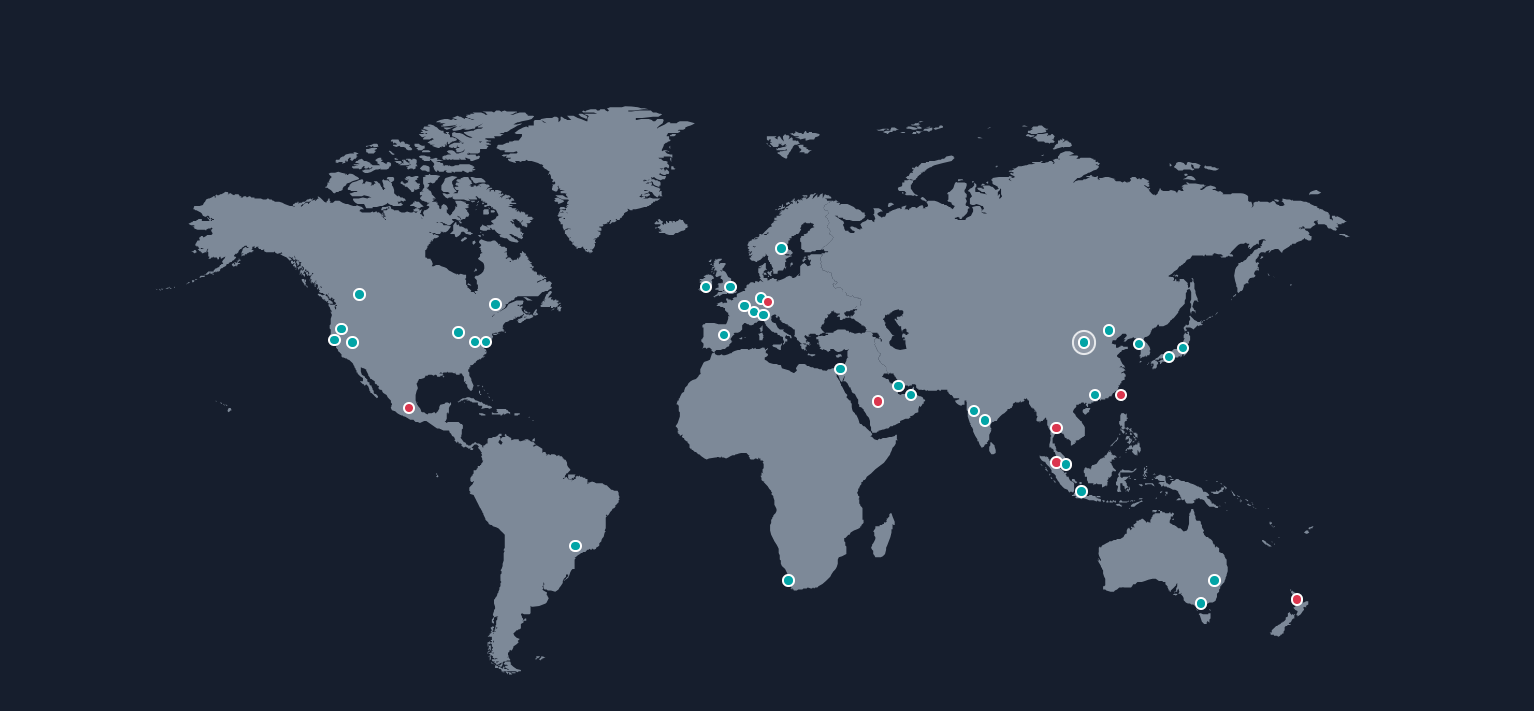
After understanding AWS as IAAS, the question arises: how does AWS manage all its infrastructure? To understand this, we need to understand important terms like region, availability zone, local zone, wavelength zone, etc. Let's go on, one by one.
AWS global infrastructure page link
Regions
Regions are physical locations where exactly your data gets stored. In technical terms, we call it a data center. The region consists of a cluster of data centers. Within a region, we have availability zones. Each AWS Region consists of at least three isolated and physically separate AZs within a geographic area. AWS has 33 regions launched to date.
Availability Zones
The logical grouping of data centers is called an availability zone. As said earlier each region consists of a minimum of three availability zones. Each AZ has independent power, cooling, and physical security and is connected via redundant, ultra-low-latency networks. AWS has 105 availability zones launched to date.
Local Zones
AWS Local Zones are an infrastructure deployment that places select AWS services closer to your end users and workloads. This feature is mainly used for media & entertainment content creation, real-time gaming, reservoir simulations, electronic design automation, and machine learning.
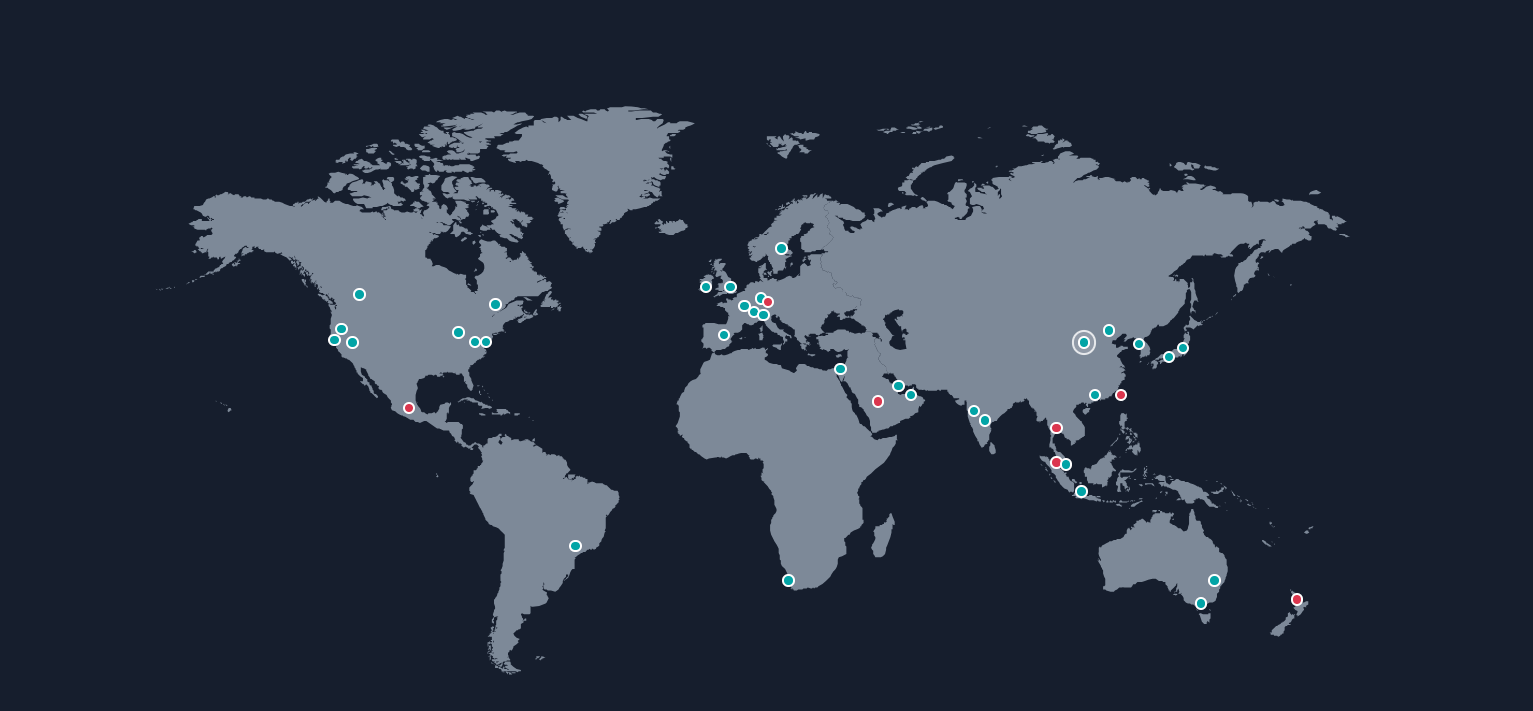
Here we can see blue dots are already launched regions and red ones are soon launching.
For example, the Mumbai region has 3 availability zones and 2 local zones, while Hyderabad has only 3 availability zones.
So in the end, we can see how AWS manages all its global infrastructure by dividing it into regions, availability zones, local zones, etc.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Jeevan directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
