Concurrency Control in Distributed Systems:
 Manish Goyal
Manish GoyalProblem :
When multiple users try to book the same seat.
Critical section: In which we are trying to access shared resources.
1st Solution:
Use synchronized blocks for the critical section. This can work on a single machine.
But this will not work in a distributed system because in a distributed system we have multiple processes running on different servers.
Concepts related to this:
What is the usage of Transaction?
- It help to achieve integrity and avoid inconsistency .
Either all success or rollback.
What is DB locking?
- It is to make sure that no other transaction update the locked rows.
| LockType | Another Shared Lock | Another Exclusive Lock |
| Have Shared Lock | Yes | No |
| Have an exclusive lock | No | No |
Shared lock is used for reading a row.
Exclusive Lock : Used for writing purpose : Others can't do anything
Isolation Levels:
Dirty Read:
If a transaction A is reading the data that is written by B and not yet even committed. If transaction B does the rollback, then whatever data read by transaction A is known as dirty read.
Non-Repeatable Read:
If suppose transaction A, Read the same data several times and there is a chance that it reads different value (non-rrepeatable read).
Phantom Read:
If Suppose transaction A, execute some query several times, and there is a chance that the rows returned are different.

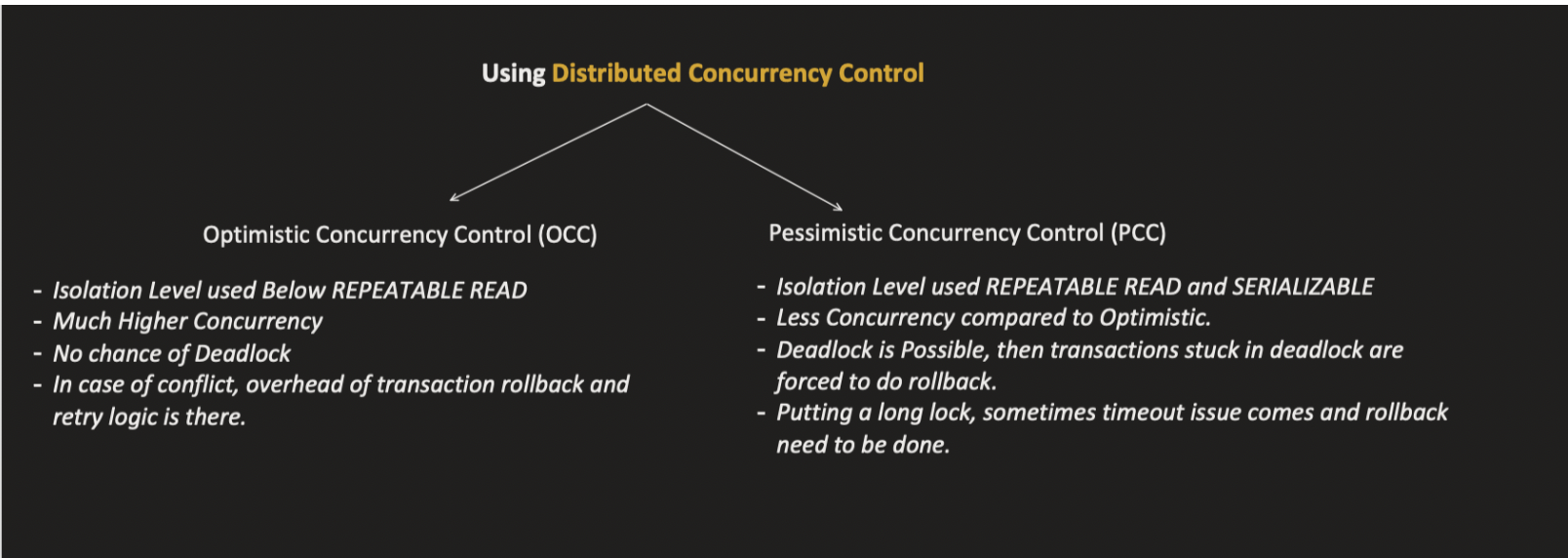
Distributed concurency control:
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Manish Goyal directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
