How to deploy editable tables in HTML using Angular 5 and Entity Framework Core
 freeCodeCamp
freeCodeCamp
By Ankit Sharma
Introduction
In this article, we are going to create a web application using ASP.NET Core 2.0 and Angular 5 with the help of the Entity Framework (EF) Core database-first approach. We will be creating a sample Employee Record Management system. To read the inputs from the user, we will use Angular forms with required field validations on the client side. We are also going to bind a dropdown list in the Angular form to a table in the database using EF Core.
We will be using Visual Studio 2017 and SQL Server version 2008 or above.
Prerequisites
- Install .NET Core 2.0.0 or above SDK from here.
- Install the latest version of Visual Studio 2017 Community Edition from here.
- Download and install the latest version of Node.js from here..
- SQL Server 2008 or above.
Source Code
Before proceeding, I recommend you get the source code from Github.
Creating the tables
We will be using two tables to store our data.
tblEmployee: used to store the details of employees. It contains fields such as EmployeeID, Name, City, Department, and Gender.tblCities: this contains the list of cities. It is used to populate the City field of the tblEmployee table. tblCities contains two fields, CityID and CityName.
Execute the following commands to create both tables:
CREATE TABLE tblEmployee ( EmployeeID int IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY, Name varchar(20) NOT NULL , City varchar(20) NOT NULL , Department varchar(20) NOT NULL , Gender varchar(6) NOT NULL ) GO CREATE TABLE tblCities ( CityID int IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY, CityName varchar(20) NOT NULL ) GO
Now we will put some data into the tblCities table. We will be using this table to bind a dropdown list in our web application. The desired city can be selected using this dropdown list. Use the following insert statements.
INSERT INTO tblCities VALUES('New Delhi'); INSERT INTO tblCities VALUES('Mumbai'); INSERT INTO tblCities VALUES('Hyderabad'); INSERT INTO tblCities VALUES('Chennai'); INSERT INTO tblCities VALUES('Bengaluru');
Now, our Database part has been completed. So, we will proceed to create the MVC application using Visual Studio 2017.
Create the ASP.NET MVC web application
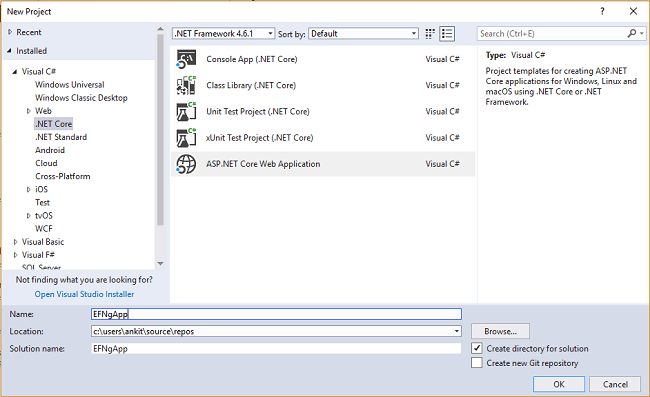
Open Visual Studio and select File >> New >> Project.
After selecting the project, a “New Project” dialog will open. Select .NET Core inside Visual C# menu from the left panel.
Then, select “ASP.NET Core Web Application” from the available project types. Put the name of the project as “EFNgApp” and press OK.
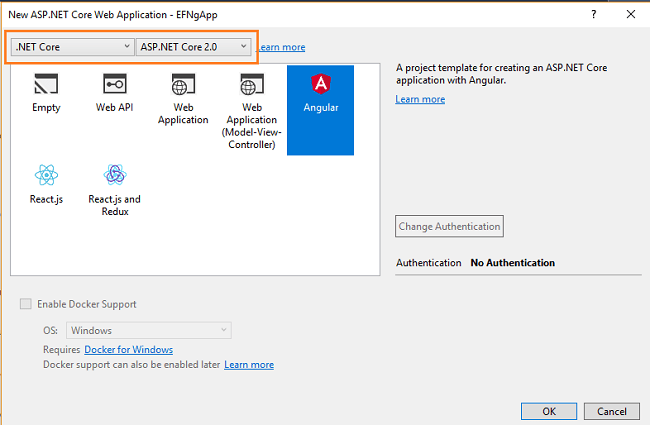
After clicking on OK, a new dialog will open asking you to select the project template. You can observe two drop-down menus at the top left of the template window. Select “.NET Core” and “ASP.NET Core 2.0” from these dropdowns. Then, select the “Angular” template and press OK.
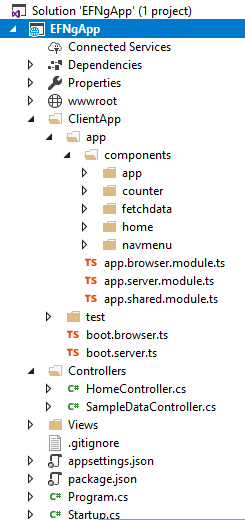
Now, our project will be created. You can see the folder structure in Solution Explorer in the below image.
Here, we have our “Controllers” and “Views” folders. We won’t be touching the Views folder for this tutorial, since we will be using Angular to handle the UI.
The Controllers folders will contain our Web API controller. The point of interest for us is the “ClientApp” folder where the client side of our application resides.
Inside the “ClientApp/app/components folder,” we already have few components created. These are provided by default with the Angular template in VS 2017. These components won’t affect our application, but for the sake of this tutorial, we will delete the “fetchdata” and “counter” folders from ClientApp/app/components.
Adding the Model to the Application
We are using Entity Framework core database first approach to create our models. Navigate to Tools >> NuGet Package Manager >> Package Manager Console.
We have to install the package for the database provider that we are targeting, which is SQL Server in this case. Now run the following command:
Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer
Since we are using Entity Framework Tools to create a model from the existing database, we will install the tools package as well. Run the following command:
Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools
After you have installed both the packages, we will scaffold our model from the database tables using the following command:
Scaffold-DbContext "Your connection string here" Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer -OutputDir Models -Tables tblEmployee, tblCities
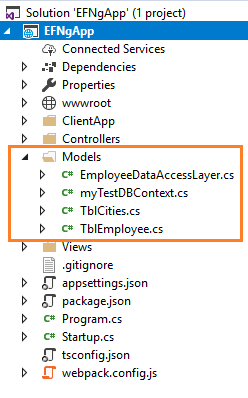
Do not forget to put your own connection string (inside double quotes “ ”). After this command gets executed successfully, a “Models” folder will be created. This folder contains three class files: myTestDBContext.cs, TblCities.cs and TblEmployee.cs. We have successfully created our Models using EF core database first approach.
Now, we will create one more class file to handle database related operations
Right click on the “Models” folder and select Add >> Class. Name your class EmployeeDataAccessLa_y_er.cs and click the “Add” button. At this point, the “Models” folder will have the following structure.
Open “EmployeeDataAccessLayer.cs” and insert the following code to handle database operations.
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore; using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace EFNgApp.Models { public class EmployeeDataAccessLayer { myTestDBContext db = new myTestDBContext(); public IEnumerable<TblEmployee> GetAllEmployees() { try { return db.TblEmployee.ToList(); } catch { throw; } } //To Add new employee record public int AddEmployee(TblEmployee employee) { try { db.TblEmployee.Add(employee); db.SaveChanges(); return 1; } catch { throw; } } //To Update the records of a particluar employee public int UpdateEmployee(TblEmployee employee) { try { db.Entry(employee).State = EntityState.Modified; db.SaveChanges(); return 1; } catch { throw; } } //Get the details of a particular employee public TblEmployee GetEmployeeData(int id) { try { TblEmployee employee = db.TblEmployee.Find(id); return employee; } catch { throw; } } //To Delete the record of a particular employee public int DeleteEmployee(int id) { try { TblEmployee emp = db.TblEmployee.Find(id); db.TblEmployee.Remove(emp); db.SaveChanges(); return 1; } catch { throw; } } //To Get the list of Cities public List<TblCities> GetCities() { List<TblCities> lstCity = new List<TblCities>(); lstCity = (from CityList in db.TblCities select CityList).ToList(); return lstCity; } } }
Now, we will proceed to create our Web API Controller.
Adding the Web API Controller to the Application
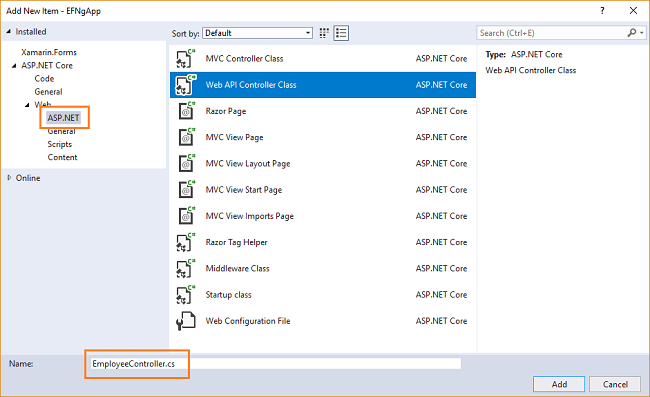
Right click on Controllers folder and select Add >> New Item.
An “Add New Item” dialog box will open. Select “ASP.NET” from the left panel. Then, select “Web API Controller Class” from templates panel and put the name as EmployeeController.cs. Click “Add”.
This will create our Web API “EmployeeController” class. We will put all our business logic in this controller. We will call the methods of “EmployeeDataAccessLayer” to fetch data and pass on the data to the Angular frontend.
Open the “EmployeeController.cs” file and insert the following code into it:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Threading.Tasks; using EFNgApp.Models; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc; namespace EFNgApp.Controllers { public class EmployeeController : Controller { EmployeeDataAccessLayer objemployee = new EmployeeDataAccessLayer(); [HttpGet] [Route("api/Employee/Index")] public IEnumerable<TblEmployee> Index() { return objemployee.GetAllEmployees(); } [HttpPost] [Route("api/Employee/Create")] public int Create([FromBody] TblEmployee employee) { return objemployee.AddEmployee(employee); } [HttpGet] [Route("api/Employee/Details/{id}")] public TblEmployee Details(int id) { return objemployee.GetEmployeeData(id); } [HttpPut] [Route("api/Employee/Edit")] public int Edit([FromBody]TblEmployee employee) { return objemployee.UpdateEmployee(employee); } [HttpDelete] [Route("api/Employee/Delete/{id}")] public int Delete(int id) { return objemployee.DeleteEmployee(id); } [HttpGet] [Route("api/Employee/GetCityList")] public IEnumerable<TblCities> Details() { return objemployee.GetCities(); } } }
We are done with our backend logic. Now we’ll code our frontend using Angular 5.
Create the Angular Service
We will create an Angular service which will convert the Web API response to JSON and pass it to our component.
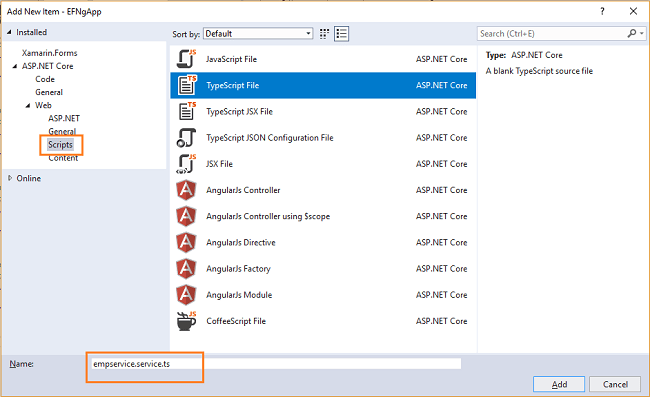
Right-click on the “ClientApp/app” folder and then Add >> New Folder and name the folder as “Services”.
Right-click on the “Services” folder and select Add >> New Item. An “Add New Item” dialog box will open. Select “Scripts” from the left panel. Then select “TypeScript File” from the templates panel, and put the name as empservice.service.ts. Click “Add”.
Open the “empservice.service.ts” file and insert the following code into it:
import { Injectable, Inject } from '@angular/core'; import { Http, Response } from '@angular/http'; import { Observable } from 'rxjs/Observable'; import { Router } from '@angular/router'; import 'rxjs/add/operator/map'; import 'rxjs/add/operator/catch'; import 'rxjs/add/observable/throw'; @Injectable() export class EmployeeService { myAppUrl: string = ""; constructor(private _http: Http, @Inject('BASE_URL') baseUrl: string) { this.myAppUrl = baseUrl; } getCityList() { return this._http.get(this.myAppUrl + 'api/Employee/GetCityList') .map(res => res.json()) .catch(this.errorHandler); } getEmployees() { return this._http.get(this.myAppUrl + 'api/Employee/Index') .map((response: Response) => response.json()) .catch(this.errorHandler); } getEmployeeById(id: number) { return this._http.get(this.myAppUrl + "api/Employee/Details/" + id) .map((response: Response) => response.json()) .catch(this.errorHandler) } saveEmployee(employee) { return this._http.post(this.myAppUrl + 'api/Employee/Create', employee) .map((response: Response) => response.json()) .catch(this.errorHandler) } updateEmployee(employee) { return this._http.put(this.myAppUrl + 'api/Employee/Edit', employee) .map((response: Response) => response.json()) .catch(this.errorHandler); } deleteEmployee(id) { return this._http.delete(this.myAppUrl + "api/Employee/Delete/" + id) .map((response: Response) => response.json()) .catch(this.errorHandler); } errorHandler(error: Response) { console.log(error); return Observable.throw(error); } }
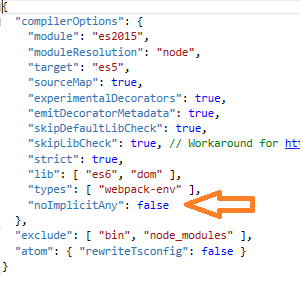
At this point, you might get the following error: “Parameter ‘employee’ implicitly has an ‘any’ type” in “empservice.service.ts” file.
If you encounter this issue, then add the following line inside the “tsconfig.json” file.
“noImplicitAny”: false
Now, we will create our components.
Creating Angular components
We will be adding two Angular components to our application:
fetchemployeecomponent: to display all the employee data or delete existing employee data.addemployeecomponent: to add a new employee data or edit an existing employee data.
Right-click on the “ClientApp/app/components” folder and select Add >> New Folder and name the folder “addem_p_loyee”.
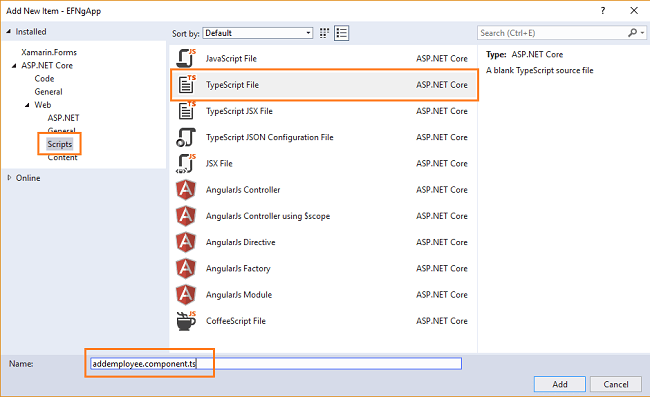
Right-click on the “addemployee” folder, and select Add >> New Item. An “Add New Item” dialog box will open.
Select “Scripts” from the left panel, then select “TypeScript File” from templates panel. Put the name as addemployee.component.ts.
Click “Add”. This will add a typescript file inside the “addemployee” folder.
Right-click on the “addemployee” folder and select Add >> New Item. An “Add New Item” dialog box will open.
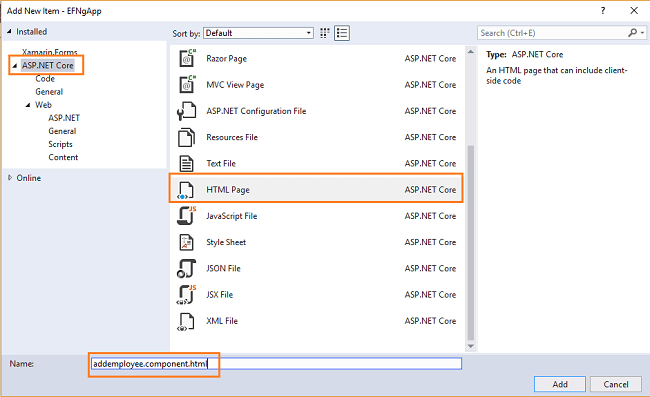
Select “ASP.NET Core” from the left panel, then select “HTML Page” from templates panel. Put the name as addemployee.component.html.
Click “Add”. This will add a HTML file inside the “addemployee” folder.
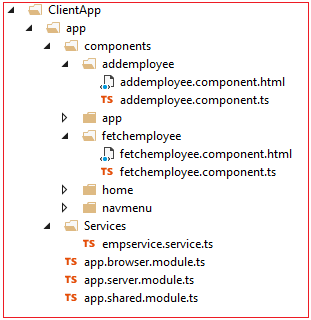
Similarly, create a “fetchemployee” folder inside the “ClientApp/app/components” folder.
Add fetchemployee.component.ts and fetchemployee.component.html files to it.
Now our “ClientApp/app/components” structure will look like the image below.
Open fetchemployee.component.ts and insert the following code:
import { Component, Inject } from '@angular/core'; import { Http, Headers } from '@angular/http'; import { Router, ActivatedRoute } from '@angular/router'; import { EmployeeService } from '../../services/empservice.service' @Component({ templateUrl: './fetchemployee.component.html' }) export class FetchEmployeeComponent { public empList: EmployeeData[]; constructor(public http: Http, private _router: Router, private _employeeService: EmployeeService) { this.getEmployees(); } getEmployees() { this._employeeService.getEmployees().subscribe( data => this.empList = data ) } delete(employeeID) { var ans = confirm("Do you want to delete customer with Id: " + employeeID); if (ans) { this._employeeService.deleteEmployee(employeeID).subscribe((data) => { this.getEmployees(); }, error => console.error(error)) } } } interface EmployeeData { employeeId: number; name: string; gender: string; city: string; department: string; }
Let’s understand this code.
At the very top we have imported Angular modules and EmployeeService references. After this we use @Component decorator to define the template URL for our component.
Inside the FetchEmployeeComponent class we have declared an array variable empList of type EmployeeData. EmployeeData is an interface having the properties same as our TblEmployeeModel class.
Inside the getEmployees method we are calling the getEmployees method of our service EmployeeService. This will return an array of Employees to be stored in the empList variable. The getEmployees method is called inside the constructor, so that the employee data will be displayed as the page loads.
Next, we have a delete method which accepts employeeID as a parameter. This will prompt the user with a confirmation box. If the user selects “yes” then it will delete the employee with this employeeID.
Open fetchemployee.component.html and insert the following code:
<h1>Employee Data</h1> <p>This component demonstrates fetching Employee data from the server.</p> <p *ngIf="!empList"><em>Loading...</em></p> <p> <a [routerLink]="['/register-employee']">Create New</a> </p> <table class='table' *ngIf="empList"> <thead> <tr> <th>EmployeeId</th> <th>Name</th> <th>Gender</th> <th>Department</th> <th>City</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> <tr *ngFor="let emp of empList"> <td>{{ emp.employeeId }}</td> <td>{{ emp.name }}</td> <td>{{ emp.gender }}</td> <td>{{ emp.department }}</td> <td>{{ emp.city }}</td> <td> <td> <a [routerLink]="['/employee/edit/', emp.employeeId]">Edit</a> | <a [routerLink]="" (click)="delete(emp.employeeId)">Delete</a> </td> </tr> </tbody> </table>
The code for this HTML file is pretty simple.
At the top it has a link to create new employee record. After that it has a table to display employee data, and two links for editing and deleting each employee record.
We are finished with our fetchemployee component.
Now open addemployee.component.ts and insert the following code.
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core'; import { Http, Headers } from '@angular/http'; import { NgForm, FormBuilder, FormGroup, Validators, FormControl } from '@angular/forms'; import { Router, ActivatedRoute } from '@angular/router'; import { FetchEmployeeComponent } from '../fetchemployee/fetchemployee.component'; import { EmployeeService } from '../../services/empservice.service'; @Component({ templateUrl: './AddEmployee.component.html' }) export class createemployee implements OnInit { employeeForm: FormGroup; title: string = "Create"; employeeId: number; errorMessage: any; cityList: Array<any> = []; constructor(private _fb: FormBuilder, private _avRoute: ActivatedRoute, private _employeeService: EmployeeService, private _router: Router) { if (this._avRoute.snapshot.params["id"]) { this.employeeId = this._avRoute.snapshot.params["id"]; } this.employeeForm = this._fb.group({ employeeId: 0, name: ['', [Validators.required]], gender: ['', [Validators.required]], department: ['', [Validators.required]], city: ['', [Validators.required]] }) } ngOnInit() { this._employeeService.getCityList().subscribe( data => this.cityList = data ) if (this.employeeId > 0) { this.title = "Edit"; this._employeeService.getEmployeeById(this.employeeId) .subscribe(resp => this.employeeForm.setValue(resp) , error => this.errorMessage = error); } } save() { if (!this.employeeForm.valid) { return; } if (this.title == "Create") { this._employeeService.saveEmployee(this.employeeForm.value) .subscribe((data) => { this._router.navigate(['/fetch-employee']); }, error => this.errorMessage = error) } else if (this.title == "Edit") { this._employeeService.updateEmployee(this.employeeForm.value) .subscribe((data) => { this._router.navigate(['/fetch-employee']); }, error => this.errorMessage = error) } } cancel() { this._router.navigate(['/fetch-employee']); } get name() { return this.employeeForm.get('name'); } get gender() { return this.employeeForm.get('gender'); } get department() { return this.employeeForm.get('department'); } get city() { return this.employeeForm.get('city'); } }
This component will be used for both adding and editing the employee data.
Since we are using a form model, along with client-side validation to add and edit employee data, we have imported classes from @angular/forms. The code to create the form has been put inside the constructor so that the form will be displayed as the page loads.
This component will handle both add and edit requests. So how will the system differentiate between both requests? The answer is routing. We need to define two different route parameters. One is for adding employee records. The other is for editing employee records. These route parameters will be defined in app.shared.module.ts in the following section.
We have declared the variable title to show on the top of the page and variable id to store the employee id passed as the parameter in case of an edit request. To read the employee ID from the URL we will use ActivatedRoute.snapshot inside the constructor, and set the value of variable id.
Inside ngOnInit we are performing two operations:
- We are fetching the list of cities by calling the
getCityListmethod from our service. We will bind the list of cities to a dropdown list in our HTML page. Since we are calling thegetCityListmethod inngOnInit, the dropdown list will be populated as the page loads. - We will check if the
idis set then we will change the title to “Edit”, get the data for thatidfrom our service, and populate the fields in our form. The value read from the database will be returned as JSON. It will have all the same properties as we declared in ourFormBuilder, hence we use thesetValuemethod to populate our form.
The save method will be called when the “Save” button of our form is clicked. The add and edit operations will call the corresponding method from our service and then, upon success, redirect back to the fetch-employee component.
In the last one we have also defined getter functions for the control names of our form to enable client-side validation.
Open addemployee.component.html and insert the following code.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <title></title> </head> <body> <h1>{{title}}</h1> <h3>Employee</h3> <hr /> <form [formGroup]="employeeForm" (ngSubmit)="save()" #formDir="ngForm" novalidate> <div class="form-group row"> <label class=" control-label col-md-12" for="Name">Name</label> <div class="col-md-4"> <input class="form-control" type="text" formControlName="name"> </div> <span class="text-danger" *ngIf="employeeForm.hasError('required', 'name') && formDir.submitted"> Name is required. </span> </div> <div class="form-group row"> <label class="control-label col-md-12" for="Gender">Gender</label> <div class="col-md-4"> <select class="form-control" data-val="true" formControlName="gender"> <option value="">-- Select Gender --</option> <option value="Male">Male</option> <option value="Female">Female</option> </select> </div> <span class="text-danger" *ngIf="employeeForm.hasError('required', 'gender') && formDir.submitted"> Gender is required </span> </div> <div class="form-group row"> <label class="control-label col-md-12" for="Department">Department</label> <div class="col-md-4"> <input class="form-control" type="text" formControlName="department"> </div> <span class="text-danger" *ngIf="employeeForm.hasError('required', 'department') && formDir.submitted"> Department is required </span> </div> <div class="form-group row"> <label class="control-label col-md-12" for="City">City</label> <div class="col-md-4"> <select class="form-control" data-val="true" formControlName="city"> <option value="">--Select City--</option> <option *ngFor="let city of cityList" value={{city.cityName}}> {{city.cityName}} </option> </select> </div> <span class="text-danger" *ngIf="employeeForm.hasError('required', 'city') && formDir.submitted"> City is required </span> </div> <div class="form-group"> <button type="submit" class="btn btn-default">Save</button> <button class="btn" (click)="cancel()">Cancel</button> </div> </form> </body> </html>
Here you can observe that we have attribute [formGroup]=“employeeForm”, which is our defined form group name in addemployee.component.ts. (ngSubmit)=“save()” will invoke our save method on form submit.
Also, every input control has attribute formControlName=“xyz”. This is used to bind FormControl to HTML. We have also defined error messages for client-side validation checks. These will be invoked on form submission only.
For binding the dropdown list we are using the cityList property that we have populated from tblCities. It was populated by calling the getCityList method from our service, inside the ngOnInit method of _addemployee.component.ts_.
Defining the route and navigation menu for our Application
Inside the “app” folder, open app.shared.module.ts and insert the following code:
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core'; import { EmployeeService } from './services/empservice.service' import { CommonModule } from '@angular/common'; import { FormsModule, ReactiveFormsModule } from '@angular/forms'; import { HttpModule } from '@angular/http'; import { RouterModule } from '@angular/router'; import { AppComponent } from './components/app/app.component'; import { NavMenuComponent } from './components/navmenu/navmenu.component'; import { HomeComponent } from './components/home/home.component'; import { FetchEmployeeComponent } from './components/fetchemployee/fetchemployee.component' import { createemployee } from './components/addemployee/AddEmployee.component' @NgModule({ declarations: [ AppComponent, NavMenuComponent, HomeComponent, FetchEmployeeComponent, createemployee, ], imports: [ CommonModule, HttpModule, FormsModule, ReactiveFormsModule, RouterModule.forRoot([ { path: '', redirectTo: 'home', pathMatch: 'full' }, { path: 'home', component: HomeComponent }, { path: 'fetch-employee', component: FetchEmployeeComponent }, { path: 'register-employee', component: createemployee }, { path: 'employee/edit/:id', component: createemployee }, { path: '**', redirectTo: 'home' } ]) ], providers: [EmployeeService] }) export class AppModuleShared { }
Here we have also imported all our components and defined the route for our application as below:
- home: which will redirect to the
homecomponent - fetch-employee: to display all employee data using the
fetchemployeecomponent - register-employee: to add new employee record using the
createemployeecomponent - employee/edit/:id: to edit existing employee record using the
createemployeecomponent
One last thing is to the define navigation menu for our application. In “/app/components/navmenu/”, open navmenu.component.html and insert the following code.
<div class='main-nav'> <div class='navbar navbar-inverse'> <div class='navbar-header'> <button type='button' class='navbar-toggle' data-toggle='collapse' data-target='.navbar-collapse'> <span class='sr-only'>Toggle navigation</span> <span class='icon-bar'></span> <span class='icon-bar'></span> <span class='icon-bar'></span> </button> <a class='navbar-brand' [routerLink]="['/home']">ASPCoreWithAngular</a> </div> <div class='clearfix'></div> <div class='navbar-collapse collapse'> <ul class='nav navbar-nav'> <li [routerLinkActive]="['link-active']"> <a [routerLink]="['/home']"> <span class='glyphicon glyphicon-home'></span> Home </a> </li> <li [routerLinkActive]="['link-active']"> <a [routerLink]="['/fetch-employee']"> <span class='glyphicon glyphicon-th-list'></span> Fetch employee </a> </li> </ul> </div> </div> </div>
And that’s it. We have created our first ASP.NET Core application using Angular 5 and Entity Framework core database first approach.
Execution Demo
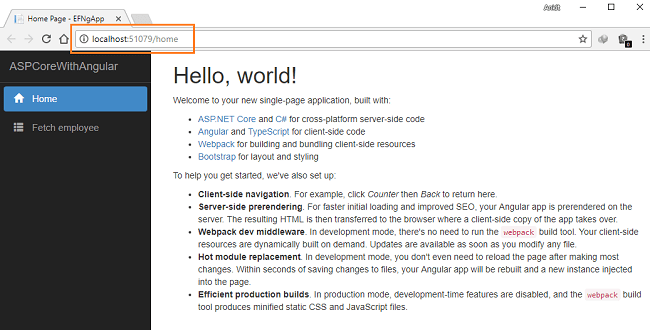
Press F5 to launch the application.
A web page will open as shown in the image below. Notice the URL showing the route for our home component. The navigation menu on the left shows the navigation link for the “Home” and “Fetch Employee” pages.
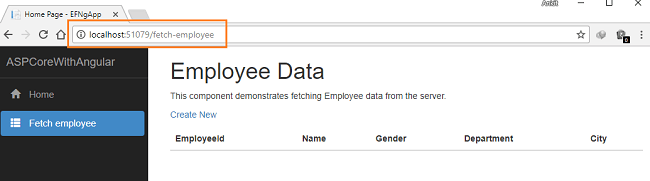
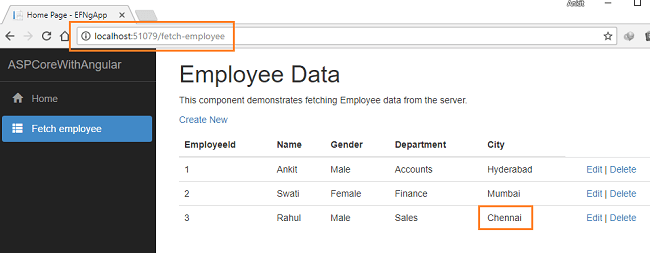
Click on “Fetch Employee” in the navigation menu. It will redirect to the fetchemployee component, and displays all the employee data on the page.
Since we have not added any data it is empty.
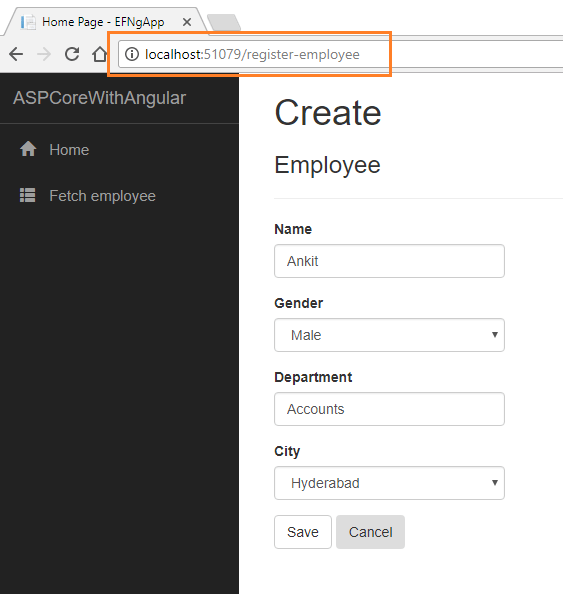
Click on “Create New” to navigate to the “/register-employee” page. Add a new Employee record as shown in the image below. You can see that the City field is a dropdown list, containing all the city names that we inserted into tblCities.
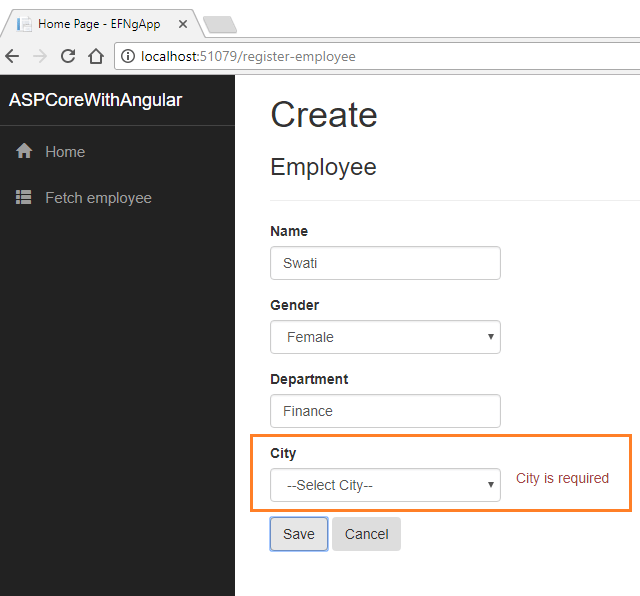
If we miss the data in any field while creating an employee record, we will get a required field validation error message
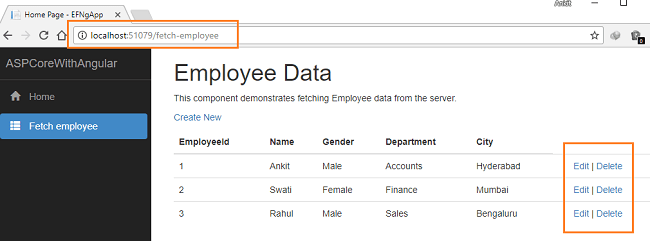
After inserting the data in all the fields, click on the “Save” button. The new employee record will be created, and you will be redirected to the “/fetch-employee” page. This page displays the records of all the employees. Here, we can also see action methods “Edit” and “Delete”.
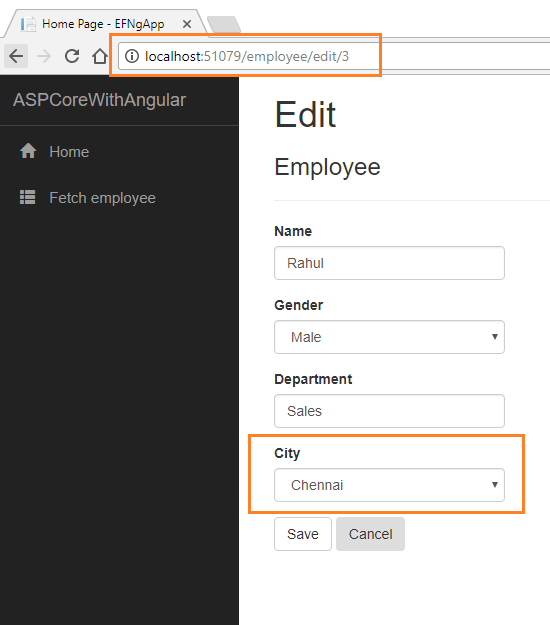
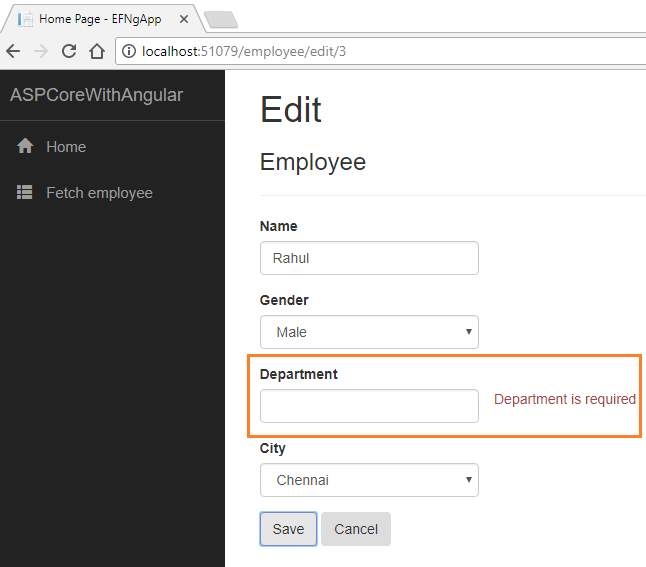
If we want to edit an existing employee record, click the “Edit” action link. It will open the “Edit” page as below, where we can change the employee data. Notice that we have passed the EmployeeId in the URL parameter.
Here we have changed the City of employee Rahul from Hyderabad to Chennai. Click on “Save” to return to the “fetch-employee” page to see the updated changes as highlighted in the image below.
If we miss any fields while editing the employee records, then Edit view will also throw a required field validation error message as shown in the image below:
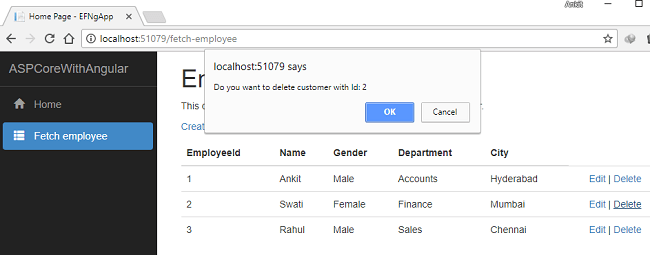
Now, we will perform a “Delete” operation on an employee named Swati with Employee Id 2. Click on the “Delete” action link. This will open a JavaScript confirmation box asking for a confirmation to delete.
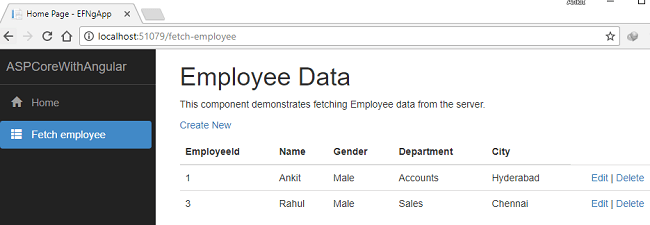
Once we click on “OK”, the Swati who is Employee Id 2 will be removed from our record. You can see the updated list of employees as shown below.
Other useful sources:
- CRUD Operations With ASP.NET Core Using Angular 5 and ADO.NET
- Getting Started With Angular 5 Using Visual Studio Code
- CRUD Operation With ASP.NET Core MVC Using Visual Studio Code and EF
- CRUD Operation With ASP.NET Core MVC Using ADO.NET and Visual Studio 2017
- CRUD Operation With ASP.NET Core MVC using Visual Studio Code and ADO.NET
- ASP.NET Core — Getting Started With Blazor
Conclusion
We have successfully created an ASP.NET Core application using Angular 5 and Entity Framework core database first approach with the help of Visual Studio 2017 and SQL Server 2012. We have used Angular forms to get data from the user and also bind the dropdown list to the database table using Entity framework.
You can check out my other articles on ASP .NET Core here.
Originally published at https://ankitsharmablogs.com/
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from freeCodeCamp directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

freeCodeCamp
freeCodeCamp
Learn to code. Build projects. Earn certifications—All for free.