How to run Laravel on Google Cloud Run with Continuous Integration - a step by step guide
 freeCodeCamp
freeCodeCamp
By Geshan Manandhar
Laravel has soared in popularity over the last few years. The Laravel community even says that Laravel has made writing PHP more enjoyable instead of a pain. Laravel 6 has some interesting new features. Getting a super scaleable working URL for your application takes hours if not days. Setting up something like Kubernetes is a huge task. This is where Google Cloud Run shines: you can get a working HTTPS URL for any of your containerized apps in minutes.
Google Cloud Run is serverless and fully managed by Google. You get super scale, billing by the second, HTTPS URLs, and your own domain mapping. If you want to run stateless containers, Cloud Run is hands down the easiest way to do it. In this post, I will detail how to get your Laravel 6 app working on Google cloud run with Continuous Integration (CI).
Prerequisites
- You are familiar with PHP/Composer and aware of Laravel (if you’ve landed here you are, I suppose)
- You know how to use Git from the CLI
- Your code is hosted on GitHub for CI/CD and you are familiar with GitHub
- Know a fair bit of Docker, maybe even multi-stage build
- Have a working Google cloud account (they give you $300 credit free for 1 yr, no reasons not to have an account)
Why is Cloud Run a great option for beginners?
For two main reasons:
- Learn about the best practices and software like docker and CI/CD
- Getting the basics going just involves clicking a button, selecting 2 things, waiting for 5 mins, and you get a working HTTPS URL. Can it be any easier than this? :)
Steps to deploy
Below are the steps to set up and deploy Laravel 6 on Cloud Run:
1. Clone Laravel or new Laravel project
Start by cloning Laravel or using composer or the Laravel CLI as indicated in the official installation guide. I am using composer to get the latest Laravel as below:
Command
I ran the following command to get the latest Laravel:
composer create-project --prefer-dist laravel/laravel laravel6-on-google-cloud-run
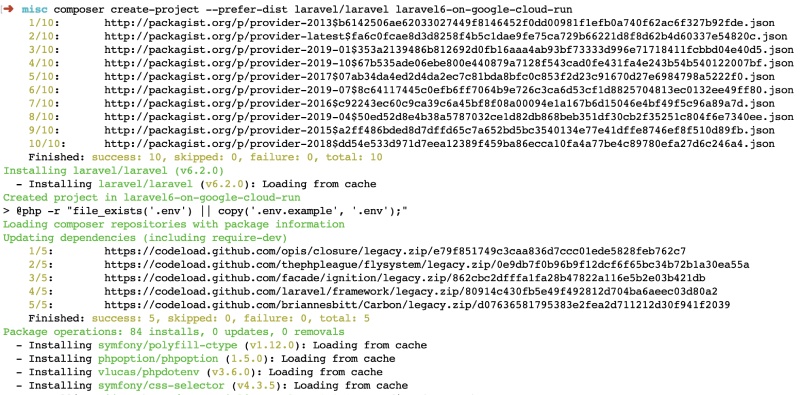 Creating a new Laravel Project with Composer
Creating a new Laravel Project with Composer
2. Test it locally first
Then run cd laravel6-on-google-cloud-run then php artisan serve to see if it is working. For me it was fine when I went to http://localhost:8000 on a web browser. I had PHP 7.2 installed locally.
 Laravel running locally without Docker
Laravel running locally without Docker
3. Create a new GitHub repo
Create a new repository on Github like below:
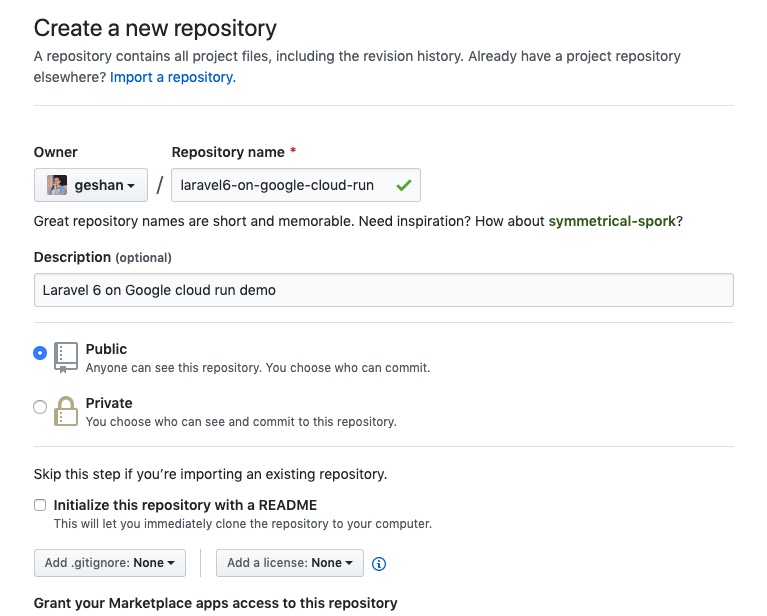 Create a new public repo on Github
Create a new public repo on Github
You can use any Git hosting provider, but for this example I will be using Github Actions to run tests (and Github is the most popular git hosting tool).
4. Add repo, push readme
Now after you have the repo created, add it to your local Laravel copy and push the Readme file. To do this run the following commands on your CLI:
git init
code . # I used VS code to change the readme
git add readme.md
git commit -m "Initial commit -- App Readme"
git remote add origin git@github.com:geshan/laravel6-on-google-cloud-run.git
git push -u origin master
After running the above commands I had this on my Github repo
 Repo after pushing the readme to master branch
Repo after pushing the readme to master branch
5. Add full Laravel, open a PR
Now let’s add the whole app as a PR to the Github repo by executing the following commands:
git checkout -b laravel6-full-app
git add .gitignore
git add .
git commit -m "Add the whole Laravel 6 app"
git push origin laravel6-full-app
After that go and open a Pull Request (PR), on the repo like this one. You might be thinking I am the only one working on this, why do I need a PR? Well, it is always better to do things methodically even if it is just one person working on the project :).
After that merge your pull request.
6. Setup tests with GitHub actions
Now the fun part: after you merged your PR now Github knows that this is a Laravel project. Click on the Actions tab on your repo page and you should be able to see something like below:
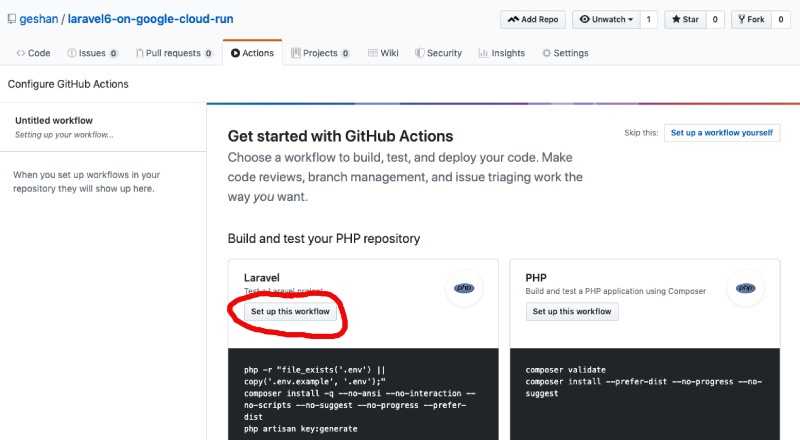 Setup the CI workflow for Laravel with Github Actions
Setup the CI workflow for Laravel with Github Actions
Click the Set up this workflow under Laravel then on the next page click the Start commit button on the top right. After that add a commit message like below and click Commit new file.
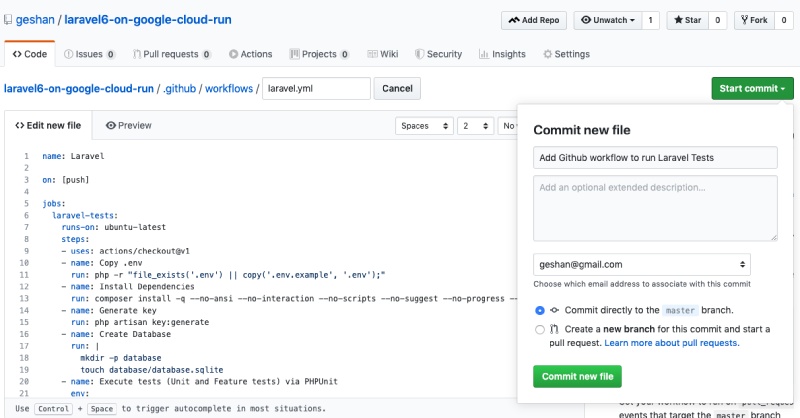 Steps to setup the CI workflow with Github Actions
Steps to setup the CI workflow with Github Actions
There you go, you have your CI setup. Laravel default tests will run on each git push now. Wasn’t that easy? Thank Github for this great intelligence. No more creating .myCIname.yml files :).
7. Add docker and docker-compose to run app locally
Now let’s add docker and docker-compose to run the app locally without PHP or artisan serve.
We will need the container to run Laravel on Google Cloud Run too. This part is inspired by the Laravel on Google Cloud Run post by Nicolas. If you want to learn more about Docker and Laravel please refer to this post.
Run the following commands first to get your master up to date as we added the workflow file from Github interface:
git checkout master
git fetch
git pull --rebase origin master # as we added the workflow file from github interface
git checkout -b docker
Add a key to the .env.example file. Copy it from the .env file like below:
APP_NAME=Laravel
APP_ENV=local
APP_KEY=base64:DJkdj8L5Di3rUkUOwmBFCrr5dsIYU/s7s+W52ClI4AA=
APP_DEBUG=true
APP_URL=http://localhost
As this is just a demo this is ok to do. For a real app always be careful with secrets. For production-ready apps do turn of the debugging and other dev related things.
Add the following Dockerfile on the project root:
FROM composer:1.9.0 as build
WORKDIR /app
COPY . /app
RUN composer global require hirak/prestissimo && composer install
FROM php:7.3-apache-stretch
RUN docker-php-ext-install pdo pdo_mysql
EXPOSE 8080
COPY --from=build /app /var/www/
COPY docker/000-default.conf /etc/apache2/sites-available/000-default.conf
COPY .env.example /var/www/.env
RUN chmod 777 -R /var/www/storage/ && \
echo "Listen 8080" >> /etc/apache2/ports.conf && \
chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/ && \
a2enmod rewrite
Then add the following file at docker/000-default.conf
<VirtualHost *:8080>
ServerAdmin webmaster@localhost
DocumentRoot /var/www/public/
<Directory /var/www/>
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
</Directory>
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/error.log
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/access.log combined
</VirtualHost>
After that add the following docker-compose.yml
version: '3'
services:
app:
build:
context: ./
volumes:
- .:/var/www
ports:
- "8080:8080"
environment:
- APP_ENV=local
Let's Boil down to main things
If you try to understand everything here it might be overwhelming, so let me boil down the main parts:
- We are using the official PHP Apache docker image to run Laravel, which has PHP version 7.3.
- We are using a multistage build to get the dependencies with Composer then we're copying them to the main docker image that has PHP 7.3 and Apache.
- As Google Cloud Run requires the web-server to be listening to port
8080and we are using000-default.confto configure this - To make things easy to run with the single command
docker-compose upwe are using docker-compose. - Now as you have read this far, run
docker-compose upon your root and then after everything runs go tohttp://localhost:8080to see that Laravel 6 is running locally on Docker. Below is mydocker-compose upoutput towards the end:
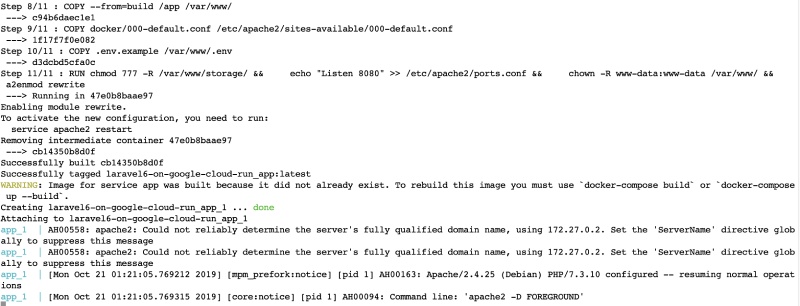 Docker compose running successfully on local machine
Docker compose running successfully on local machine
As Laravel is running fine with Docker, let’s open a PR like this one to add Docker to our project. I ran the following commands on the root of the project before opening the Pull Request (PR):
git status
It should give you something like below:
On branch docker
Untracked files:
(use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed)
Dockerfile
docker-compose.yml
docker/
nothing added to commit but untracked files present (use "git add" to track)
Now run the following commands:
git add .
git commit -m "Add docker and docker compose"
git push origin docker
As a bonus it will run the Laravel default test on the push, like you can see below:
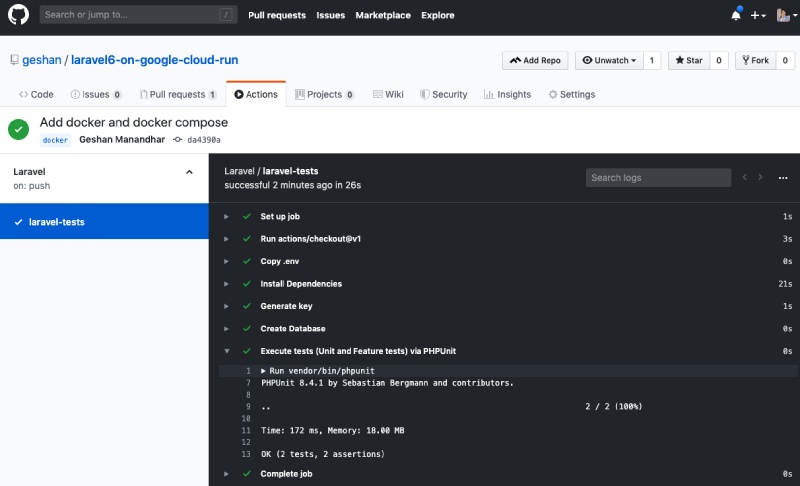 Default Laravel tests running with Github Actions
Default Laravel tests running with Github Actions
Only the owner of the repo has access to the Actions tab so other people don’t necessarily need to know the results of your test builds :).
8. Add deploy to Google Cloud button
Now let’s deploy this Laravel setup to Google Cloud Run the easy way. Given that you have merged your PR from the docker branch, let’s run the following commands:
git checkout master
git fetch
git pull --rebase origin master
git checkout -b cloud-run-button
Then add the following to your readme.md file:
### Run on Google cloud run
[](https://console.cloud.google.com/cloudshell/editor?shellonly=true&cloudshell_image=gcr.io/cloudrun/button&cloudshell_git_repo=https://github.com/geshan/laravel6-on-google-cloud-run.git)
Be careful and replace the last part with your repo’s HTTPs URL. For example, if your repo is at https://github.com/ghaleroshan/laravel6-on-google-cloud-run it will be https://github.com/ghaleroshan/laravel6-on-google-cloud-run.git, then commit and push. Your PR should look something like this one.
9. Deploy on Google Cloud Run
After you merge your Pull Request (PR), then go to your repo page and click on the Run on Google Cloud button.
 Github readme after adding the Run on Google Cloud button
Github readme after adding the Run on Google Cloud button
After that, if you are logged into your Google account and have Google cloud setup with 1 project, click “Proceed”. You might need to wait a bit, then
- Choose the project –
Choose a project to deploy this application - Choose the region –
Choose a region to deploy this application, I usually go withus-central-1 - Then wait for the container to be built and deployed. You can see my process below:
If everything goes fine on your Google Cloud Shell, you will see the HTTPS URL that you can hit to see your Laravel app running like below:
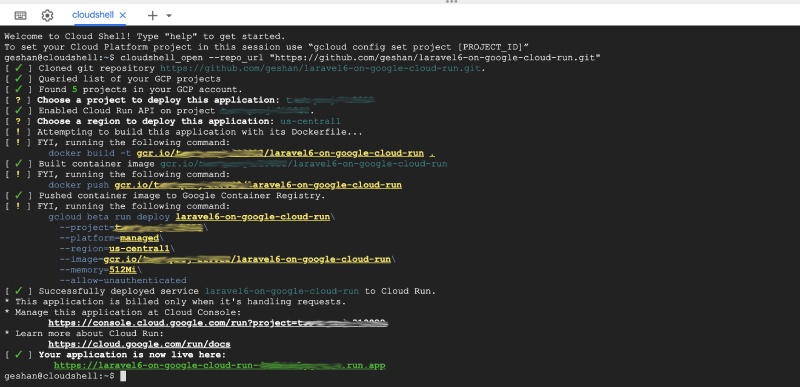 Deploy screen of Google Cloud Shell for Laravel 6 on Cloud Run
Deploy screen of Google Cloud Shell for Laravel 6 on Cloud Run
What just happened above is:
- After choosing the region, the script built a docker container image from the
Dockerfilein the repo - Then it pushed the built image to Google Container Registry
- After that using the gcloud CLI it deployed the built image to Cloud Run, which gave back the URL.
10. Hurray, your app is working
After you git the URL you should see your app working on Google Cloud Run like below:
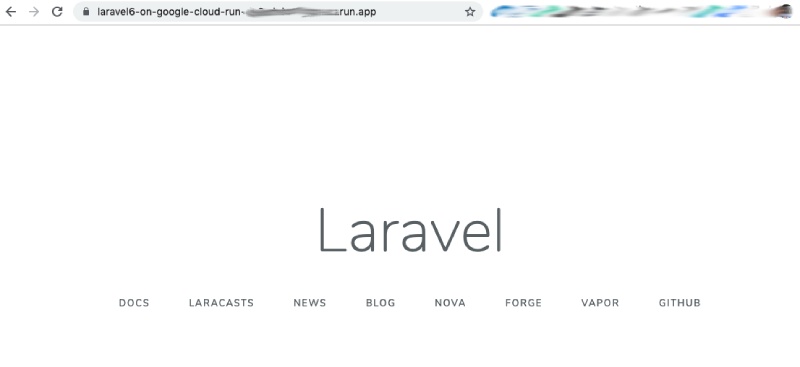 Laravel running on Google Cloud Run with Serverless HTTPS URL :)
Laravel running on Google Cloud Run with Serverless HTTPS URL :)
If you want to deploy another version you can merge your PR to master and click the button again to deploy.
More about Google Cloud Run
The pricing for Google Cloud Run is very generous. You can run any containerized app or web app on Google cloud run. I ran a pet project that got ~ 1 request per minute and I did not have to pay anything.
Behind the scenes, it is using Knative and Kubernetes. It can also be run on your Kubernetes cluster but who would choose to manage a K8s cluster if you can just push and get a scaleable serverless fully managed app :).
TLDR
To run Laravel 6 on Google Cloud Run quickly follow the steps below:
- Make sure you are logged into your Google Cloud Account
- Go to https://github.com/geshan/laravel6-on-google-cloud-run
- Click the “Run On Google Cloud” blue button
- Select your project
- Select your region
- Wait and get the URL of your Laravel App as below, Enjoy!
 Deploy log of Cloud Run button to deploy Laravel on Google Cloud Run
Deploy log of Cloud Run button to deploy Laravel on Google Cloud Run
 Laravel Running successfully on Google Cloud Run
Laravel Running successfully on Google Cloud Run
Conclusion
There you go – running a Laravel app on Google cloud run was pretty easy. You have even got test running on Github with Github actions. Hope it helps. To do a CI/CD approach you can check out this post. It shows deployment using Cloud build. As the same container is running for local and production (Google Cloud Run) environment you don’t need to learn a new framework to go Serverless.
Any containerized web app can be run on Google Cloud Run, it is a great service. You can read more at https://geshan.com.np
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from freeCodeCamp directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

freeCodeCamp
freeCodeCamp
Learn to code. Build projects. Earn certifications—All for free.