Learn Networking Essentials: Public IP, Private IP, NAT, DHCP, and Routers
 VIJAY KAMMARI
VIJAY KAMMARI🔍 Public vs. Private IP
Public IP: A unique IP address assigned to a device that can be accessed over the internet.
Private IP: An IP address assigned to devices within a private network, not accessible from the internet directly.
Difference: Public IPs allow devices to communicate over the internet, while private IPs enable communication within local networks.
🌐 NAT (Network Address Translation)
Function: NAT translates private IP addresses into a public IP, enabling devices on a local network to access the internet using a single public IP.
Why It's Important: NAT helps conserve public IP addresses and adds a layer of security by hiding private IP addresses.
Basically when data is transferred from your mobile your data is bound with the Private IP address which is provided by the router consists of DHCP. After reaching to the Router it consists of NAT. The work of the NAT is to take the data and bound with the Public IP to its and sends it to the internet.
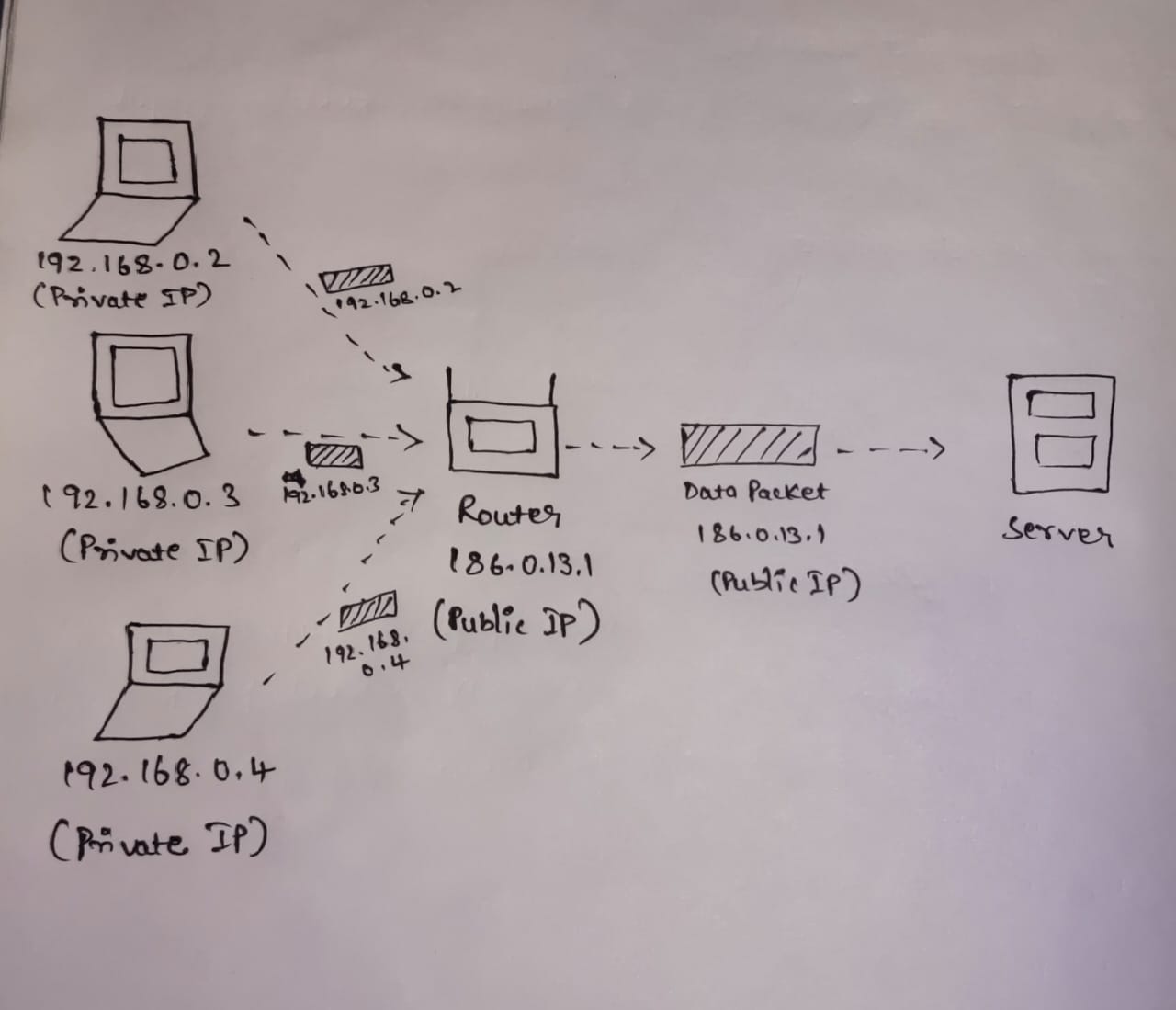
🔄 DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
Role: Automatically assigns IP addresses to devices on a network, ensuring each device has a unique and valid IP without manual configuration. These IP addresses are Private IP addresses which is given by the DHCP.
Benefits: Simplifies network management and reduces the chances of IP conflicts.
📡 Router
Definition: A device that connects different networks and directs data between them.
Purpose: Routers manage traffic between devices on a local network and between the local network and the internet.
Basically its lets you connect to the larger network that is internet.
Understanding these core networking concepts is essential for anyone looking to dive deeper into the world of networking and IT infrastructure.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from VIJAY KAMMARI directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
