Day 2 of Kubernetes 40-Day Series : How to Dockerize a Project
 Rahul Vadakkiniyil
Rahul Vadakkiniyil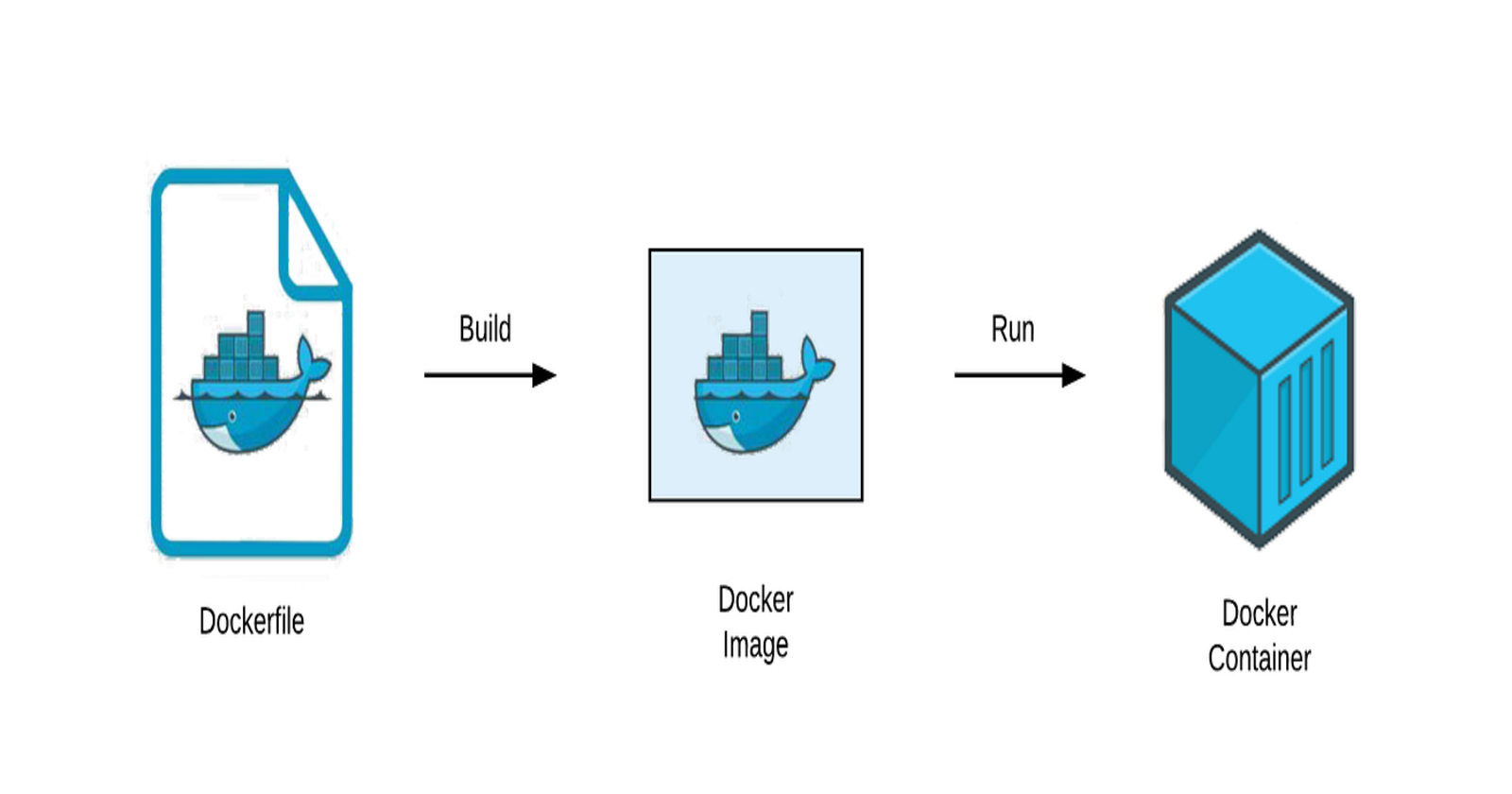
Docker is a popular tool for packaging and running applications in containers. Containers are isolated environments that share the host operating system's kernel, making them lightweight and efficient. In this blog post, we will learn how to dockerize a project using a simple to-do list app as an example.
- Clone a sample git repository using the below command or use your project for the demo:
git clone https://github.com/docker/getting-started-app.git
cd into the
getting-started-appdirectory.Create a file named Dockerfile using the command below.
nano Dockerfile
or
vim Dockerfile
- Paste the following code into your Dockerfile.
FROM node:18-alpine
WORKDIR /app
COPY . .
RUN yarn install --production
CMD ["node", "src/index.js"]
EXPOSE 3000
Explanation of this code:
FROM node:18-alpine
This line specifies the base image for your Docker image. In this case, it uses the official Node.js image with version 18, based on the Alpine Linux distribution. Alpine is a minimal Docker image, which helps keep the final image size small.
WORKDIR /app- This line sets the working directory inside the Docker container to
/app. Any subsequentCOPY,ADD,RUN,CMD, or other instructions will be executed in this directory.
- This line sets the working directory inside the Docker container to
COPY . .- This line copies the contents of your local directory (where the Dockerfile is located) into the
/appdirectory in the Docker container. The first.represents the source on your local machine, and the second.represents the destination inside the container.
- This line copies the contents of your local directory (where the Dockerfile is located) into the
RUN yarn install --production:- This line runs the
yarn install --productioncommand inside the container. It installs the production dependencies listed in yourpackage.jsonfile. The--productionflag ensures that only dependencies required for running the application are installed, excluding development dependencies.
- This line runs the
CMD ["node", "src/index.js"]:- This line specifies the command to run when the container starts. It uses the Node.js runtime to execute the
src/index.jsfile. TheCMDinstruction is an array where the first element is the executable (node) and the subsequent elements are the arguments to that executable (src/index.js).
- This line specifies the command to run when the container starts. It uses the Node.js runtime to execute the
EXPOSE 3000:- This line informs Docker that the container listens on port 3000 at runtime. It's a way of documenting the port that the application inside the container uses. However, it doesn't actually publish the port on the host machine; you need to use the
-pflag when running the container to map the container's port to a port on the host.
- This line informs Docker that the container listens on port 3000 at runtime. It's a way of documenting the port that the application inside the container uses. However, it doesn't actually publish the port on the host machine; you need to use the
Now build the Docker image with the following command:
docker build -t day02-todo .Verify the image has been created and stored locally using the below command
docker imagesCreate a public repository on Docker Hub and push the image to the remote repo
docker login docker tag day02-todo:latest username/new-reponame:tagname docker push username/new-reponame:tagnameNow you can use this application in any environment by pulling the image from Docker Hub to your machine.
To verify, pull the image to your local machine using the following command:
docker pull username/new-reponame:tagnameRun the container by following command
docker run -dp 3000:3000 username/new-reponame:tagname
Reference
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Rahul Vadakkiniyil directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
