What is Consensus in Blockchain
 sai phanindra
sai phanindra
What is Consensus in Blockchain?
Consensus in blockchain refers to the process by which all nodes (participants) in the network agree on a single version of the truth. This is essential for maintaining the integrity and security of the blockchain. Without consensus, the blockchain would be vulnerable to attacks and inconsistencies.
Types of Consensus Mechanisms
There are several consensus mechanisms used in blockchain networks, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The most well-known are:
Proof of Work (PoW)
Proof of Stake (PoS)
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)
Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT)
For this blog, we’ll focus on Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS).
Proof of Work (PoW)
Proof of Work is the original consensus mechanism used by Bitcoin and many other cryptocurrencies. In PoW, miners compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles. The first one to solve the puzzle gets to add a new block to the blockchain and is rewarded with newly minted coins and transaction fees.
Diagram: Proof of Work Process
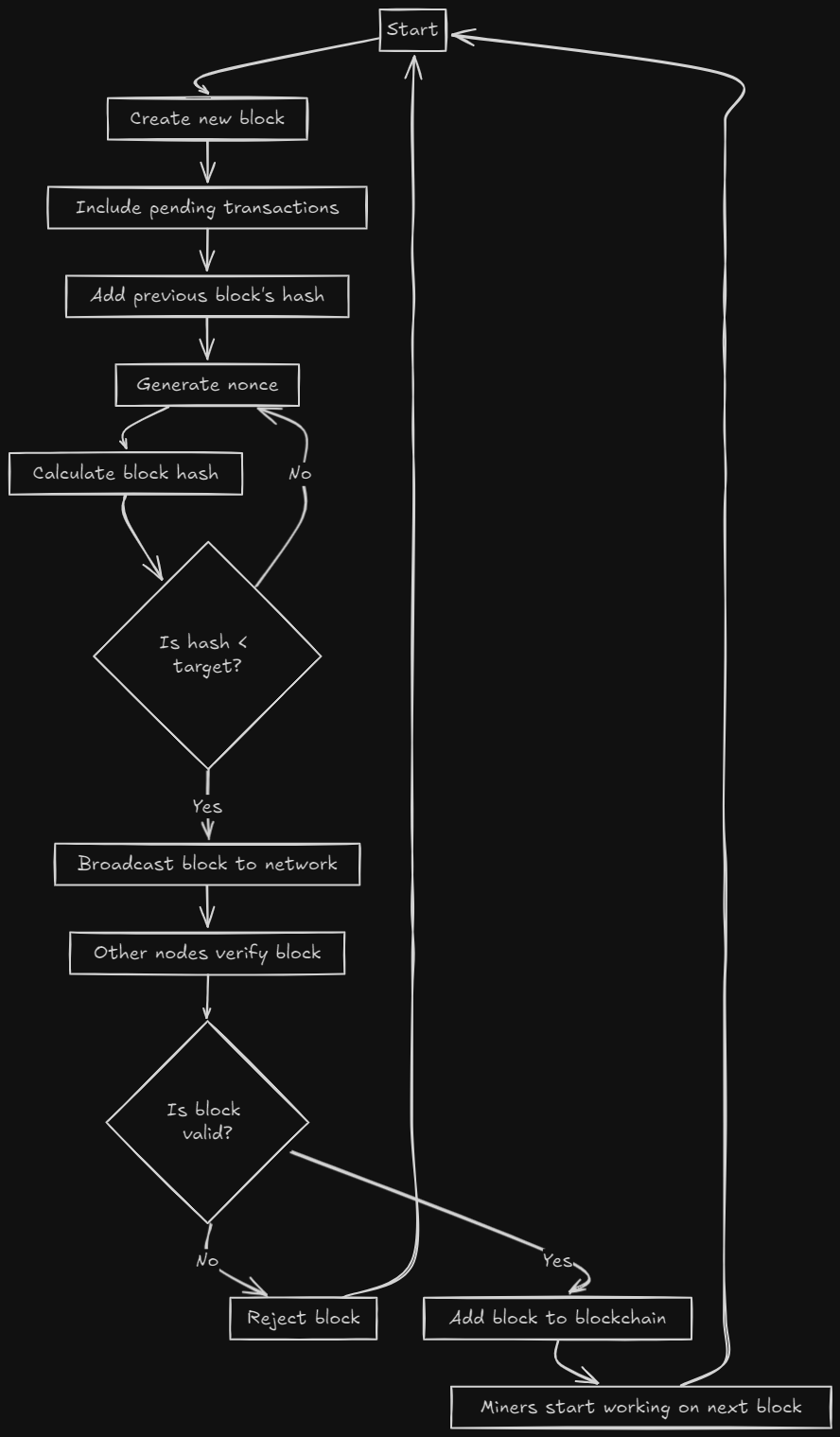
The Role of Mining in PoW
Mining is the process by which new blocks are added to the blockchain in a PoW system. Here’s how it works:
Transaction Validation: Miners collect transactions from the network and validate them to ensure they are legitimate.
Puzzle Solving: Miners compete to solve a cryptographic puzzle. This requires significant computational power and energy.
Block Creation: The first miner to solve the puzzle gets to create a new block and add it to the blockchain.
Consensus Achievement: Other nodes in the network verify the new block. If the majority agree, the block is added to the blockchain, achieving consensus.
Real-World Example: Bitcoin
Bitcoin, the first and most well-known cryptocurrency, uses PoW as its consensus mechanism. Miners use specialized hardware, such as ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits), to solve complex puzzles, and the first to solve it gets to add a new block to the Bitcoin blockchain.
Proof of Stake (PoS)
Proof of Stake is an alternative consensus mechanism that aims to address some of the limitations of PoW, such as high energy consumption. In PoS, validators are chosen to create new blocks based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral.
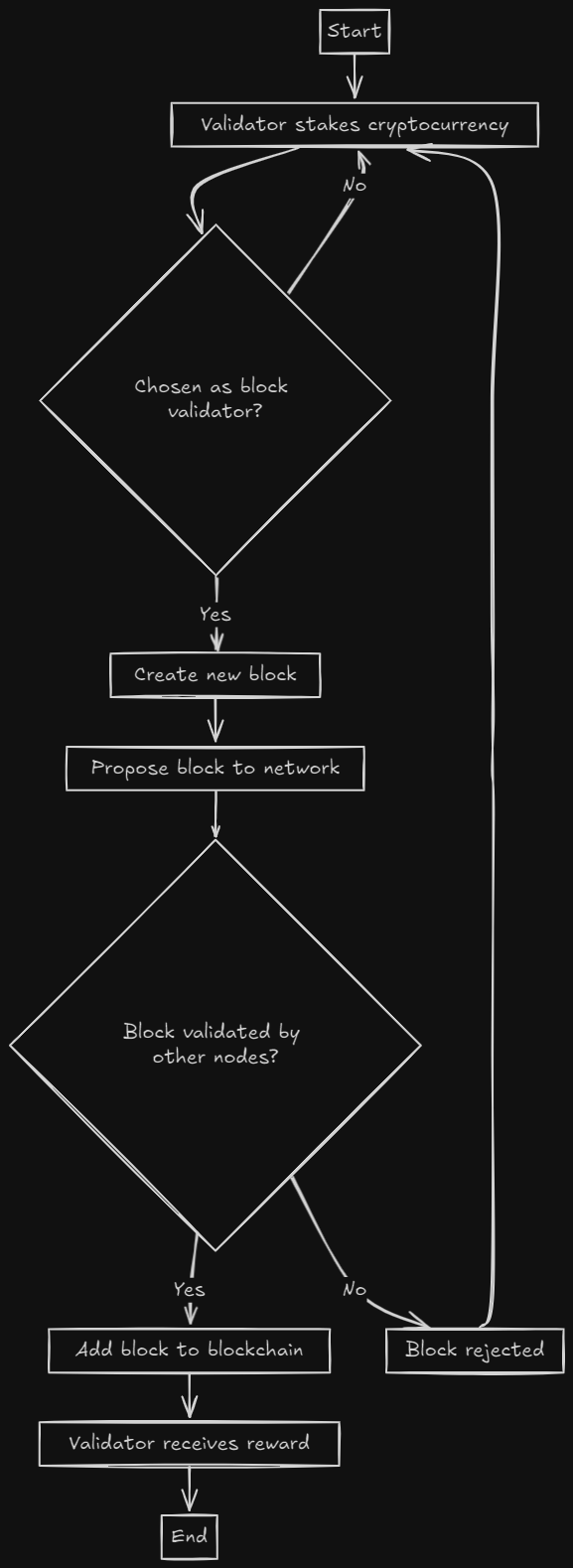
The Role of Staking in PoS
Staking involves locking up a certain amount of cryptocurrency to participate in the network as a validator. Here’s how it works:
Validator Selection: Validators are chosen based on the amount of cryptocurrency they have staked.
Block Creation: Selected validators create new blocks and add them to the blockchain.
Consensus Achievement: Other validators verify the new block. If the majority agree, the block is added to the blockchain, achieving consensus.
Real-World Example: Ethereum 2.0
Ethereum, the second-largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization, is transitioning from PoW to PoS with Ethereum 2.0. Validators will be selected based on the amount of ETH they stake, reducing the network’s energy consumption and increasing scalability.
Technical Comparison: PoW vs. PoS
Table
| Feature | Proof of Work (PoW) | Proof of Stake (PoS) |
| Energy Consumption | High, due to computational power required | Low, as it relies on staking rather than computation |
| Hardware Requirement | Specialized hardware (ASICs) | Standard hardware |
| Security | High, but susceptible to 51% attacks | High, with economic penalties for malicious behavior |
| Scalability | Limited by block size and mining speed | Higher, due to faster block creation |
| Incentives | Mining rewards and transaction fees | Staking rewards and transaction fees |
Summary
Both PoW and PoS have their strengths and weaknesses, and the choice between them depends on the specific needs and goals of the blockchain network. PoW is well-suited for networks prioritizing security and decentralization, while PoS offers a more energy-efficient and scalable alternative.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from sai phanindra directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
