Day 35/40 Days of K8s: Kubernetes ETCD Backup And Restore Explained !!
 Gopi Vivek Manne
Gopi Vivek Manne
❇ Introduction
ETCD is a highly available, distributed key-value store used by Kubernetes to store all cluster data. It's an important component for maintaining and recovering the state of your Kubernetes cluster.
🤔 Why Backup ETCD?
Backing up ETCD is important while:
Cluster version upgrades
Major releases
Disaster recovery scenarios
Note: For cloud-managed Kubernetes services, you may need to use 3rd party tools as direct ETCD access might not be available(ex: EKS,GKE,AKS..)
Example 3rd party tools: Valero,Kasten..etc
❇ Key Directories
ETCD data:
/var/lib/etcdControl plane static manifests:
/etc/kubernetes/manifestsCertificates:
/etc/kubernetes/pki
These directories are typically mounted as volumes into the ETCD pod/ container level.
❇ Backup Methods
1. ETCD Built-in Snapshot
Use the etcdctl tool to create a snapshot:
ETCDCTL_API=3 etcdctl --endpoints $ENDPOINT snapshot save snapshot.db
2. Volume Snapshot
For ETCD running on a storage volume that supports backups (ex: AWS EBS), create a snapshot of the entire storage volume.
❇ Backup Process
- Use
etcdctlwith appropriate flags:
sudo etcdctl --endpoints=<api-server-endpoint> \
--cacert=<trusted-ca-file> \
--cert=<cert-file> \
--key=<key-file> \
snapshot save /opt/etcd-backup.db
- Verify the backup:
etcdctl --write-out=table snapshot status /opt/etcd-backup.db
❇ Restore Process
Important: Before restoring, ensure you must:
Stop all API server instances
Restore state in all ETCD instances
Restart all API server instances
Reason: The API server communicates with etcd to read and write data. During the restoration process of etcd, the API server will continue attempting to interact with ETCD, which can lead to data corruption. Therefore, it's important to stop all API servers before initiating the restoration.
❇ Steps for Restoration
- Use
etcdutlto restore from a snapshot:
etcdutl --data-dir <data-dir-location> snapshot restore snapshot.db
- Restart Kubernetes components (kube-scheduler, kube-controller-manager, kubelet) to ensure they don't rely on outdated/stale data.
⭐ Best Practices
Regularly schedule backups
Store backups in a secure, off-site location
Test your restore process periodically
Keep multiple backups, not just the most recent one
Remember: A well-maintained ETCD backup strategy is imperative for the overall health and stability of your Kubernetes cluster.
⭐ Hand's on
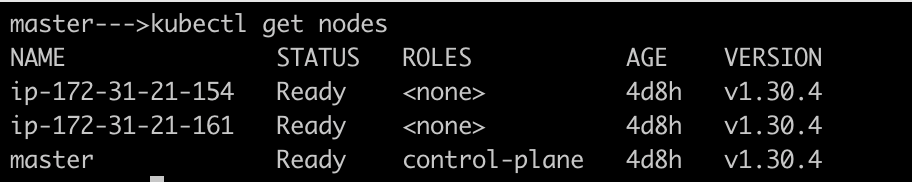
Login to your control plane node,Ensure all the nodes are in ready status
Find out version of etcd server using the command like
etcd --version # If not present, intall using the below command sudo apt install etcd-server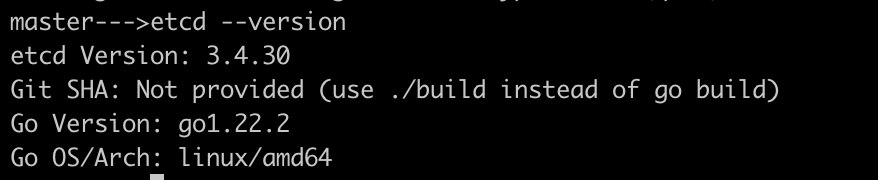
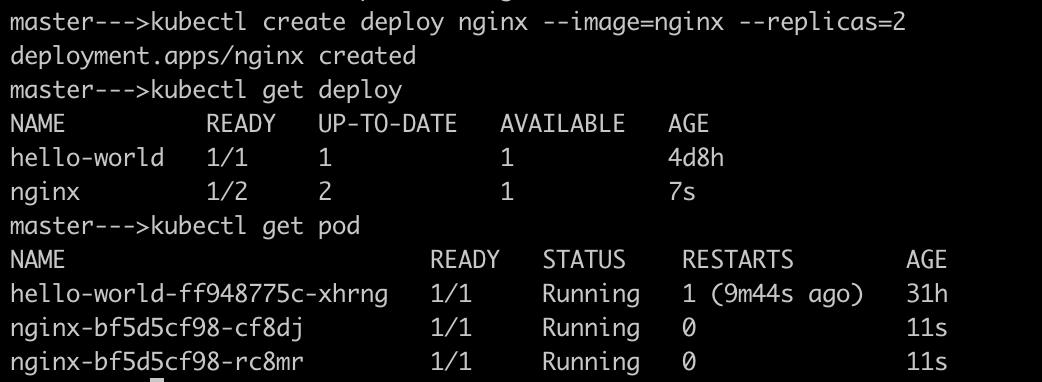
Create an nginx deployment with 2 pods
Identify endpoint url, server certs and ca certs by describing the etcd pod in your Kubernetes control plane.
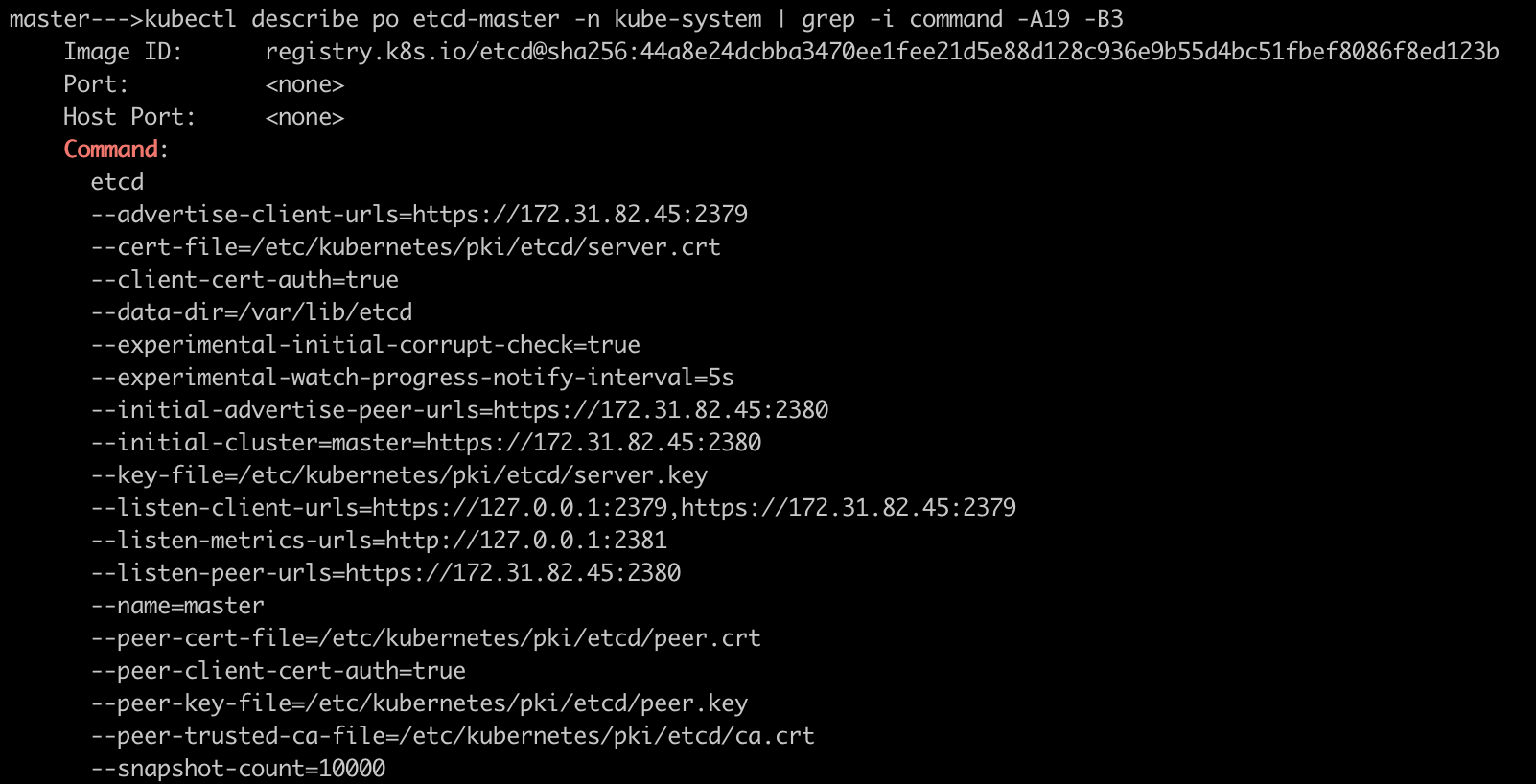
Set the
ETCDCTL_API=3as the env variable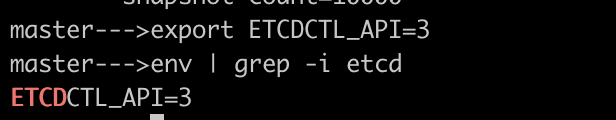
Run
etcdctl snapshotcommand to view different option, take the backup of etcd cluster to/opt/etcd-snapshot.dbdirectoryetcdctl --endpoints=https://127.0.0.1:2379 \ --cacert=<trusted-ca-file> --cert=<cert-file> --key=<key-file> \ snapshot save <backup-file-location>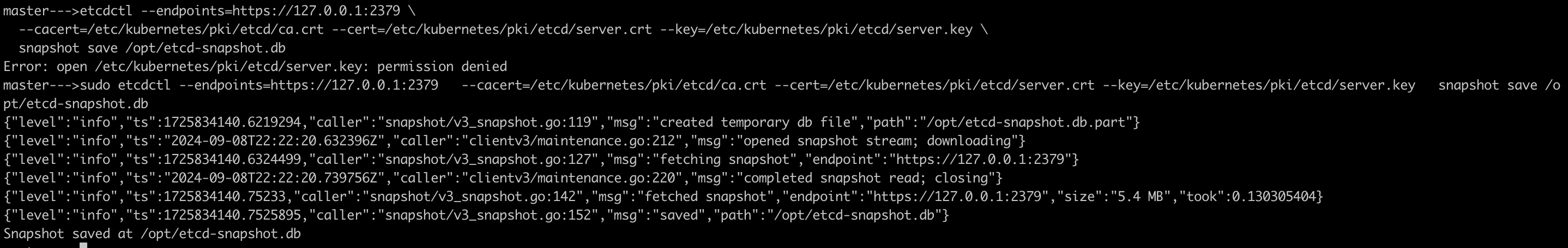
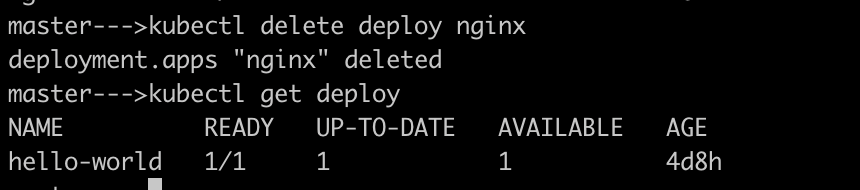
Delete the deployment of nginx
Restore the original state of the cluster from backup file at
/opt/etcd-snapshot.dbto the directory/var/lib/etcd-from-backupMove the existing etcd data directory to avoid conflicts:
sudo mv /var/lib/etcd /var/lib/etcd-backupRestore the etcd snapshot to the new directory
sudo ETCDCTL_API=3 etcdctl snapshot restore /opt/etcd-snapshot.db \ --data-dir /var/lib/etcd-from-backup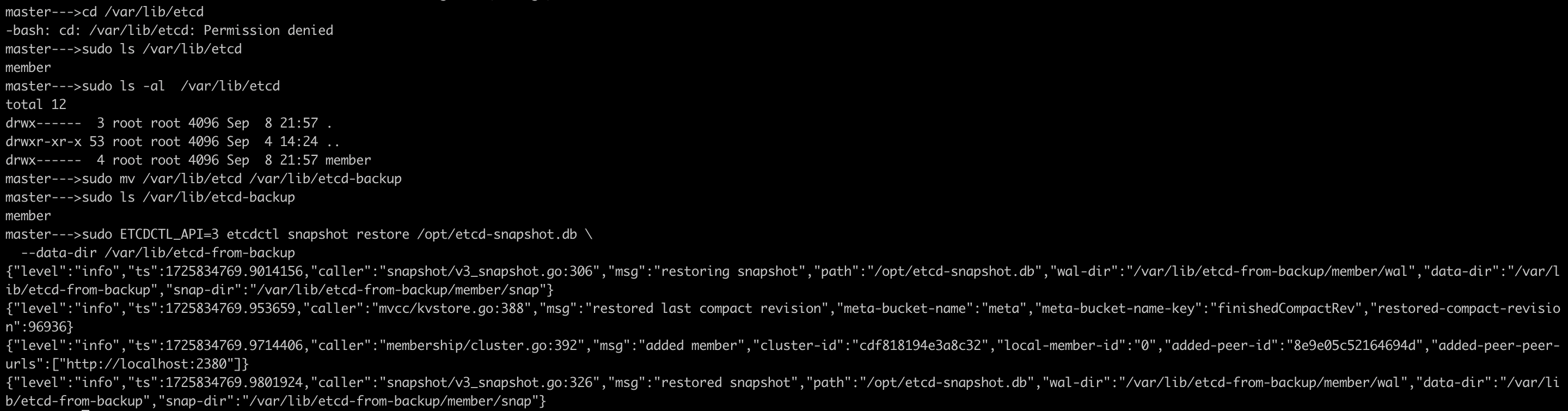
This command restores the snapshot into
/var/lib/etcd-from-backupUpdate the etcd manifest file to use the restored data directory. The etcd manifest file is located at
/etc/kubernetes/manifests/etcd.yaml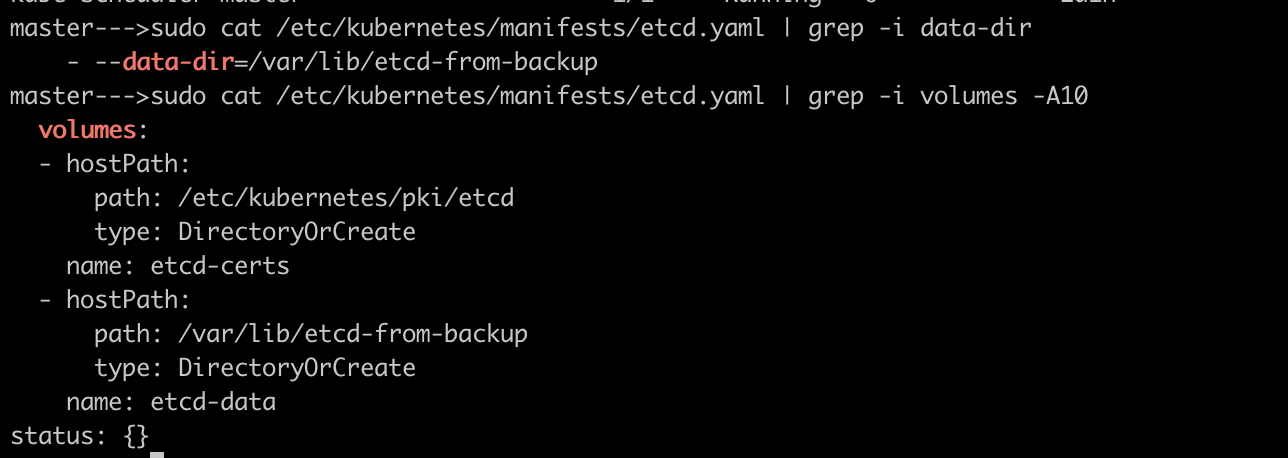
This ensures that etcd dir
/var/lib/etcd-from-backupis being updated inetcd.yamlmanifest at both--data-dirandvolumessection as well because this path was being mounted as a volume inside the pod.NOTE:
Make sure to restart the kube-apiserver: As this runs as a static pod, we can restart like
Move all static pod manifests files to
tmpdir likesudo mv * /tmpMove back again all pod yaml files to the current location
sudo mv /tmp/*.yaml .The above command will restart all static pods again. Confirm to check if the pods are running in
kube-systemnamespace.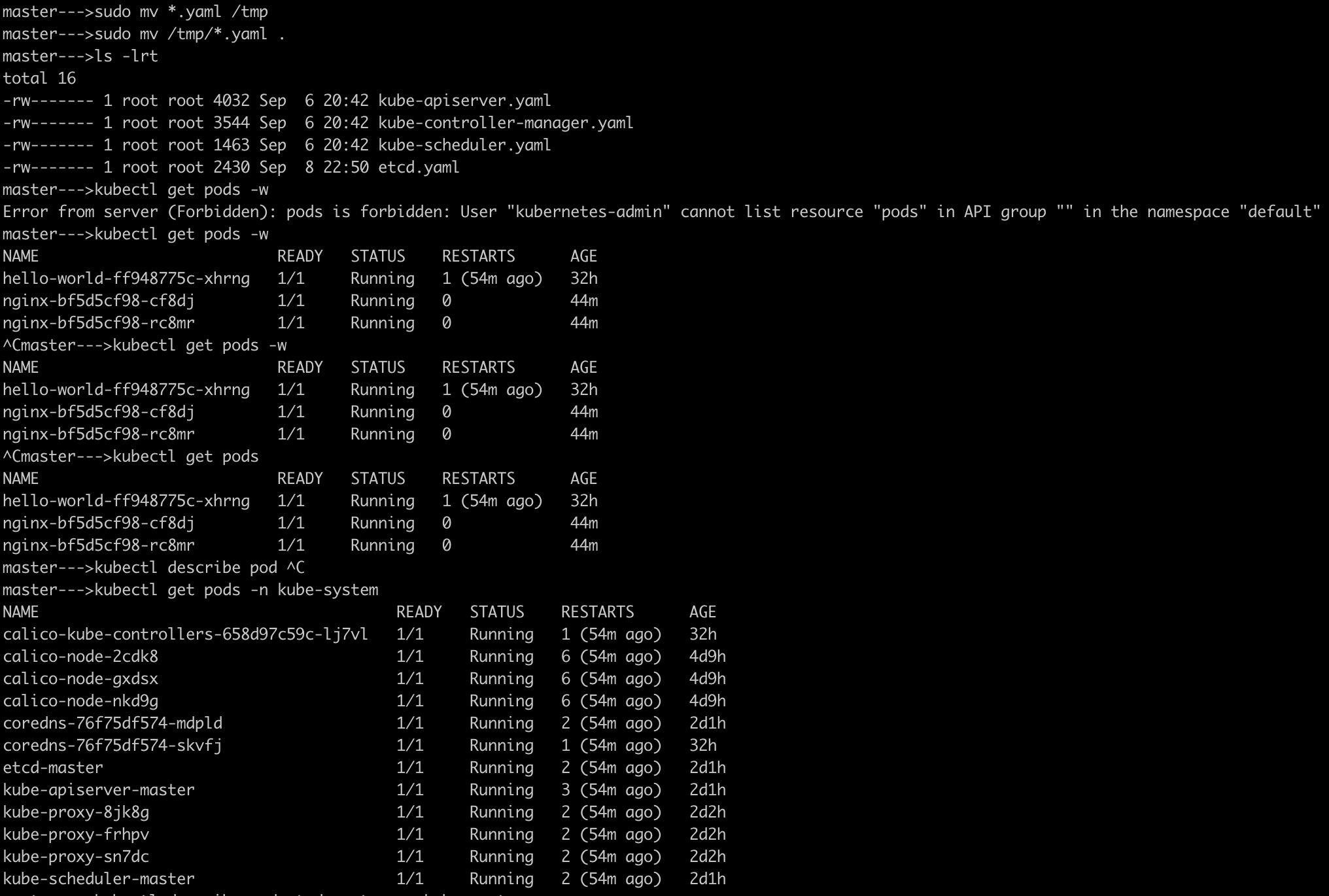
Also, make sure to restart
kubeletservice to ensure that they don't rely on some stale dataReason: The kubelet continuously monitors a specific directory (usually
/etc/kubernetes/manifests/) for any changes to the manifest files.sudo systemctl restart kubelet sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl status kubelet
Check the deployment using
kubectl get deploy, make sure that it is available as you have restored the backup prior to deleting the deployment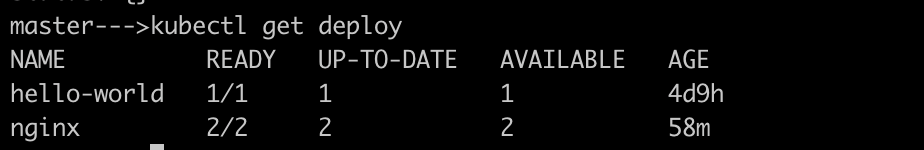
Important Points
Ideally, Use a single-node etcd cluster only for testing purposes and for durability and high availability, run etcd as a multi-node cluster in production and back it up periodically.
An odd number(3 or 5) etcd cluster is recommended in production to maintain Quorum.
For a multi-node etcd cluster, Configure a load balancer in front of the etcd cluster. where api-server is load balanced and etcd is distributed storage.
#Kubernetes #Kubeadm #ETCD #Backup #Restore #Multinodecluster #40DaysofKubernetes #CKASeries
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Gopi Vivek Manne directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Gopi Vivek Manne
Gopi Vivek Manne
I'm Gopi Vivek Manne, a passionate DevOps Cloud Engineer with a strong focus on AWS cloud migrations. I have expertise in a range of technologies, including AWS, Linux, Jenkins, Bitbucket, GitHub Actions, Terraform, Docker, Kubernetes, Ansible, SonarQube, JUnit, AppScan, Prometheus, Grafana, Zabbix, and container orchestration. I'm constantly learning and exploring new ways to optimize and automate workflows, and I enjoy sharing my experiences and knowledge with others in the tech community. Follow me for insights, tips, and best practices on all things DevOps and cloud engineering!