Automate Docker Image Deployment to AWS ECR Using GitHub Actions
 Balraj Singh
Balraj Singh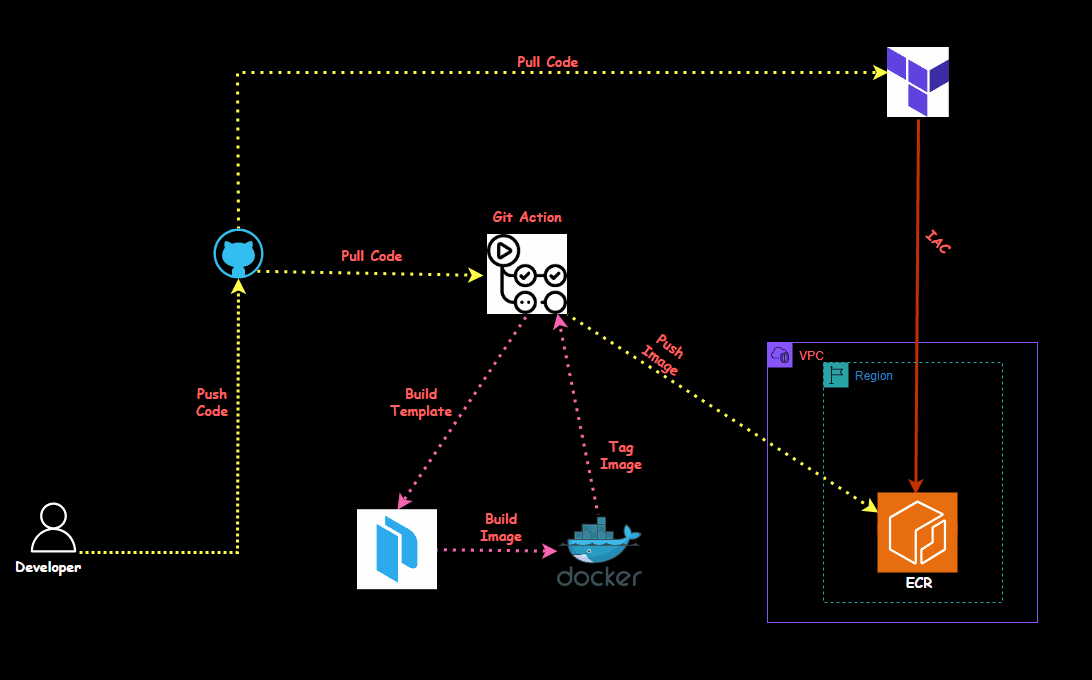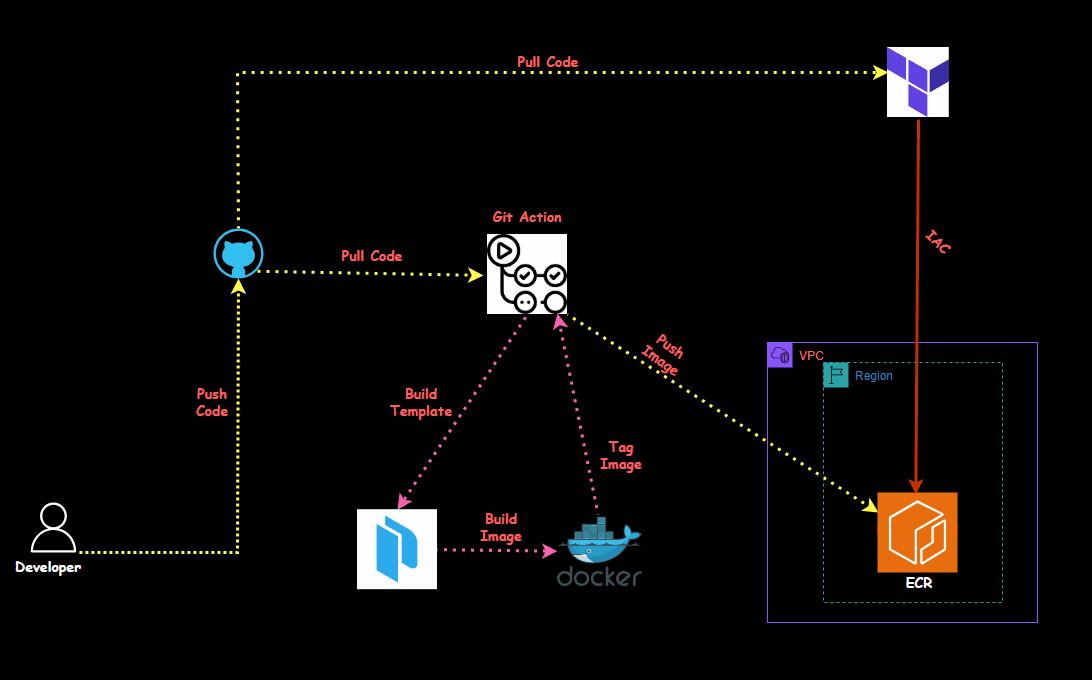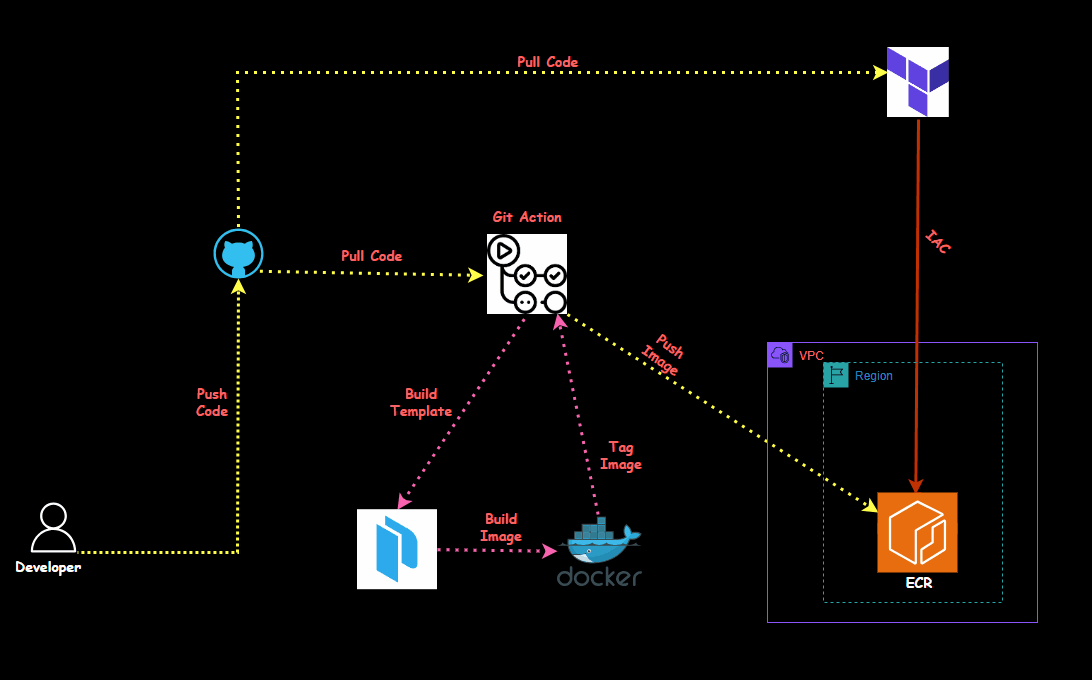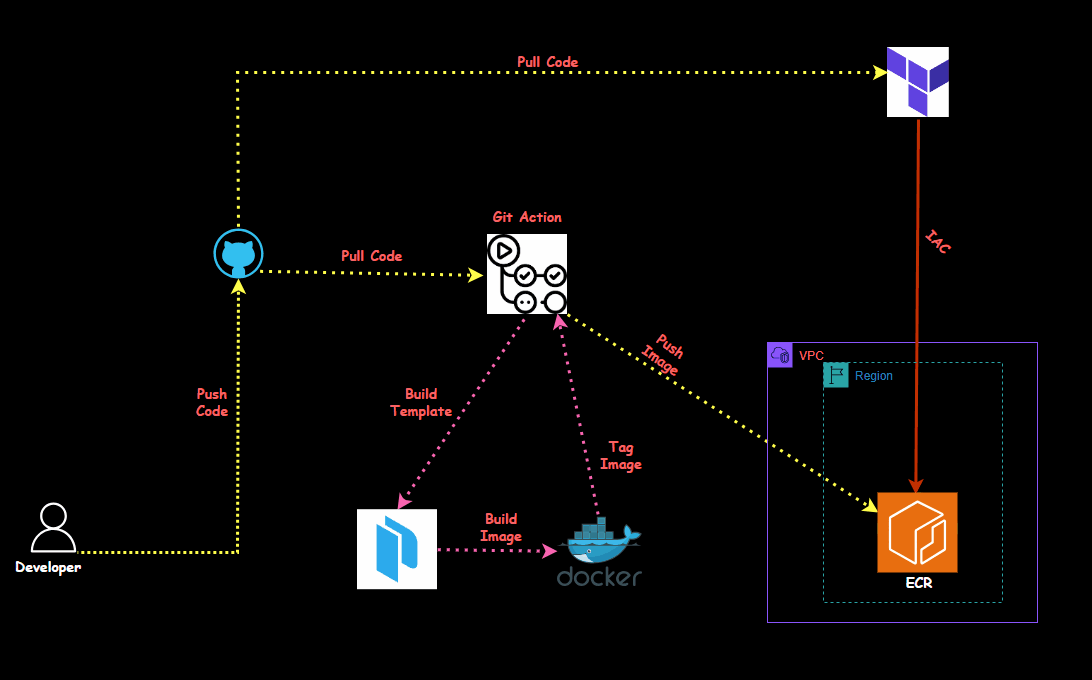
In this session, we'll dive into automating the process of building Docker images using Packer and deploying them to Amazon ECR (Elastic Container Registry) with GitHub Actions. By the end of this, you'll understand how to create an ECR repository, set up credentials, build and tag a Docker image using Packer, and automate the entire workflow using GitHub Actions.
Prerequisites
Before you start, ensure you have the following:
AWS Account: Set up with IAM access (access key & secret key) for ECR.
GitHub Repository: A repository to hold your Packer configuration and GitHub Actions workflow.
Basic Knowledge of Docker: Familiarity with Docker images and containers.
Installed Tools: AWS CLI, GitHub Actions, and Packer installed on your local machine.
Setting Up the Environment
I have created a Terraform file to set up the entire environment, including installing the required applications and tools and automatically creating the ECR.
Setting Up the ECR
First, we'll create the necessary virtual machines using terraform.
Below is a terraform configuration:
Once you clone repo then go to folder "10.Real-Time-DevOps-Project/Terraform_Code" and run the terraform command.
cd Terraform_Code/
$ ls -l
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
da---l 10/09/24 7:32 PM Terraform_Code
Note ⇒ Make sure to run main.tf from inside the folders.
cd 11.Real-Time-DevOps-Project/Terraform_Code"
Mode LastWriteTime Length Name
---- ------------- ------ ----
-a---l 21/08/24 2:56 PM 500 .gitignore
-a---l 10/09/24 7:29 PM 4287 main.tf
You need to run main.tf the file using the following terraform command.
Now, run the following command.
terraform init
terraform fmt
terraform validate
terraform plan
terraform apply --auto-approve
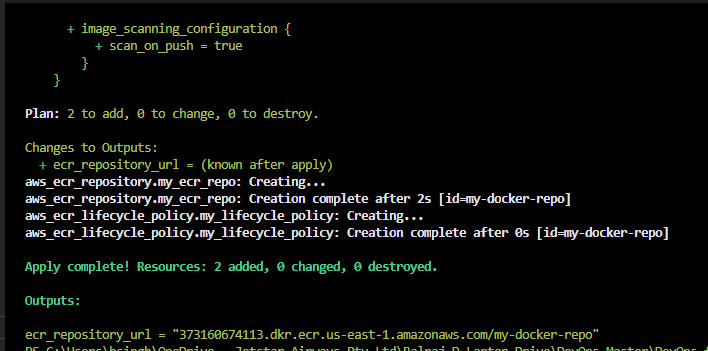
It will create an ECR and give you an ECR name and ID; that ID and name need to be updated in the git action code.
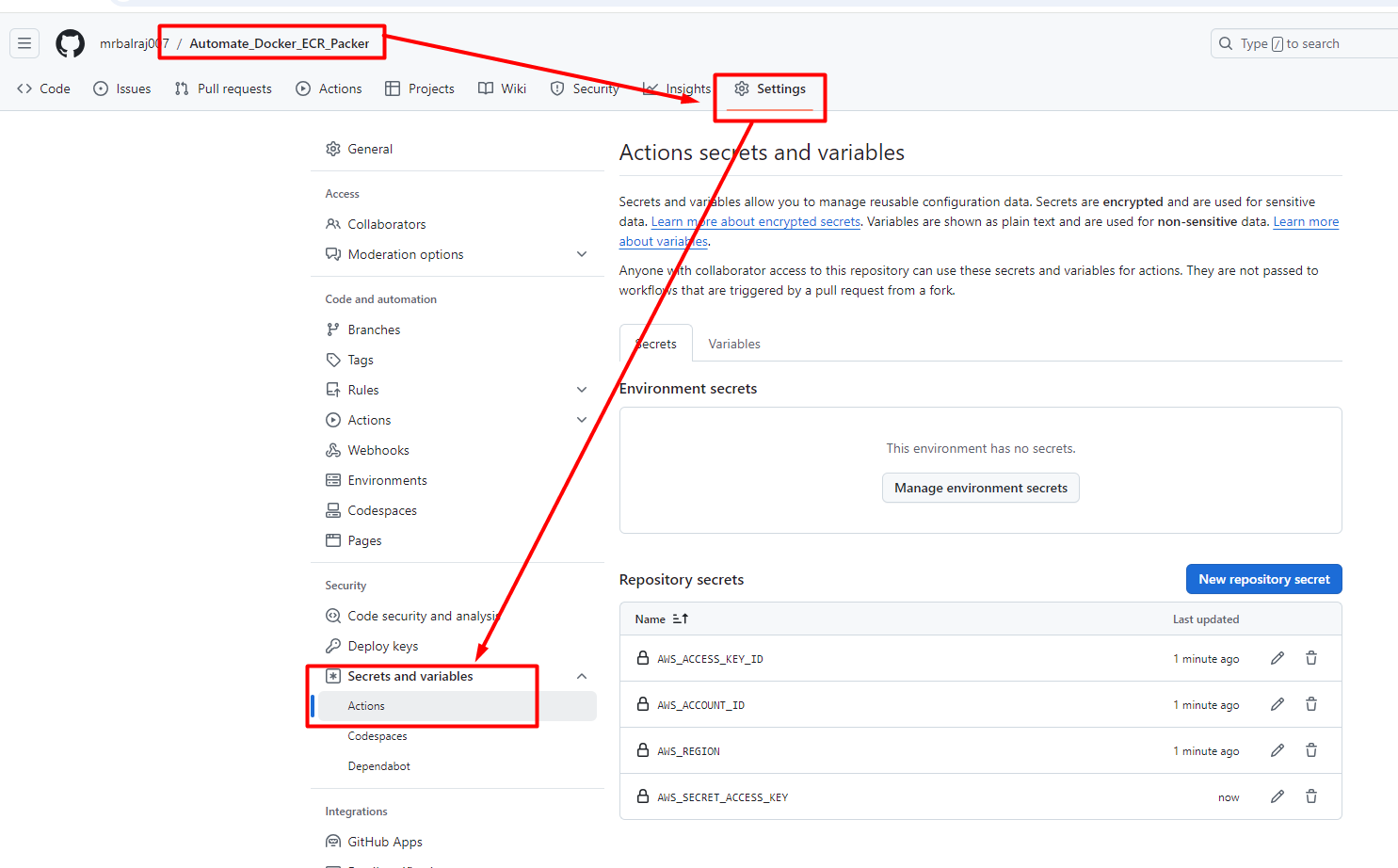
On the git repo, select the repo "Automate_Docker_ECR_Packer" and go to settings- Secrets and variables, click on action and create the following environment variable which will be used in the pipeline.
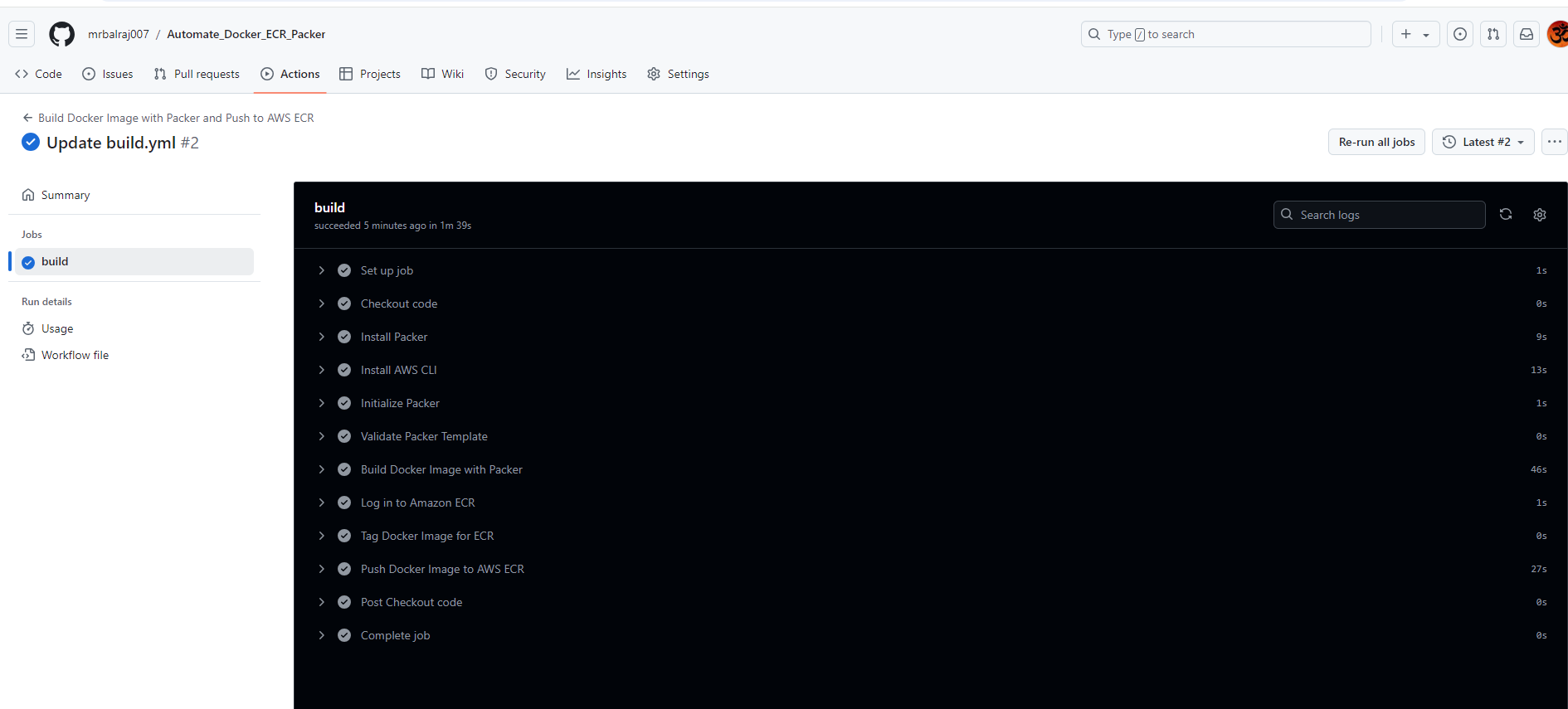
will go to .github/workflows/build.yml and will update and run the ECR ID and name in the pipeline.
Note*-* 373160674113Update it in the pipeline below as per your ECR ID.
name: Build Docker Image with Packer and Push to AWS ECR
on:
push:
branches:
- main
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Install Packer
run: |
sudo apt-get update -y
sudo apt-get install -y wget unzip
wget https://releases.hashicorp.com/packer/1.9.0/packer_1.9.0_linux_amd64.zip
unzip packer_1.9.0_linux_amd64.zip
sudo mv packer /usr/local/bin/
- name: Install AWS CLI
run: |
sudo apt-get update -y
sudo apt-get install -y awscli
- name: Initialize Packer
run: packer init .
- name: Validate Packer Template
run: |
packer validate packer.pkr.hcl
- name: Build Docker Image with Packer
run: |
packer build packer.pkr.hcl
- name: Log in to Amazon ECR
env:
AWS_REGION: ${{ secrets.AWS_REGION }}
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID: ${{ secrets.AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID }}
AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY: ${{ secrets.AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY }}
run: |
aws ecr get-login-password --region $AWS_REGION | docker login --username AWS --password-stdin 373160674113.dkr.ecr.$AWS_REGION.amazonaws.com
- name: Tag Docker Image for ECR
run: |
docker tag docker-image:latest ${{ secrets.AWS_ACCOUNT_ID }}.dkr.ecr.${{ secrets.AWS_REGION }}.amazonaws.com/docker-image:latest
docker tag docker-image:v1.0.0 ${{ secrets.AWS_ACCOUNT_ID }}.dkr.ecr.${{ secrets.AWS_REGION }}.amazonaws.com/docker-image:v1.0.0
- name: Push Docker Image to AWS ECR
run: |
docker push 373160674113.dkr.ecr.${{ secrets.AWS_REGION }}.amazonaws.com/docker-image:latest
docker push 373160674113.dkr.ecr.${{ secrets.AWS_REGION }}.amazonaws.com/docker-image:v1.0.0
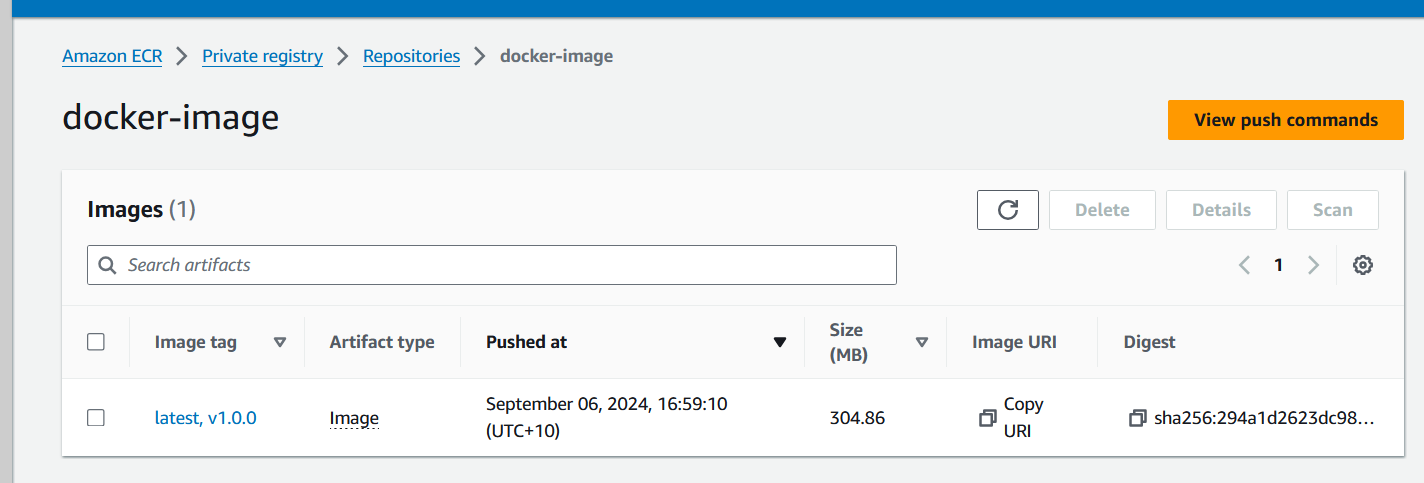
Outcomes in ECR:
Key Steps Covered
01. Create AWS ECR Repository:
Set up a new ECR repository on AWS to store your Docker images.
Generate an IAM user with appropriate permissions for pushing images to ECR.
Store the IAM credentials securely for later use.
02. Set Up Packer Configuration:
Write a Packer configuration file to build a Docker image.
Use the base Ubuntu 20.04 image and install necessary packages.
Tag the Docker image (e.g., latest, v1.0.0).
Configure GitHub Actions Workflow:
03. Set up a GitHub Actions workflow that triggers on every commit.
Install Packer and AWS CLI in the GitHub runner.
Log in to AWS ECR using stored credentials and push the Docker image.
04. Store Secrets in GitHub:
- Store sensitive AWS credentials in GitHub Secrets (Access Key, Secret Key, Region, and Account ID).
05. Trigger Workflow and Validate:
After committing code, GitHub Actions will automatically trigger the build, push the image, and update the ECR repository.
Verify the Docker image in the ECR console.
Key Benefits of Using GitHub Actions for Docker Image Deployment
Automation: Every time you push changes to your repository, the GitHub Actions workflow will automatically build and deploy the Docker image to AWS ECR.
Consistency: Using Packer ensures that the image-building process is consistent and reproducible.
Integration: Direct integration between GitHub Actions and AWS services (ECR in this case) simplifies the CI/CD process.
What to Avoid
Exposing Credentials: Always store your credentials in secure locations like GitHub Secrets. Never hardcode sensitive information in your configuration files.
Skipping Validation: Before pushing images, validate your Packer configuration to avoid issues during deployment.
Use Case:
This approach is ideal for teams using Docker in production environments who want to automate the process of building, tagging, and pushing Docker images to AWS ECR. It’s especially useful for DevOps teams practicing continuous integration and deployment (CI/CD) in cloud-native environments.
Conclusion
By using GitHub Actions, you can automate the Docker image build and deployment process to AWS ECR, ensuring a smooth CI/CD pipeline. Packer ensures your Docker images are built consistently, and GitHub Actions automates the entire process.
Ref Link
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Balraj Singh directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Balraj Singh
Balraj Singh
Tech enthusiast with 15 years of experience in IT, specializing in server management, VMware, AWS, Azure, and automation. Passionate about DevOps, cloud, and modern infrastructure tools like Terraform, Ansible, Packer, Jenkins, Docker, Kubernetes, and Azure DevOps. Passionate about technology and continuous learning, I enjoy sharing my knowledge and insights through blogging and real-world experiences to help the tech community grow!