How to use Git and GitHub in Linux on Red Hat systems
 Thirdy Gayares
Thirdy Gayares
1. Install Git (if not already installed)
First, install Git on your Linux system using the following command (Ubuntu/Debian):
sudo yum update
sudo yum install git
Please see this as a reference
https://software-engineer.thirdygayares.com/package-manager-in-linux
Configure Git
Before using Git, set your name and email:
git config --global user.name "Thirdy Gayares"
git config --global user.email "gayaresthird@gmail.com"

Create a Repository
You can create a new Git repository (repo) in your project directory.
Create a Directory
mkdir myRepository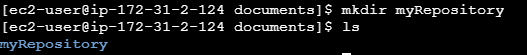
Navigate to your project folder:
cd myRepository
Initialize the Git repository:
git init
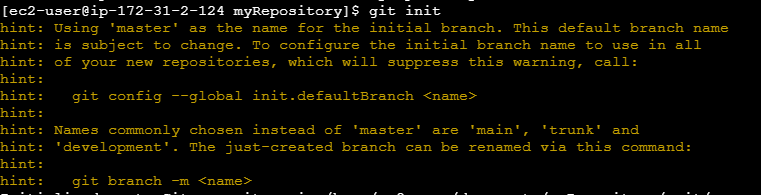
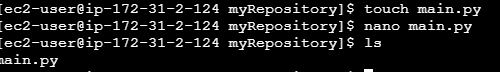
Create File
How to create a file in Linux? https://software-engineer.thirdygayares.com/linux-basic-commands#heading-create-a-file
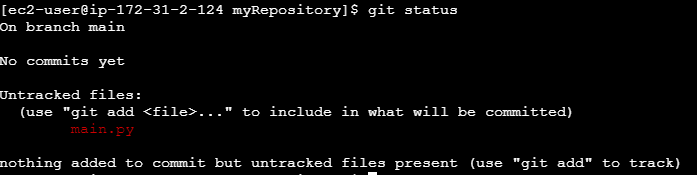
Git Status
This will show you the changes in your working directory, such as new files or modified files.
Add Files to Staging Area
git add .
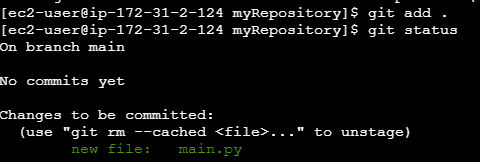
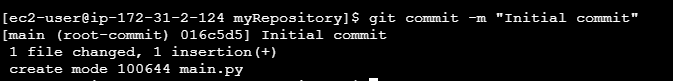
Commit Changes
Once the files are staged, you can commit them. A commit is like saving a snapshot of your project at that point.
git commit -m "Initial commit with project files"
Check Commit History
You can see your commit history with:
git log
Set Up Github Repository


Push to a Remote Repository
You can push your changes.
Add a remote repository:
git remote add origin https://github.com/Thirdy-Lecture/Github_Push_Example_2.git
Push changes to the remote repository:
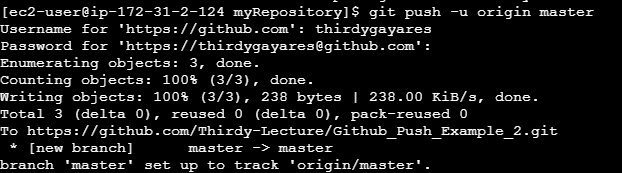
git push -u origin master

How to resolve this issue ?
Go to https://github.com/settings/tokens
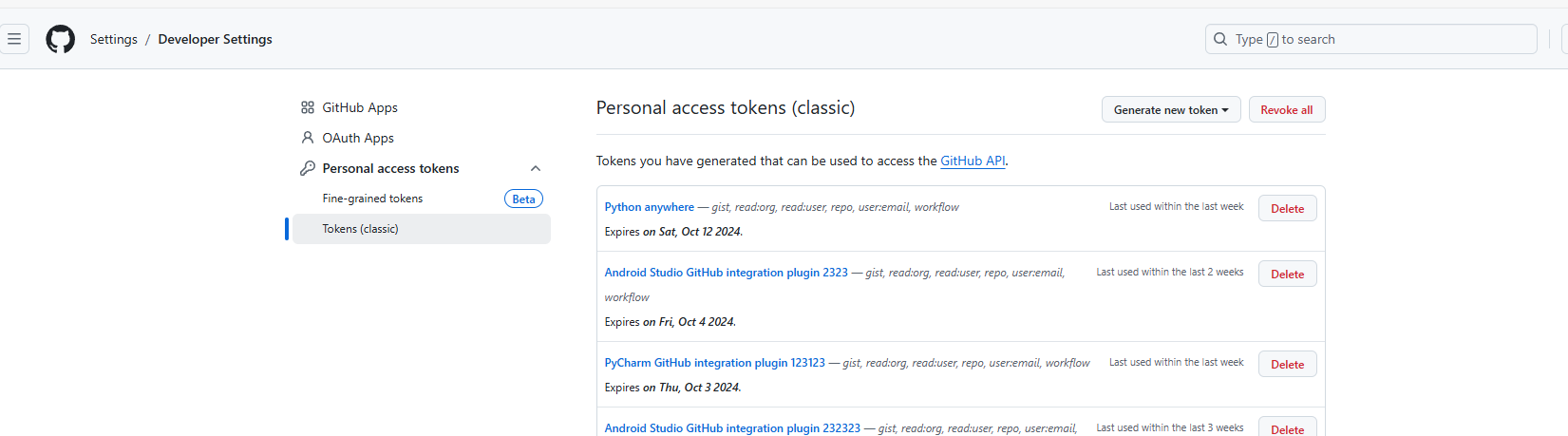
Choose classic
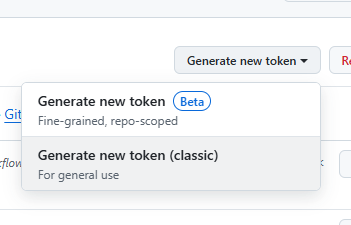
Check The Repo and Set note and Expiration then click generate token
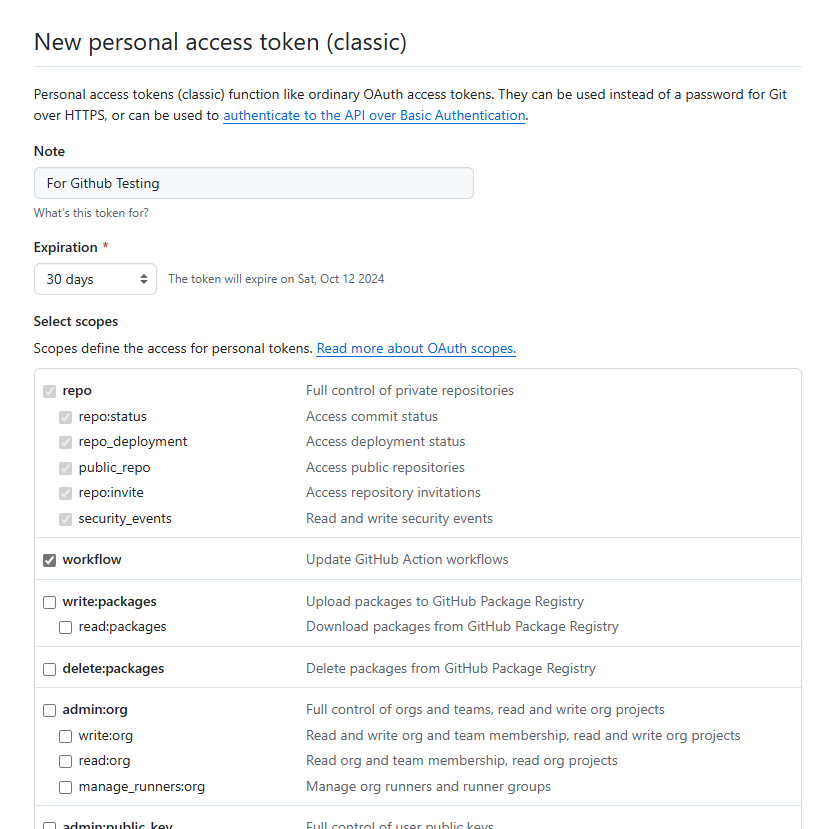
Copy and paste the token key
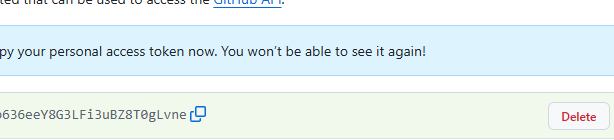
git push -u origin master
Username for 'https://github.com': thirdgyayares
Password for 'https://thirdgayares@github.com': <Paste your Personal Access Token here>
Set up Credential Caching
If you don’t want to enter your token every time, you can cache your credentials using:
git config --global credential.helper cache
This will save your credentials for a while.
Alternatively, you can permanently store your credentials by using:
git config --global credential.helper store
This way, Git will store the credentials in a file, and you won’t be prompted for them again.
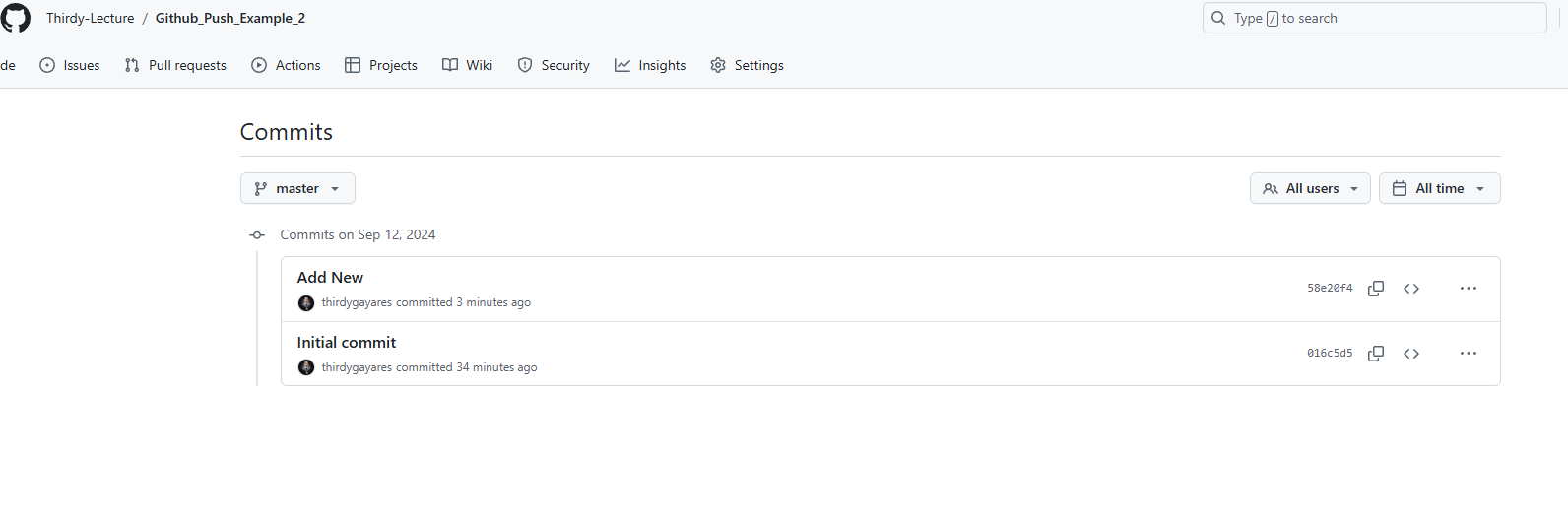
Check the repository on your Github
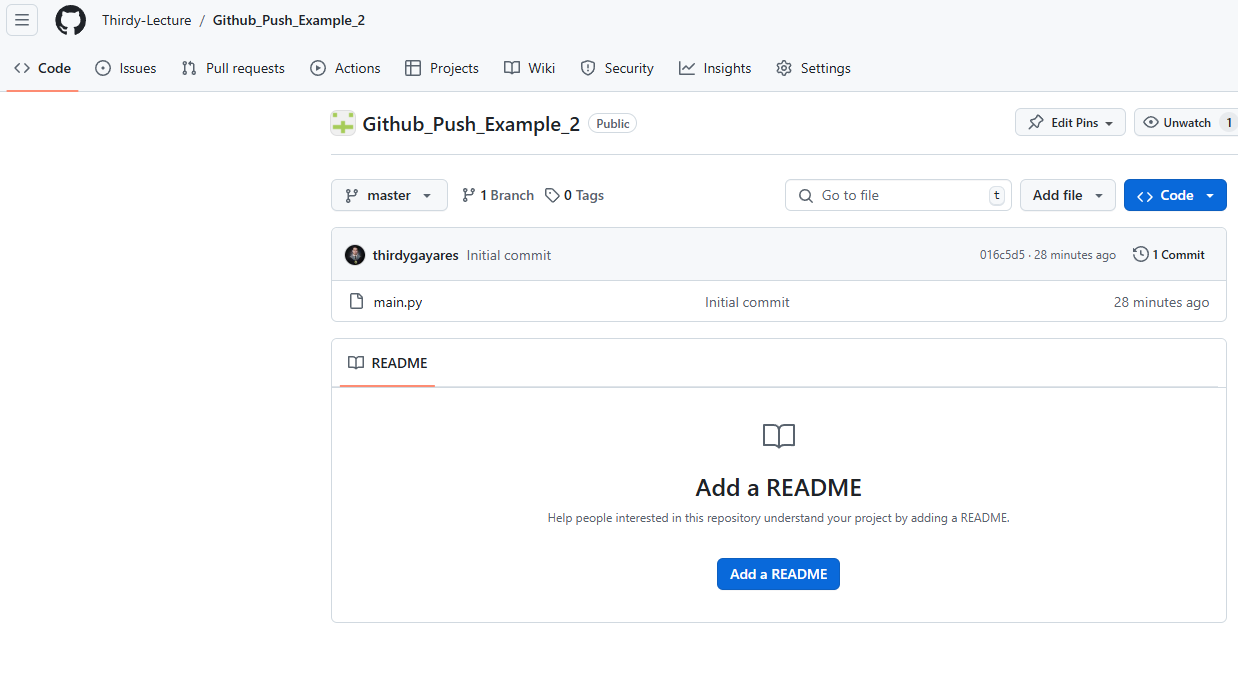
I try to commit and push again
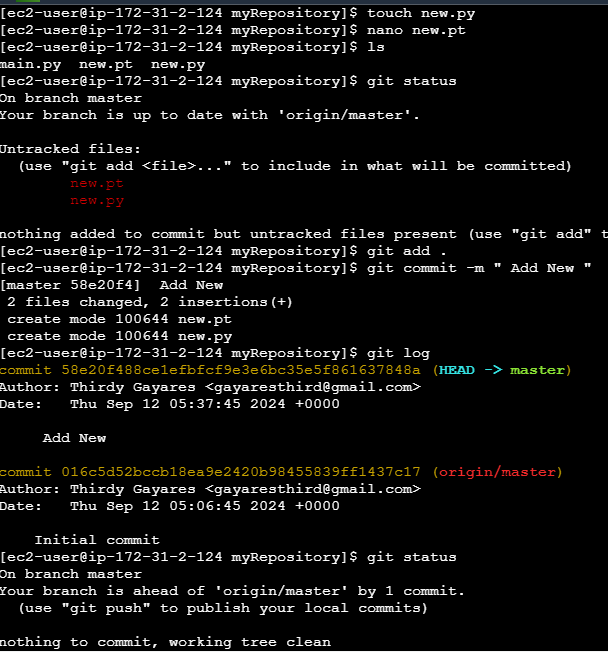
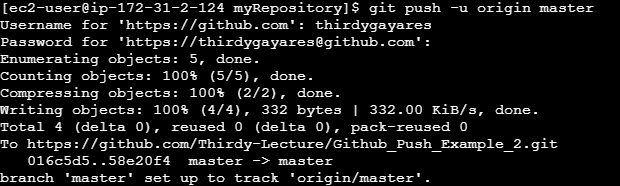
When I refresh my repository on github
Pull Changes from Remote
To pull updates from a remote repository:
git pull origin master
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Thirdy Gayares directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Thirdy Gayares
Thirdy Gayares
I am a dedicated and skilled Software Engineer specializing in mobile app development, backend systems, and creating secure APIs. With extensive experience in both SQL and NoSQL databases, I have a proven track record of delivering robust and scalable solutions. Key Expertise: Mobile App Development: I make high-quality apps for Android and iOS, ensuring they are easy to use and work well. Backend Development: Skilled in designing and implementing backend systems using various frameworks and languages to support web and mobile applications. Secure API Creation: Expertise in creating secure APIs, ensuring data integrity and protection across platforms. Database Management: Experienced with SQL databases such as MySQL, and NoSQL databases like Firebase, managing data effectively and efficiently. Technical Skills: Programming Languages: Java, Dart, Python, JavaScript, Kotlin, PHP Frameworks: Angular, CodeIgniter, Flutter, Flask, Django Database Systems: MySQL, Firebase Cloud Platforms: AWS, Google Cloud Console I love learning new things and taking on new challenges. I am always eager to work on projects that make a difference.