Why is my internet so slow & How to Fix
 BrowserScan
BrowserScan
Ever had that moment when the internet just won’t cooperate? You’re trying to load a webpage, but it’s taking forever. Or maybe you’re on a video call, and you’re seeing a lot of frozen smiles. You might have complained for thousand times:”Why is my internet so slow?!”
Don’t worry, In this article, we’ll help you identify common causes and offer solutions to get your internet running smoothly again. Now let’s get started and wave goodbye to those buffering blues!
Why is My Internet So Slow & How to Fix
Reason1: Router overheated or cache overload
Routers, like any electronic device, can overheat if they run for long periods without a break. Overheating can cause your router to slow down or even drop the connection.
Additionally, extended operation can lead to cache overload, this happens because routers store temporary data (or “cache”) to quickly manage the flow of internet traffic. Every time a device requests data from the internet, the router processes that request and forwards the data to the device. Over time, this can create a backlog of stored data and fill up router’s memory.
How to Fix
- Restarte your router regularly. It’s enough to fix minor issues for most users, here’s how to do it :
Unplug your router from the power source.
Wait at least 10–15 seconds to allow the router to fully reset, or wait for longer until it cool down.
Plug the router back in and wait for it to fully reboot, which can take a few minutes.
- But if you’re troubleshooting persistent issues that can’t be fixed by restarting, you can consider to reset it. This method will restore the router to its factory settings, erasing all your personalized settings such as passwords, network names (SSID), and any custom configurations. Hence, avoid resetting to factory settings unless absolutely necessary, and if you’re unsure, consult a professional before proceeding.Here’s how to reset your router:
Locate the small reset button on the back of your router (often inside a pinhole).
Press and hold the reset button for about 10–15 seconds using a paperclip or similar object.
During the reset process, watch the indicator light change until the router has completed the reset.
Open a browser and enter your router’s IP address (usually something like
192.168.1.1or192.168.0.1) in the address bar.Enter the admin username and password. The default details are often on a label on your router or in its manual.
After logging in to your router’s admin panel, reconfigure the router settings.
- To prevent overheating, place your router in a well-ventilated area, away from heat sources. If it continues to overheat, consider using a cooling pad or upgrading to a newer model designed to handle higher loads.

Reason2: Improper router placement
The placement of your router can significantly impact your internet speed. If the router is hidden in a cabinet, placed on the floor, or located far from where you use the internet most, the signal might be weak or obstructed by walls and furniture.
How to Fix
Place your router in a central, elevated location within your home, ideally in an open area. Avoid placing it near metal objects, thick walls, or electronic devices that could interfere with the signal.
Reason3: Insufficient router signal to cover the usage area
If your router’s signal isn’t strong enough to reach all areas of your home or office, you may experience slow speeds or dead zones where the internet connection drops entirely. This can be especially problematic in larger homes, offices with multiple floors, or buildings with thick walls and partitions.
How to Fix
Consider using Wi-Fi extenders, or upgrading to a more powerful router that can cover a larger area.
If you need to access the same network for multiple devices that are distributed across different areas, you can use mesh networking systems to boost the signal throughout the entire area.It ensures better simultaneous connection quality in every room or workspace.
Reason4: Router aging
Old routers can have weaker signal senders, slower CPUs, and less memory, which might make the Wi-Fi cover a smaller area and slow down how fast it handles data. Plus, if the router model is too old, the company that made it might not give updates anymore. This means the router might not work with the newest Wi-Fi rules and could have trouble dealing with lots of data really fast.
How to Fix
Check the age and specifications of your router. If it’s older than durable years or doesn’t support the latest Wi-Fi standards (like Wi-Fi 6), it might be time to upgrade.

Reason5: Wire issues
Your internet speed can also be affected by the physical lines connecting your devices. For example, ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line) is an older technology that uses telephone lines for internet access. While it was once common, ADSL is now slower than modern fiber or cable connections, especially if the lines are old or in poor condition.
Additionally, Ethernet cables connecting your modem or router to your devices can also degrade your network performance if they are damaged or aging.
In what situations will your wires get damaged? Common causes include mechanical damage, which often occurs when cables are pinched or crushed under furniture during movement. Environmental factors such as moisture or extreme temperatures can also degrade your cables.
Moreover, if you have pets like cats or dogs, the risk of damage increases significantly. They can easily access high places or tight corners and may chew on the cables.
How to Fix
If you’re still using ADSL, it might be time to upgrade to a more modern connection type, like fiber or cable, to improve your internet speed.
Inspect your cables regularly for any signs of wear or damage, such as frayed wires or bent connectors. Replace any cables that show signs of aging or damage.
For minor damage to Ethernet cables, you can use crimping tools to cut the damaged portion and reattach a new connector to the remaining cable.
To prevent pets from chewing on cables, consider using network cable protective covers or routing the cables out of reach. In addition, provide pets with special chew toys to divert their interest in Internet.

Reason6: Insufficient bandwidth
Bandwidth refers to the maximum transmission rate of a network connection, and it is like the lane of a highway, the more lanes, the more vehicles can pass at the same time, and the faster the speed of data transmission. Your internet speed might be slow because your bandwidth isn’t enough to handle all your online activities.
At present, broadband services mainly include optical fiber and cable two categories, and fiber-optic connections generally offer higher bandwidth and faster speeds compared to traditional cable connections, making them a better option if you frequently experience slowdowns. Additionally, some Internet Service Providers (ISPs) may throttle your connection if you exceed certain data limits, further reducing your speed.
How to Fix
Consider upgrading to a higher-speed internet plan, especially if you have a lot of devices or frequently use data-intensive services.
If you are using traditional cable connections and are tired of slow internet speeds, check if your ISP offers fiber-optic services. Although switching to fiber-optic services requires additional installation costs, the user experience can be greatly optimized.
If your ISP imposes data caps, don’t forget to monitor your usage more closely or upgrade to a plan with unlimited data to avoid throttling.

Reason7: Overloaded Bandwidth From Multiple Devices
When multiple devices in your home are performing high-bandwidth activities like streaming 4K videos, gaming online, or downloading large files simultaneously, it can overload your internet connection.
How to Fix
Prioritize certain devices or activities using your router’s Quality of Service (QoS) settings, which allow you to allocate more bandwidth to specific devices.
Try staggering high-bandwidth activities to avoid network congestion. For example, if someone in your household is in an important online meeting, others should avoid gaming or downloading large files at the same time.
If your household regularly uses multiple devices for data-intensive tasks, upgrading to a higher bandwidth plan might be necessary.

Reason8: Unauthorized Internet Access
Sometimes, unauthorized users accessing your network can also slow down your internet speed. This is known as hijacking. That’s because when someone gains access to your Wi-Fi, they can use your bandwidth for their own activities, such as streaming, downloading, or even illegal activities.
How to Fix
Secure your Wi-Fi network with a strong, unique password and use WPA3 encryption if your router supports it.
Regularly check the list of connected devices in your router’s settings to ensure only authorized devices are using your network. If you notice any unfamiliar devices, change your Wi-Fi password immediately. Here’s how to change your Wi-Fi password:
log in to your router’s admin panel, the specific steps can be found in the method of resetting your router
Once logged in, find the Wireless or Wi-Fi settings section.
Look for the Password or Security settings. Here, you can change your Wi-Fi password. Make sure to choose a strong, unique password.
Save the changes, and your router will apply the new password. You will need to reconnect all your devices using the updated password.

Reason9: Channel Congestion
Wi-Fi signals operate on different channels, and if too many routers in your area are using the same channel, it can lead to congestion. That means your router has to compete with others for bandwidth. This is especially common in apartment buildings or densely populated areas where many networks overlap.
How to Fix
Log into your router’s settings and switch to a less congested channel. Many modern routers can automatically choose the best channel, but you can manually select one using tools like Wi-Fi analyzers to find the least crowded option.
Switching to the 5 GHz frequency band can also reduce congestion. Although it may not reach as far through walls as the 2.4 GHz band, it has more channels and is less crowded than the 2.4 GHz band.
Reason10: Malware Impact
Malware can infect your devices, consume memory and processing resources, including viruses, spyware, and other malicious software. This not only slows down the infected device but can also reduce your overall internet speed as malware often communicates with external servers, using up bandwidth.
How to Fix
Regularly scan your devices with updated antivirus software to detect and remove malware.
Keep your operating system and applications updated to protect against vulnerabilities that malware might exploit.
Avoid downloading software or files from untrusted sources, and be cautious of phishing emails or suspicious links that might introduce malware to your devices.
Reason11: Background Applications Consuming Bandwidth Resources
Many applications and programs on your devices, such as automatic updates, cloud backups, or streaming services, can run in the background without your notice. These background tasks can consume significant amounts of bandwidth for other activities, making your internet speed slower.
How to Fix
Check your device’s task manager or activity monitor to see which applications are using bandwidth in the background. Disable or pause unnecessary background activities, especially when you’re trying to join an online conference, play games, or perform other high-bandwidth tasks. Consider scheduling updates or backups during times when you’re not actively using the internet.
Reason12: ISP service issues
Sometimes, slow internet isn’t your fault but is due to issues with your Internet Service Provider (ISP). ISPs may experience outages, maintenance periods, or congestion during peak usage times, all of which can force you to bear the slow internet speed.
How to Fix
Perform internet speed tests to check if the speeds you’re getting match the speeds promised by your ISP
If you suspect your ISP is the problem, check their service status online or contact their support team for updates.
Consider switching to an ISP that offers better customer service or more reliable speeds, especially if you frequently experience slowdowns during peak hours.
Reason13: Domain Connection Failures/Platform Service Outages
Sometimes, specific websites or online platforms experience their own issues, leading to slow speeds or connection failures. These problems are usually temporary but can be frustrating if you rely on a particular service. If these outages are frequent, consider using alternative services that are more reliable.
How to Fix
Try visiting other websites to verify that your Internet connection is working.
Sometimes, problems with the browser cache or cookies may cause the website disable to not load properly. Clear your browser’s cache and cookies and try again.
Try using another browser to see if you can access the website.
Use an online service to check that the website Is online, such as “Down for Everyone or Just Me” or “Is It Down Right Now?”

Reason14: VPN Server Issues
Using a VPN can protect your privacy, but if the VPN server is far from your location, that may be the answer to “Why is my internet so slow?” The further the server, the longer it takes for data to travel, leading to noticeable lag or reduced speeds.
How to Fix
Choose a VPN server that is geographically closer to your location to minimize latency.
If you’re still experiencing slow speeds, consider switching to a different VPN provider that offers faster servers or optimized connections.
Reason15: Public Network Infrastructure Issues
Although the probability of this happening is very low, it is not impossible. When there are force majeure factors, or when the public network infrastructure is accidentally damaged, this can also lead to network outages. You can confirm it by checking with your ISP or ask your neighbors. But when encountering such problems, you can only wait for the network to recover.
What’s The Key Point In Troubleshooting?
Monitor Your Internet Speed Regularly and Note Abnormality
First, check if there is something wrong with your network cables or network devices. If not, keep an eye on your internet speed over time and note the abnormal situations, which can help you spot patterns and detect issues early.
Whenever you notice a significant drop in speed, note the time, day, and your online activities. It can help you identify whether the issue is consistent or sporadic and whether it correlates with high-traffic periods or specific device usage.
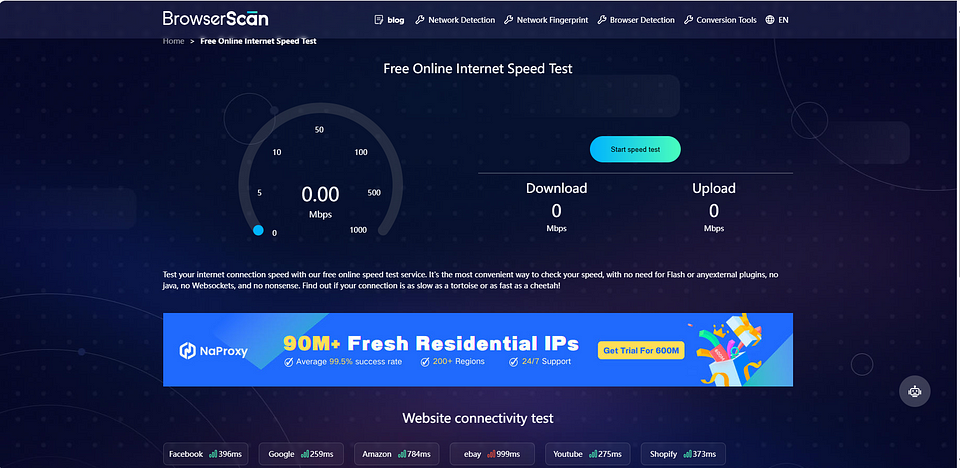
Keep Tracking Your Internet Speed After Making a Change
After making any changes, such as adjusting router placement or upgrading your plan, continue monitoring your speed to see if the issue is resolved. Consistent tracking will confirm whether the steps you took were effective or if further action is needed.
Finally
Now that you’re equipped with the knowledge to identify and fix various internet speed issues, it’s time to choose a suitable internet speed test tool. BrowserScan’s speed test is a powerful and user-friendly tool. It’s well integrated with multiple operating systems and devices, and you can easily understand your network speed with fast test results and comprehensible metrics.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from BrowserScan directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

BrowserScan
BrowserScan
Am I 100% anonymous? Check your browser fingerprints and IP address to find how your online identity looks👉www.browserscan.net