What You Need to Know About Cloud Computing
 Mohsin Khansab
Mohsin Khansab
Traditional IT Overview
IT Terminology
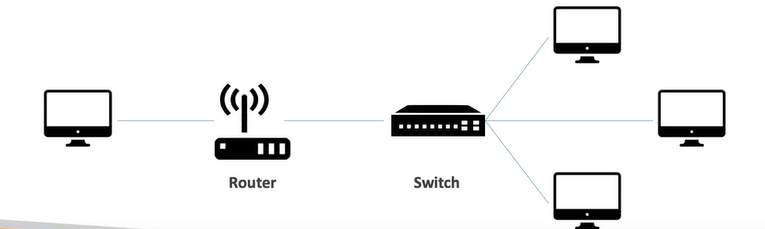
Network
Cables, routers and servers connected with each other.
Router
A networking device that forwards data packets between computer networks. They know where to send your packets on the internet.
Switch
Takes a packet and send it to the correct server / client on your network.
Problems with traditional IT approach
Pay for the rent for the data centre
Pay for power supply, cooling, maintenance
Adding and replacing hardware takes time
Scaling is limited
Hire 24/7 team to monitor the infrastructure
How to deal with disasters (earthquake, power shutdown, fire, …)
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of compute power, database storage, applications, and other IT resources
Through a cloud services platform with pay-as-you-go pricing
You can provision exactly the right type and size of computing resources you need
You can access as many resources as you need, almost instantly
Simple way to access servers, storage, databases and a set of application services
Amazon Web Services owns and maintain the network-connected hardware required for these application services, while you provision and use what you need via a web application
The Deployment Models of the Cloud
| Private Cloud | Public Cloud | Hybrid Cloud |
| Cloud services used by a single organisation, not exposed to the public | Cloud resources owned and operated by a third-party cloud service provider delivered over the Internet | Keep some servers on premises and extend some capabilities to the Cloud |
| Complete control & Security for sensitive applications | Six advantages of Cloud Computing | Control over sensitive assets in your private infrastructure |
| Meet specific business needs | Flexibility and cost-effectiveness of the public cloud | |
| Ex: Rackspace | Ex: Azure, GCP, AWS | Ex: On-premises ↔ AWS |
The Five Characteristics of Cloud Computing
On-demand self service:
Users can provision resources and use them without human interaction from the service provider
Broad network access:
Resources available over the network, and can be accessed by diverse client platforms
Multi-tenancy and resource pooling:
Multiple customers can share the same infrastructure and applications with security and privacy
Multiple customers are serviced from the same physical resources
Rapid elasticity and scalability:
Automatically and quickly acquire and dispose resources when needed
Quickly and easily scale based on demand
Measured service:
Usage is measured, users pay correctly for what they have used
Six Advantages of Cloud Computing
Trade capital expense (CAPEX) for operational expense (OPEX)
Pay On-Demand: don’t own hardware
Reduced Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) & Operational Expense (OPEX)
Benefit from massive economies of scale
Prices are reduced as AWS is more efficient due to large scale
Stop guessing capacity
Scale based on actual measured usage
Increase speed and agility
Stop spending money running and maintaining data centres
Go global in minutes: leverage the AWS global infrastructure
Problems solved by the Cloud
Flexibility: change resource types when needed
Cost-Effectiveness: pay as you go, for what you use
Scalability: accommodate larger loads by making hardware stronger or adding additional nodes
Elasticity: ability to scale out and scale-in when needed
High-availability and fault-tolerance: build across data centres
Agility: rapidly develop, test and launch software applications
Types of Cloud Computing
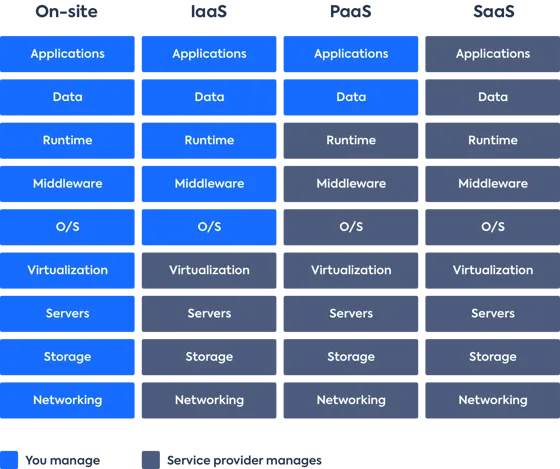
Infrastructure as a Service(IaaS)
Provide building blocks for cloud IT
Provides networking, computers, data storage space
Highest level of flexibility
Easy parallel with traditional on-premises IT
Ex: Amazon EC2(AWS), GCP, Azure, Rackspace, Digital Ocean, Linode
Platform as a Service(PaaS)
Removes the need for your organizationo to manage the underlying infrastructure
Focus on the deployment and management of your applications
Elastic Beanstalk(AWS), Heroku, Google App Engine(GCP), Windows Azure(Microsoft)
Software as a Service(SaaS)
- Completed product that is run and managed by the service provider
On-premises vs Iaas vs Paas vs Saas
AWS Cloud Overview
AWS Regions
AWS has Regions all around the world
Names can be us-east-I, eu-west-3, …
A region is a cluster of data centers
Most AWS services are region-scoped
How to choose an AWS Region?
Compliance with data governance and legal requirements: data never leaves a region without your explicit permission
Proximity to customers: reduced latency
Available services within a Region: new services and new features aren’t available in every Region
Pricing: pricing varies region to region and is transparent in the service pricing page
AWS Availability Zones
Each region has many availability zones. (usually3, min is 3, max is 6). Example:
ap-southeast-2a
ap-southeast-2b
ap-southeast-2c
Each availablity zone (AZ) is one or more discrete data centers with redundant power, networking, and connectivity
They’re separate from each other, so that they’re isolated from disasters
They’re connected with high bandwidth, ultra-low latency networking
AWS Points of Presence (Edge Locations)
Amazon has 400+ Points of Presence (400+ Edge Locations & 10+ Regional Caches) in 90+cities across 40+ countries
Content is delivered to end users with lower latency
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Mohsin Khansab directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Mohsin Khansab
Mohsin Khansab
Software engineer skilled in building web applications and REST APIs using Java, ReactJS, and Spring Boot. Experienced in agile teams, performance optimization, and code quality. Passionate about engineering and building scalable systems.