Understanding the Laravel Life Cycle
 Aman jain
Aman jain
Before you start with a Laravel project, it's great to get a sense of how Laravel operates behind the scenes. Knowing the journey of a request, from clicking a button to how Laravel processes it step by step, can boost your confidence. This understanding will make the development process easier and more intuitive, helping you feel more in control and ready to tackle any challenges that come your way.
Summary
First, the request heads to the
entry pointwhere Laravel starts up.Next, the Laravel application is set up and essential components are initialized.
Service providersare then registered and activated. After that, the request moves through therouting system, reaching its designatedrouteorcontroller. Finally, Laravel generates aresponseand sends it back to theentry point. Understanding this flow will help you see how Laravel handles requests efficiently, making the development process more manageable and enjoyable.
Here’s a reassuring breakdown of what happens when you Hit a request:
The Laravel Lifecycle: From Request to Response.
Entry Point:
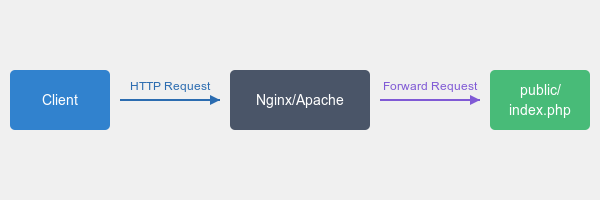
When a user hits a request for your Laravel application, the process begins with the
web server(like Apache or Nginx) receiving that request. Laravel’s entry point is thepublic/index.phpfile. This file is like thefront door to your application, greeting every request and preparing it for processing.
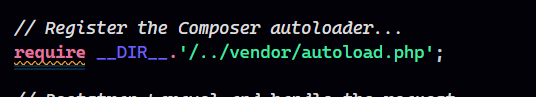
In this step, we have a brilliant autoloader.
The index.php file loads the autoloader, which is generated by Composer. The autoloader helps PHP find the necessary files and classes to run your application.
The index.php the file then retrieves instance the Laravel application from the bootstrap/app.php file. This is like getting the keys to the app's engine room.
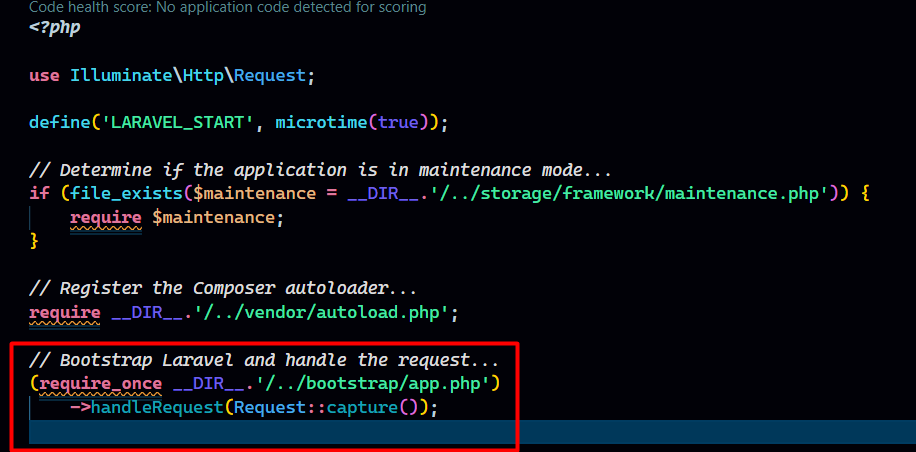
The first thing Laravel does is create an instance of the application/service container. This container is like a toolbox that holds all the necessary components and services for your application to run.
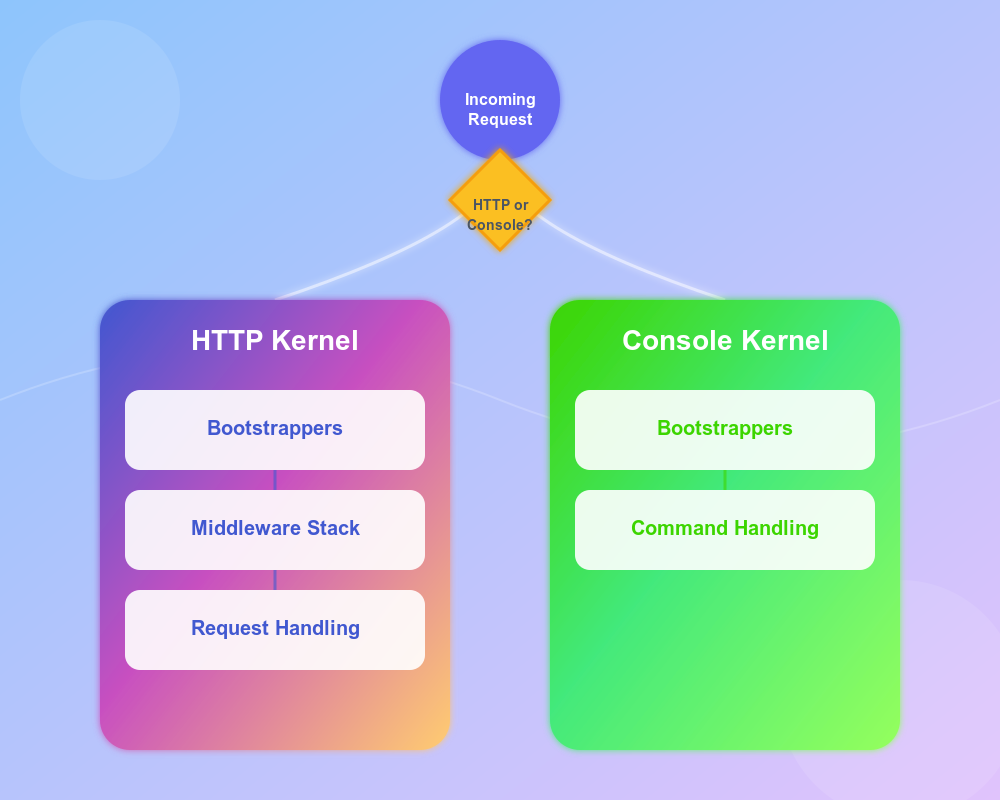
HTTP / Console Kernels
This is the second step of lifecycle . These two kernels are the central point of all requests flow.Depending on the type of
request(HTTP or Console), the appropriate kernel isbootstrapped. This process sets up essential services and prepares the application tohandle the incoming request.
$kernel = $app->make(Illuminate\Contracts\Http\Kernel::class);
$response = $kernel->handle(
$request = Illuminate\Http\Request::capture()
);
Now Break Down the Above Code.
$kernel = $app->resolve(Illuminate\Contracts\Http\Kernel::class);
The code is instantiating the
HTTPKernel. The Kernel manages incoming requests and processes them within the application. Themake()method is utilized to instantiate an object from theIlluminate\Contracts\Http\Kernel class, which specifies howHTTPrequests should be managed.Illuminate\Http\Request::capture() is used to capture the request.
This line captures the existing HTTP request. The
Request::capture()method is utilized to generate a Request class instance that holds information from the incoming HTTP request, including GET or POST parameters, headers, and additional data.$response is obtained by utilizing the handle method from the kernel with the input request.
After the request is received, this line sends it to the Kernel's
handle()function. The request is then handled by the Kernel as it passes through themiddleware,routingsystem, andcontrollers. Once the request is processed by the application, it creates aresponsethat is then stored in the$responsevariable.
3: Service Providers
It is one of the most important operations to bootstrapping action is loading all the service providers for your application.
Service providers are the backbone of Laravel's bootstrap process, as they configure and bootstrap almost every major feature offered by the framework. This makes them the most important aspect of the entire Laravel bootstrap process.
The application instance registers all the service providers listed in the config/app.php file. These providers boot the various components of the framework, such as routing, caching, and database connections.
These providers are responsible for bootstrapping various framework components, including:
Database
Queue
Validation
Routing
The Bootstrapping Process
Here's how Laravel bootstraps service providers:
Instantiation: Laravel iterates through the list of providers and instantiates each one.
Registration: The
registermethod is called on all providers.Boot: Once all providers are registered, the
bootmethod is called on each provider. This ensures that service providers can depend on all container bindings being registered and available.
4: Routing
After bootstrapping and registering all service providers, the request is handed off to the router.
The router directs the request to the appropriate route or controller and runs any route-specific middleware.
Middleware filters or examines HTTP requests. For example, authentication middleware checks if a user is logged in:
If the user is not authenticated, they will be redirected to the login screen.
If authenticated, the request proceeds further.
Middleware can be applied to all routes (e.g.,
PreventRequestsDuringMaintenance) or to specific routes or route groups.If the request passes all assigned middleware, the route or controller method is executed.
The response then travels back through the middleware chain before reaching the client.
5:Finishing Up
After the route or controller method returns a response, it travels back through the route's middleware. This allows the application to modify or examine the outgoing response.
Once through the middleware, the HTTP kernel’s
handlemethod returns the response object to the application instance’shandleRequestmethod.The
handleRequestmethod then calls thesendmethod on the response object.The
sendmethod transmits the response content to the user's web browser.This completes the entire Laravel request lifecycle.
Conclusion
This article explains the step-by-step process of how Laravel handles a request, from the initial entry point through service provider registration, routing, and middleware, to generating and sending a response back to the client. Understanding this flow makes Laravel development more intuitive and manageable.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Aman jain directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
Aman jain
Aman jain
I'm a developer who shares advanced insights and expertise through technology-related articles. Passionate about creating innovative solutions and staying up-to-date with the latest tech trends. Let's connect and explore the world of technology together!