Integrating eSewa Payment in a MERN Stack Web Application (part 1)
 Samir Pokhrel
Samir Pokhrel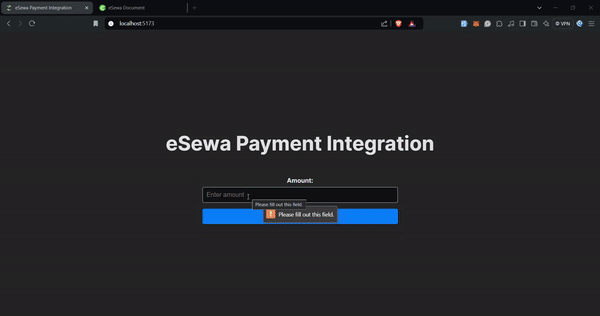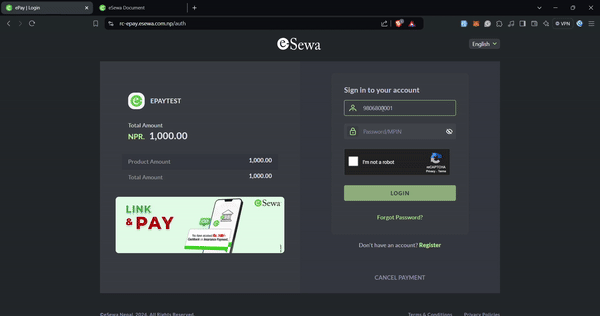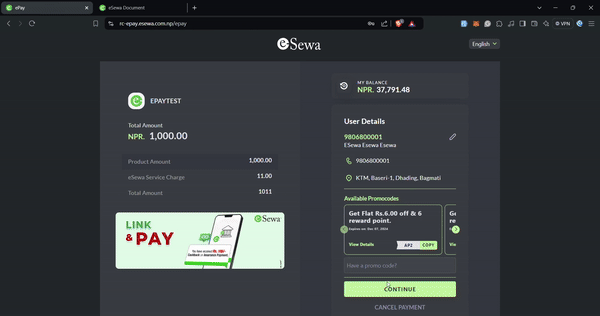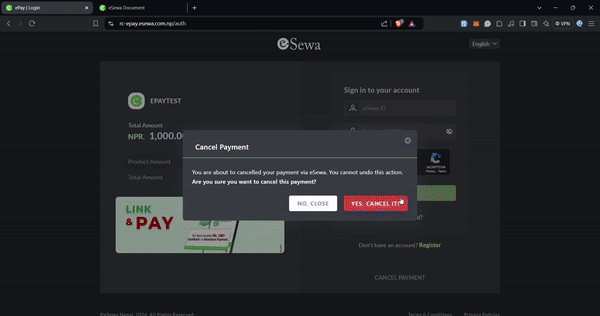
Integrating a payment gateway is an essential feature for any web application that deals with financial transactions. In this blog post, we’ll walk through the process of integrating the eSewa payment gateway into a MERN stack web application. eSewa is a popular digital payment platform in Nepal that allows secure online transactions.
Overview of the MERN Stack
The MERN stack is a robust combination of technologies used to build full-stack web applications. It comprises:
MongoDB: A NoSQL database for storing application data.
Express.js: A minimal web application framework for Node.js.
React.js: A JavaScript library for building interactive user interfaces.
Node.js: A JavaScript runtime that executes JavaScript code on the server side.
Setting Up the Project
To get started, we’ll set up a basic MERN stack application. If you already have a MERN application, you can skip ahead to the eSewa Integration section.
Step 1: Initialize the Backend with Express.js
- Create a New Directory and Initialize NPM:
mkdir esewa-payment-integration
cd esewa-payment-integration
mkdir server
cd server
npm init -y
- Install Necessary Packages:
npm install express cors body-parser axios
- Set Up Express Server:
Create a file named app.js in the root directory:
const express = require('express');
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
const cors = require('cors');
const bodyParser = require("body-parser");
const app = express();
const PORT = 3000;
app.use(cors());
app.use(bodyParser.json());
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: true }));
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('eSewa Payment Integration');
});
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`Server running on http://localhost:${PORT}`);
});
Step 2: Initialize the Frontend with React
- Set Up React App:
Navigate back to the root directory(esewa-payment-integration) and create a new React app:
npm create vite client --template react
cd client
npm install axios react-router-dom
- Set Up Basic Routing:
Edit src/App.jsx to set up basic routing:
import { BrowserRouter as Router, Route, Routes } from "react-router-dom";
import Failure from "./components/Failure";
import PaymentForm from "./components/PaymentForm";
import Success from "./components/Success";
function App() {
return (
<Router>
<div className="App">
<Routes>
<Route path="/" element={<PaymentForm />} />
<Route path="/payment-success" element={<Success />} />
<Route path="/payment-failure" element={<Failure />} />
</Routes>
</div>
</Router>
);
}
export default App;
- Create Payment, Success, Failure Components and CSS:
In the src/components folder, create and PaymentForm.jsx:
PaymentForm.jsx:
import React, { useState } from "react";
import axios from "axios";
const PaymentComponent = () => {
const [amount, setAmount] = useState("");
const handlePayment = async (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
};
return (
<div>
<h1>eSewa Payment Integration</h1>
<div className="form-container" onSubmit={handlePayment}>
<form className="styled-form">
<div className="form-group">
<label htmlFor="Amount">Amount:</label>
<input
type="number"
value={amount}
onChange={(e) => setAmount(e.target.value)}
required
placeholder="Enter amount"
/>
</div>
<button type="submit" className="submit-button">
Pay with eSewa
</button>
</form>
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default PaymentComponent;
. Success.jsx :
import React from "react";
import { useNavigate } from "react-router-dom";
const Success = () => {
const navigate = useNavigate();
return (
<div>
<h1>Payment Successful!</h1>
<p>Thank you for your payment. Your transaction was successful.</p>
<button onClick={() => navigate("/")} className="go-home-button">
Go to Homepage
</button>
</div>
);
};
export default Success;
. Failure.jsx :
import React from "react";
import { useNavigate } from "react-router-dom";
const Failure = () => {
const navigate = useNavigate();
return (
<div>
<h1>Payment Failed!</h1>
<p>There was an issue with your payment. Please try again.</p>
<button onClick={() => navigate("/")} className="go-home-button">
Go to Homepage
</button>
</div>
);
};
export default Failure;
. index.css
:root {
font-family: Inter, system-ui, Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
line-height: 1.5;
font-weight: 400;
color-scheme: light dark;
color: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.87);
background-color: #242424;
font-synthesis: none;
text-rendering: optimizeLegibility;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
}
a {
font-weight: 500;
color: #646cff;
text-decoration: inherit;
}
a:hover {
color: #535bf2;
}
body {
margin: 0;
display: flex;
place-items: center;
min-width: 320px;
min-height: 100vh;
}
h1 {
font-size: 3.2em;
line-height: 1.1;
}
button {
border-radius: 8px;
border: 1px solid transparent;
padding: 0.6em 1.2em;
font-size: 1em;
font-weight: 500;
font-family: inherit;
background-color: #1a1a1a;
cursor: pointer;
transition: border-color 0.25s;
}
button:hover {
border-color: #646cff;
}
button:focus,
button:focus-visible {
outline: 4px auto -webkit-focus-ring-color;
}
#root {
max-width: 1280px;
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 2rem;
text-align: center;
}
/* Hide spinner for Chrome, Safari, Edge, and Opera */
input[type="number"]::-webkit-outer-spin-button,
input[type="number"]::-webkit-inner-spin-button {
-webkit-appearance: none;
margin: 0;
}
/* Hide spinner for Firefox */
input[type="number"] {
-moz-appearance: textfield;
}
/* FormComponent.css */
.form-container {
max-width: 500px;
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 20px;
/* background-color: #f9f9f9; */
border-radius: 8px;
box-shadow: 0 4px 8px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
}
.styled-form {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
}
.form-group {
margin-bottom: 15px;
}
.form-group label {
display: block;
margin-bottom: 5px;
font-weight: bold;
}
.form-group input,
{
width: 100%;
padding: 10px;
border: 1px solid #ccc;
border-radius: 4px;
font-size: 16px;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.submit-button {
padding: 10px 15px;
background-color: #007bff;
color: #fff;
border: none;
border-radius: 4px;
cursor: pointer;
font-size: 16px;
transition: background-color 0.3s ease;
}
.submit-button:hover {
background-color: #0056b3;
}
.go-home-button {
padding: 10px 20px;
background-color: #007bff;
color: white;
border: none;
border-radius: 4px;
cursor: pointer;
font-size: 16px;
transition: background-color 0.3s ease;
}
.go-home-button:hover {
background-color: #0056b3;
}
@media (prefers-color-scheme: light) {
:root {
color: #213547;
background-color: #ffffff;
}
a:hover {
color: #747bff;
}
button {
background-color: #f9f9f9;
}
}
Creating eSewa Payment Gateway route
Now, let’s create the eSewa payment endpoint functionality into our application.
Step 3: Implement Payment Endpoint in Express
Add a payment route to app.js:
// eSewa Configuration //Later we will serve it from .env
const esewaConfig = {
merchantId: "EPAYTEST", // Replace with your eSewa Merchant ID
successUrl: "http://localhost:5173/payment-success", //Replace with front-end success route page
failureUrl: "http://localhost:5173/payment-failure", //Replace with front-end failure route page
esewaPaymentUrl: "https://rc-epay.esewa.com.np/api/epay/main/v2/form",
secret: "8gBm/:&EnhH.1/q",
};
// Route to initiate payment
app.post("/initiate-payment", async (req, res) => {
const { amount, productId } = req.body;
let paymentData = {
amount,
failure_url: esewaConfig.failureUrl,
product_delivery_charge: "0",
product_service_charge: "0",
product_code: esewaConfig.merchantId,
signed_field_names: "total_amount,transaction_uuid,product_code",
success_url: esewaConfig.successUrl,
tax_amount: "0",
total_amount: amount,
transaction_uuid: productId,
};
const data = `total_amount=${paymentData.total_amount},transaction_uuid=${paymentData.transaction_uuid},product_code=${paymentData.product_code}`;
const signature = generateHmacSha256Hash(data, esewaConfig.secret);
paymentData = { ...paymentData, signature };
try {
const payment = await axios.post(esewaConfig.esewaPaymentUrl, null, {
params: paymentData,
});
const reqPayment = JSON.parse(safeStringify(payment));
if (reqPayment.status === 200) {
return res.send({
url: reqPayment.request.res.responseUrl,
});
}
} catch (error) {
res.send(error);
}
});
const crypto = require("crypto");
/**
* Generates a Base64-encoded HMAC SHA256 hash.
*
* @param {string} data - The data to be hashed.
* @param {string} secret - The secret key used for hashing.
* @returns {string} The Base64-encoded HMAC SHA256 hash.
*/
function generateHmacSha256Hash(data, secret) {
if (!data || !secret) {
throw new Error("Both data and secret are required to generate a hash.");
}
// Create HMAC SHA256 hash and encode it in Base64
const hash = crypto
.createHmac("sha256", secret)
.update(data)
.digest("base64");
return hash;
}
function safeStringify(obj) {
const cache = new Set();
const jsonString = JSON.stringify(obj, (key, value) => {
if (typeof value === "object" && value !== null) {
if (cache.has(value)) {
return; // Discard circular reference
}
cache.add(value);
}
return value;
});
return jsonString;
}
module.exports = { generateHmacSha256Hash, safeStringify };
Running the Application
- Before running the node server include the nodemon package to watch the server everytime the file changes.
npm install nodemon --save-dev
//Update the package.json
{
"name": "server",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "app.js",
"scripts": {
"start": "node app.js",
"dev": "nodemon app.js"
},
"keywords": [],
"author": "",
"license": "ISC",
"dependencies": {
"axios": "^1.7.5",
"body-parser": "^1.20.2",
"cors": "^2.8.5",
"express": "^4.19.2"
},
"devDependencies": {
"nodemon": "^3.1.4"
}
}
2. Run the node server
npm run dev

Integrating eSewa Payment api on frontend
let’s update the PaymentForm.jsx
import React, { useState } from "react";
import axios from "axios";
import { generateUniqueId } from "../utils/generateUniqueId";
const PaymentComponent = () => {
const [amount, setAmount] = useState("");
const handlePayment = async (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
try {
const response = await axios.post(
"http://localhost:3000/initiate-payment", //server payment route
{
amount,
productId: generateUniqueId(),
}
);
window.location.href = response.data.url;
} catch (error) {
console.error("Error initiating payment:", error);
}
};
return (
<div>
<h1>eSewa Payment Integration</h1>
<div className="form-container" onSubmit={handlePayment}>
<form className="styled-form">
<div className="form-group">
<label htmlFor="Amount">Amount:</label>
<input
type="number"
value={amount}
onChange={(e) => setAmount(e.target.value)}
required
placeholder="Enter amount"
/>
</div>
<button type="submit" className="submit-button">
Pay with eSewa
</button>
</form>
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default PaymentComponent;
Create utils folder on the root of the project and generate a file generateUniqueId.js for generating unique id for product
export function generateUniqueId() {
return `id-${Date.now()}-${Math.random().toString(36).substr(2, 9)}`;
}
Conclusion
In Part 1 of this tutorial series, we set up a basic MERN stack application and integrated the eSewa payment gateway. In the next part, we will explore advanced features such as handling payment status callbacks, storing transaction data in MongoDB, serving config from .env file and improving security measures.
Stay tuned for Part 2 where we’ll dive deeper into handling payment confirmations and improving the overall user experience!
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Samir Pokhrel directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Samir Pokhrel
Samir Pokhrel
With a background in computer science and more than 2 years of hands-on experience in the field, I thrive on turning innovative ideas into reality through code. My journey in web development began when I discovered the limitless potential of the MERN stack. In addition to technical skills, I am a strong advocate for collaboration and effective communication. Outside of coding, I enjoy staying updated with the latest web development trends and technologies. I'm a lifelong learner who loves tackling new challenges and embracing emerging tools to enhance my skill set.