Global COVID-19 Vaccination Progress: Analysis, Insights & Recommendations
 Innocent Ezama
Innocent Ezama
Introduction
As part of my journey in data analysis, I explored the global vaccination progress against COVID-19 using data from February 2021 to January 2022. The dataset provided a snapshot of a critical phase in the global fight against the pandemic, when vaccines were being rapidly rolled out to curb the spread of the virus. Now that COVID-19 has been largely dealt with in most parts of the world, this analysis offers insights into how different regions and manufacturers contributed to global vaccination efforts and where we stand today. Additionally, I’ve included a reflective section to assess whether the recommendations based on this analysis were put into effect.
Problem Statement
The primary objective of this project was to analyze vaccination trends to understand which regions and manufacturers played leading roles, identify patterns in daily vaccinations, and provide actionable insights for future pandemics or health crises.
Key Business Questions:
Which countries and regions led the vaccination efforts globally?
How did the rate of daily vaccinations fluctuate over the one-year period?
Which vaccine manufacturers contributed the most, and which were less widely used?
How did vaccination efforts compare across continents?
Data
The dataset used in this analysis, from Our World in Data, covers global COVID-19 vaccinations from February 2021 to January 2022. It provides details on the total number of vaccinations administered in different countries and regions, alongside data from major vaccine manufacturers.
Analysis
To ensure data accuracy, the following steps were taken:
Data Cleaning: Checking for duplicates, handling missing values, and verifying data consistency to ensure accurate and reliable analysis.
Feature Engineering: New columns such as ‘continent’ were created for more insightful analysis.
Data Aggregation: Key variables like total vaccinations by country, continent, and manufacturer were aggregated to enable a high-level view of global trends.
Visualizations & Insights
The analysis revealed several important insights into the global vaccination progress:
Top Vaccinated Countries:
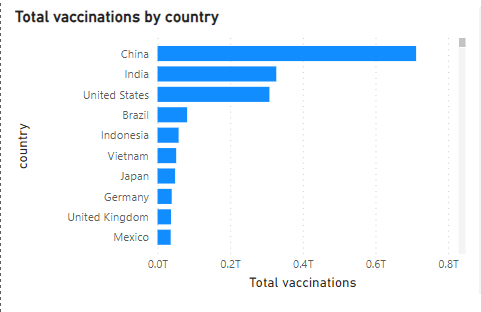
China led the world with the highest number of total vaccinations, followed by India and the United States. Together, these countries administered billions of doses, contributing significantly to global efforts.
Fluctuations in Daily Vaccinations
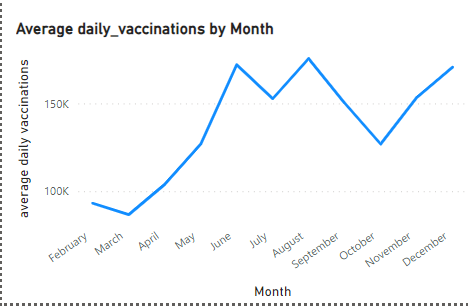
Key periods of rising vaccination rates occurred in June, August, and December 2021. These spikes were likely driven by various factors, including the availability of vaccines, government mandates, and public health campaigns. In contrast, two major decreases in October 2021 and January 2022 were possibly linked to supply chain issues or vaccine hesitancy in some regions.
Vaccination Rates Over Time (Germany vs. US)
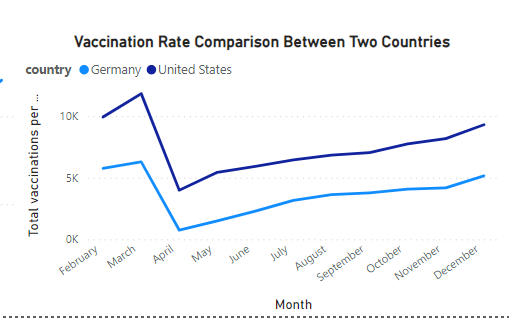
Germany and the US showed similar trends in vaccination uptake, with Germany emerging slightly ahead towards the end of the period. These trends highlight the importance of continuous vaccination drives in countries with large populations.
Vaccinations by Region
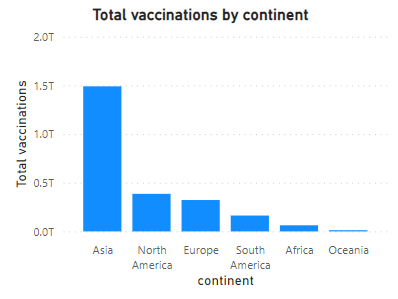
Asia, home to China and India, unsurprisingly had the highest number of vaccinations by a significant margin. This was followed by North America and Europe. Africa and Oceania had the lowest numbers, reflecting unequal access to vaccines during the early rollout phases.
Manufacturer Insights
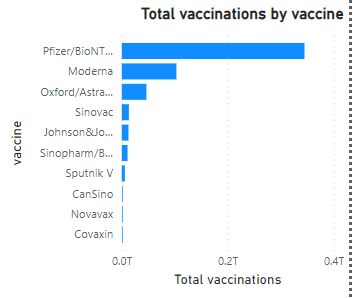
Pfizer was the dominant vaccine globally, followed by Moderna. Lesser-used vaccines such as CanSino, Novavax, and Covaxin were not widely distributed during this period.
Key Findings
China, India, and the US played pivotal roles in global vaccination efforts. Vaccination rates saw substantial increases in mid-2021, particularly in June and December. Europe and North America were among the most vaccinated regions after Asia, while Africa and Oceania lagged behind. Pfizer was the most widely administered vaccine, with Moderna following, but others like CanSino and Novavax saw minimal use globally.
Dashboard
The findings were shared through interactive dashboards and visualizations using Power BI, enabling stakeholders to drill down into vaccination trends by country, region, and manufacturer. Visualizations such as horizontal bar charts and time series graphs helped in clearly communicating the trends.
Recommendations
Based on the insights, several recommendations were made during the analysis period:
Increase Vaccine Availability in Africa and Oceania: Targeted global initiatives were recommended to improve vaccine access in under-vaccinated regions.
Address Vaccine Hesitancy in Specific Periods: Governments were encouraged to deploy public health campaigns, particularly in October 2021 and January 2022, when vaccination rates dipped.
Focus on High-Performing Vaccines: Scaling up production of widely accepted vaccines like Pfizer and Moderna was advised to meet global demand.
Retrospective: Where Recommendations Were Implemented
Vaccine Availability in Africa and Oceania: Despite the recommendation to increase vaccine availability in under-vaccinated regions, the global response was mixed. While efforts like COVAX aimed to distribute vaccines equitably, logistical challenges and limited manufacturing capacity in some areas meant that vaccine distribution remained unequal well into 2022.
Vaccine Hesitancy: Public health campaigns addressing vaccine hesitancy were implemented in several countries, particularly in Europe and North America, leading to increased vaccination rates. However, in some regions, particularly in parts of Africa and South Asia, hesitancy remained a barrier, largely due to misinformation or mistrust in government institutions.
Focus on High-Performing Vaccines: Pfizer and Moderna indeed ramped up production and were central to vaccination drives in most parts of the world. However, some countries, especially those with limited financial resources, had to rely on vaccines like AstraZeneca, which were more affordable.
Conclusion
This analysis provided valuable insights into the global COVID-19 vaccination efforts during a crucial period. While the world has largely moved past the pandemic, the lessons learned from this time will remain relevant for managing future global health crises. The analysis highlighted key areas of success, such as the rapid scaling of vaccination efforts in countries like China, India, and the US, as well as areas where more effort is needed, such as ensuring equitable vaccine access across all regions.
Recommendations for the Future
Strengthen Global Vaccine Distribution Networks: Future pandemics will require even more coordinated efforts to ensure vaccines reach all corners of the globe quickly and equitably.
Combat Vaccine Hesitancy: Building trust in vaccines through continuous education and transparent communication is crucial for increasing uptake in times of crisis.
Prioritize High-Performing Vaccines Early: Governments and manufacturers should focus on scaling the production of vaccines that are both effective and widely accepted. By taking these lessons into account, the world can better prepare for the next global health emergency and ensure a more resilient response.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Innocent Ezama directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Innocent Ezama
Innocent Ezama
Data Analyst| Data Scientist | Technical Writer | Seeking Opportunities to Drive Impactful Solutions in Tech