Python Dictionaries Explained: Day 5 Tutorial
 Archana Prusty
Archana Prusty
Introduction:
Welcome to Day 5 of my Python journey!
Today, I explored the fascinating world of data structures in Python, specifically dictionaries. These data types are crucial for storing and manipulating complex data.
Dictionary predefine class / data type / data structure
- \ dict () → dictionary*
dict () is predefine class.
len () is used to get length of dictionary class .
help (dict) is used to get manual about dictionary class .
dict collection of pair of elements ( key & value ), but don’t divided with :
dict elements can be represent with in {} .
it is a iterable object .
it is a immutable object (hashable) .
it is mapping object .
key cannot be duplicate if duplicate it overwrite with last value but value may be duplicate.
definition using class:
key can be all immutable object like (int, float, complex, none, bool, str, tuple & frozenset)
but value can be all types.
Index/key :
dictionary does not support index, it supports key.
key is used to get value inside dictionary & update value inside dictionary
invalid key return keyError
Dictionary predefine class:
predefine function :
all predefine functions only works with keys.
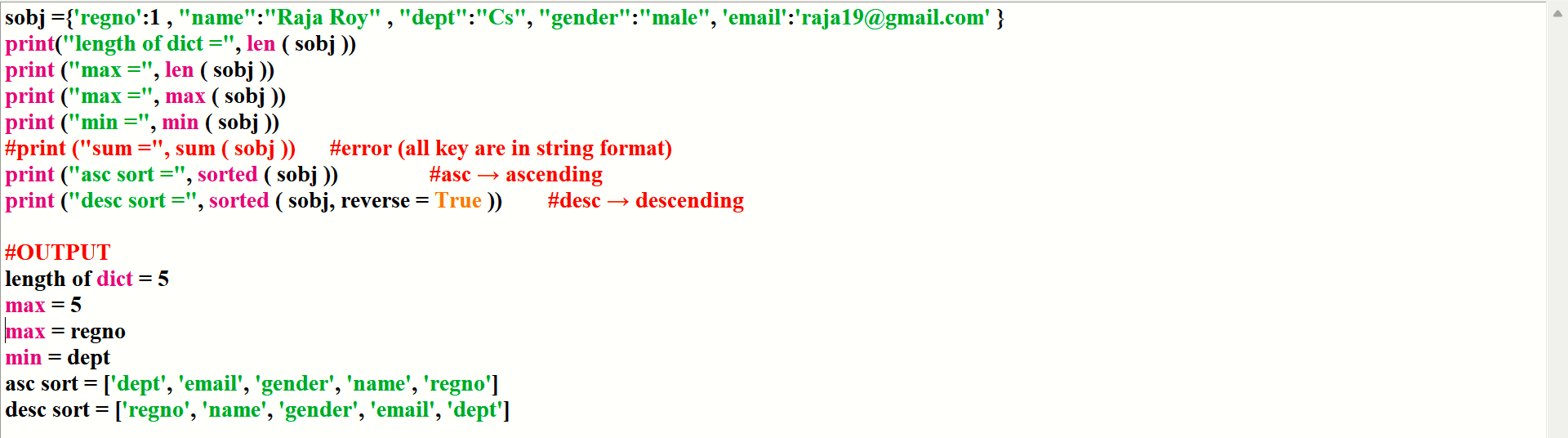
example:-
sobj ={'regno':1 , "name":"Raja Roy" , "dept":"Cs", "gender":"male", 'email':'raja19@gmail.com' }
print("length of dict =", len ( sobj ))
print ("max =", len ( sobj ))
print ("max =", max ( sobj ))
print ("min =", min ( sobj ))
#print ("sum =", sum ( sobj )) #error (all key are in string format)
print ("asc sort =", sorted ( sobj )) asc → ascending
print ("desc sort =", sorted ( sobj, reverse = True )) desc → descending
predefine method:
get() : return value of given key
keys() : return list of all key
values() : return list of all values
items () : return pair of elements
pop() : remove value from dict of given keys
popitem() : remove pair of element (key:value) from last position
setdefault() : add a new key in a dict without value
update() : update value
clear() : delete all element from dict
copy() : move a shallow copy
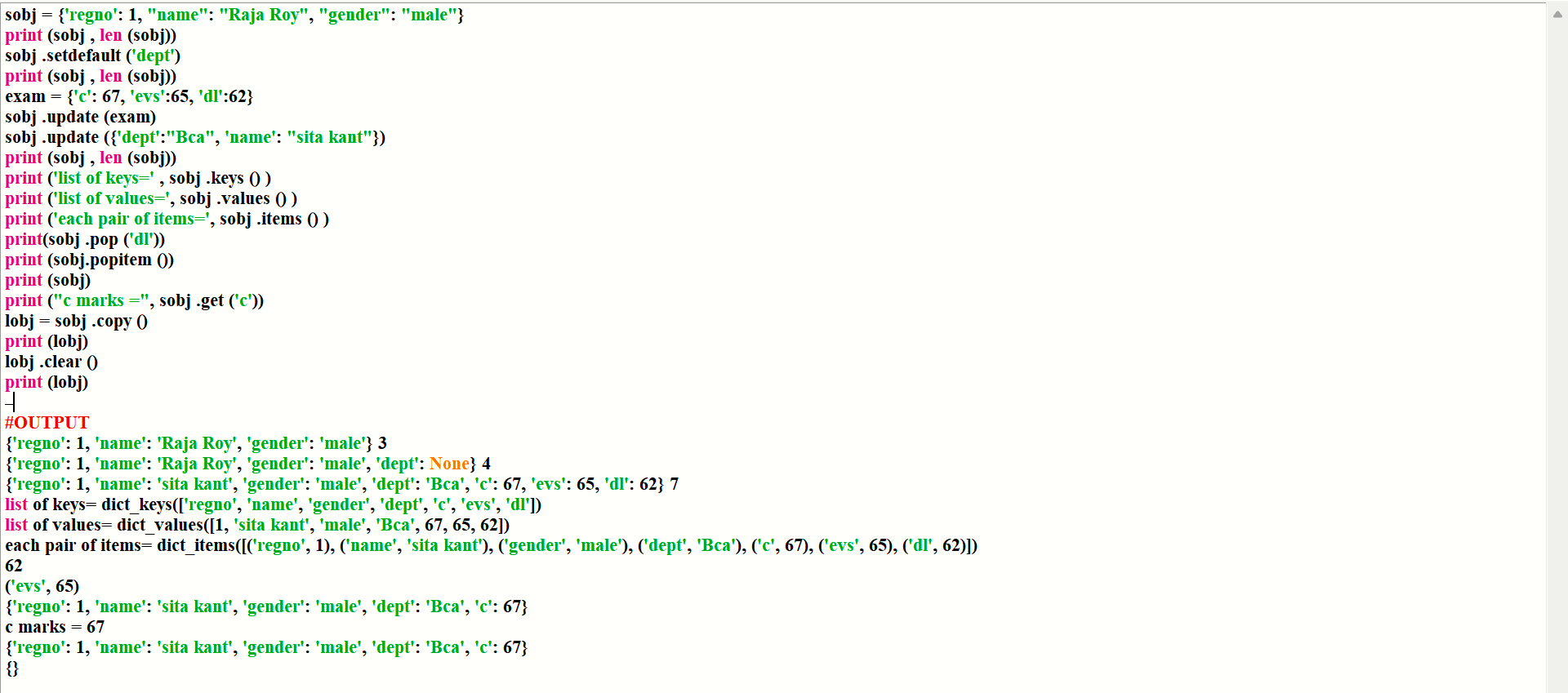
example:-
sobj = {'regno': 1, "name": "Raja Roy", "gender": "male"}
print (sobj , len (sobj))
sobj .setdefault ('dept')
print (sobj , len (sobj))
exam = {'c': 67, 'evs':65, 'dl':62}
sobj .update (exam)
sobj .update ({'dept':"Bca", 'name': "sita kant"})
print (sobj , len (sobj))
print ('list of keys=' , sobj .keys () )
print ('list of values=', sobj .values () )
print ('each pair of items=', sobj .items () )
print(sobj .pop ('dl'))
print (sobj.popitem ())
print (sobj)
print ("c marks =", sobj .get ('c'))
lobj = sobj .copy ()
print (lobj)
lobj .clear ()
print (lobj)
Challenges:
Understanding list comprehension.
Handling dictionary key errors.
Resources:
Official Python Documentation: Data Structures
W3Schools' Python Tutorial: Dictionaries
Scaler’s Python Course: Data Structures
Goals for Tomorrow:
- Explore sets and frozensets.
Conclusion:
Day 5 was a blast! Dictionaries are now under my belt.
What are your favorite data structures in Python? Share in the comments below.
Connect with me:
LinkedIn: [https://www.linkedin.com/in/archana-prusty-4aa0b827a/]
GitHub: [https://github.com/p-archana1]
Join the conversation:
Share your own learning experiences or ask questions in the comments.
Next Post:
Day 6 : Sets, Frozensets .
Happy Learning!!
THANK YOU.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Archana Prusty directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Archana Prusty
Archana Prusty
I'm Archana, pursuing Graduation in Information technology and Management. I'm a fresher with expertise in Python programming. I'm excited to apply my skills in AI/ML learning , Python, Java and web development. Looking forward to collaborating and learning from industry experts.