Load Balancing: Why It’s Essential for Your Network
 Armaan Singh
Armaan Singh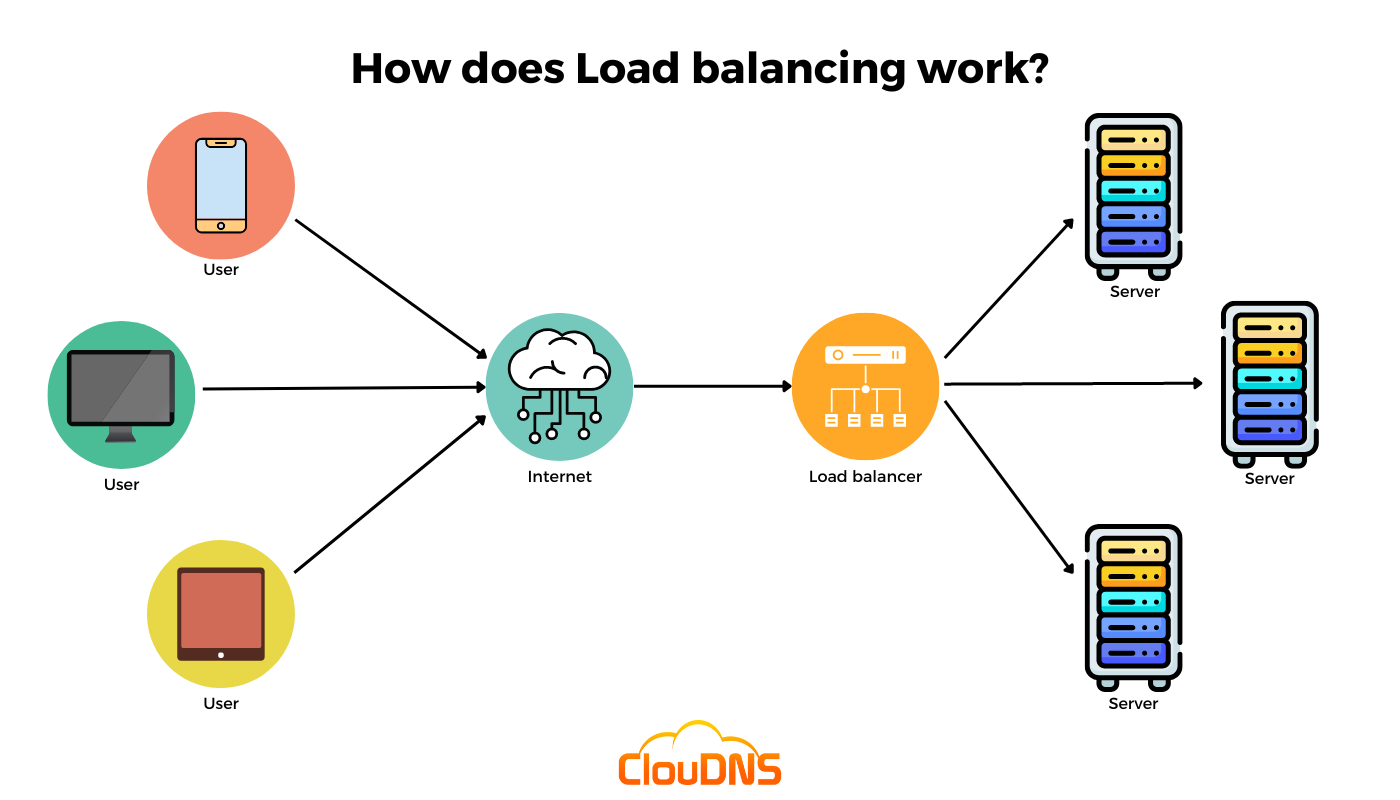
Load balancing is a process that evenly distributes network or application traffic across multiple servers.
Why to use:
Distributes Traffic: Load balancers spread incoming traffic (such as user requests) across multiple servers.
Prevents Overload: By distributing the workload, it prevents any one server from getting overloaded.
Improves Reliability: If one server goes down, the load balancer can redirect traffic to other servers, ensuring continuous service (high availability).
Enhances Performance: It reduces latency and increases the speed of handling requests by optimizing resource use.
How It Works:
Client Request: A user sends a request (like visiting a website).
Load Balancer: The load balancer receives the request and decides which server to send it to.
Server Response: The selected server handles the request and sends the response back to the user.
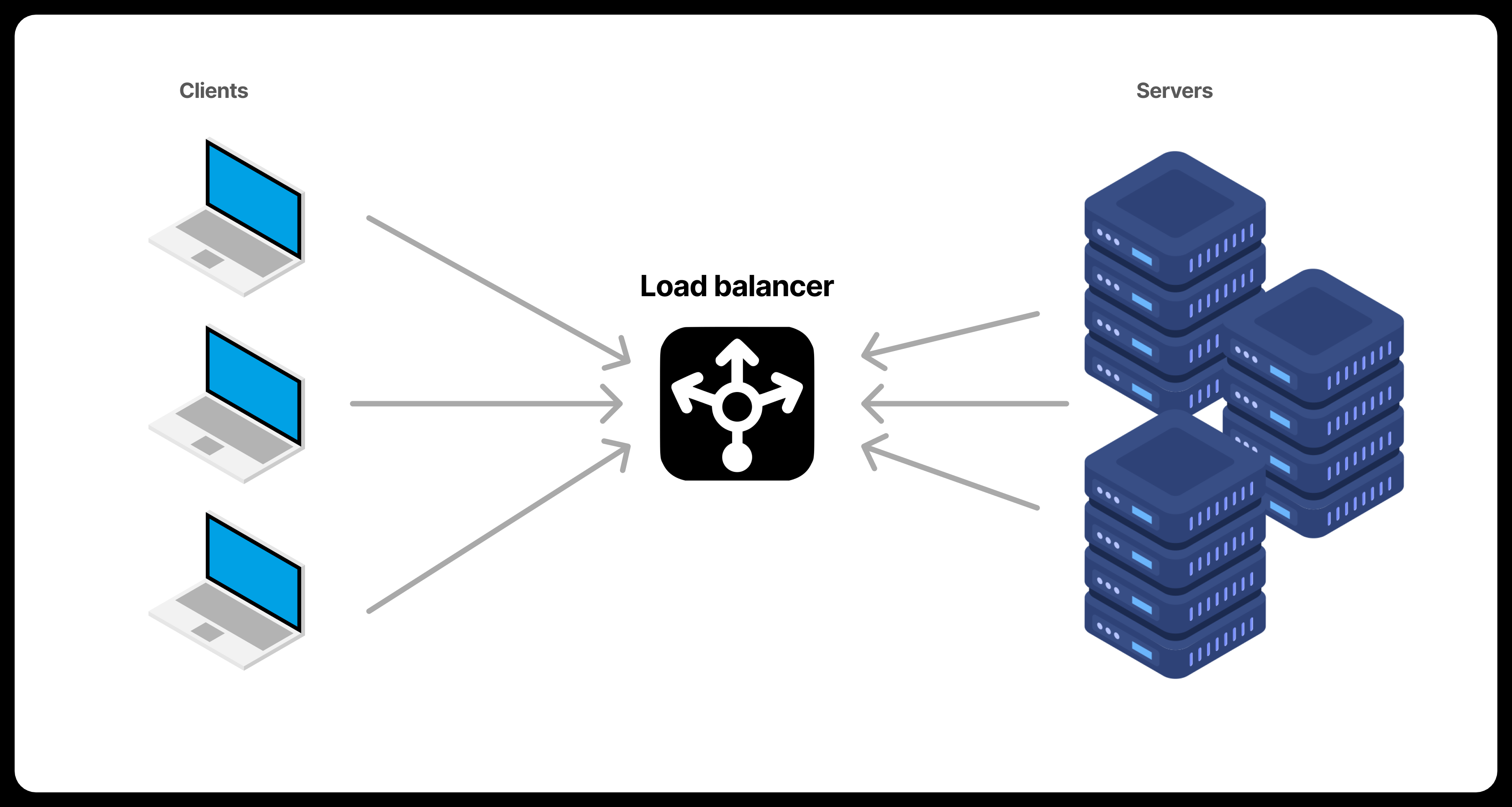
Types of Load Balancing:
Round Robin: Distributes requests sequentially across servers.
Least Connections: Sends traffic to the server with the fewest active connections.
IP Hash: Uses the client's IP address to assign a specific server.
Example:
In a web application, if you have three servers, a load balancer will ensure that when users visit the site, their requests are spread across all three servers instead of one being overworked.
In short, load balancing helps maintain the stability, speed, and scalability of systems!
Thanks for reading!
CodeBetter 💻
Stay updated with my articles ....
Connect with me on:
📩 Subscribe to Newsletter, 👨🏻💻 LinkedIn, 🌍 Personal Website, and 📸 Instagram,🎬 YouTube
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Armaan Singh directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Armaan Singh
Armaan Singh
Aspiring Cloud Engineer ☁️ | DevOps Enthusiast 🧑💻 | Top #250 Contributor @GSSoC 🌍 | HTML | CSS | JS | React | C++ | Building Impactful Projects & Solving Real-World Problems 🚀