Streaming data from Kafka to BigQuery using Apache Beam
 Rahul Das
Rahul DasIn this guide, we will walk through the process of reading data from Kafka and storing it in BigQuery using Apache Beam. Apache Beam is a unified programming model for defining both batch and streaming data-parallel processing pipelines.
Prerequisites
Before proceeding, ensure you have the following:
Access to a Google Cloud Platform (GCP) project.
Kafka cluster with accessible bootstrap servers. (Setup Kafka cluster)
BigQuery dataset created within your GCP project.
Basic understanding of Apache Beam.
Step 1: Setup Environment
Ensure you have Python installed on your system along with the necessary libraries. You can install required libraries using pip:
pip install apache-beam[gcp] faker kafka-python
Step 2: Create a Producer
Below code snippet generates fake latitude and longitude data in an infinite loop, and sends this data to configured Kafka topic
import time
import json
import random
from datetime import datetime
from kafka import KafkaProducer
from faker import Faker
faker = Faker()
config = {}
with open("config.json",'r') as f:
config = json.loads(f.read())
# Messages will be serialized as JSON
def serializer(message):
return json.dumps(message).encode("utf-8")
def generate_message():
return {
"timestamp": time.time(),
"latitude": float(faker.latitude()),
"longitude": float(faker.longitude()),
"id": faker.pyint(),
}
# Kafka Producer
producer = KafkaProducer(
bootstrap_servers=[config['KAFKA_HOST']],
value_serializer=serializer
)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Infinite loop - runs until you kill the program
try:
while True:
# Generate a message
dummy_message = generate_message()
# Send it to our 'messages' topic
print(
f"Producing message @ {datetime.now()} | Message = {str(dummy_message)}"
)
producer.send(config["KAFKA_TOPIC"], dummy_message)
# Sleep for a random number of seconds
time_to_sleep = random.randint(1,5)
time.sleep(time_to_sleep)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
producer.close()
Step 3: Understanding the Code
Let's understand the Python code:
The code uses Apache Beam to define a pipeline.
Passing arguments
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument(
"--bootstrap_servers",
dest="bootstrap_servers",
required=True,
help="Bootstrap servers for the Kafka cluster. Should be accessible by "
"the runner",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--topic",
dest="topic",
default="messages",
help="Kafka topic to write to and read from",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--with_metadata",
default=False,
action="store_true",
help="If set, also reads metadata from the Kafka broker.",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--bq_dataset",
type=str,
default="",
help="BigQuery Dataset to write tables to. ",
)
parser.add_argument(
"--bq_table_name",
default="kafka_geo_data",
help="The BigQuery table name. Should not already exist.",
)
known_args, pipeline_args = parser.parse_known_args()
pipeline_options = PipelineOptions(
pipeline_args, save_main_session=True, streaming=True
)
# We also require the --project option to access --bq_dataset
project = pipeline_options.view_as(GoogleCloudOptions).project
if project is None:
parser.print_usage()
print(sys.argv[0] + ": error: argument --project is required")
sys.exit(1)
run(
known_args.bootstrap_servers,
known_args.topic,
known_args.with_metadata,
known_args.bq_dataset,
known_args.bq_table_name,
project,
pipeline_options,
)
Here we accept the arguments passed to the python script such as the
kafka server address
kafka topic
metadata
big query dataset name
big query table name
and pass these arguments to the run() function which will start the apache beam pipeline execution.
Reading messages from Kafka
with beam.Pipeline(options=pipeline_options) as pipeline:
get_col = (
pipeline
| ReadFromKafka(
consumer_config={"bootstrap.servers": bootstrap_servers},
topics=[topic],
with_metadata=with_metadata,
)
| beam.Map(lambda record: convert_kafka_record_to_dictionary(record))
)
A pipeline is created using beam.Pipeline which reads messages from Kafka using the ReadFromKafka transform from the topic passed as argument to the python script. Once the messages are fetched from Kafka next step in the pipeline is to convert the messages to python dictionaries/JSON formatted objects using the convert_kafka_record_to_dictionary. Here the pipeline is stored in a variable get_col
Write data to sink
with beam.Pipeline(options=pipeline_options) as pipeline:
get_col = (
pipeline
| ReadFromKafka(
consumer_config={"bootstrap.servers": bootstrap_servers},
topics=[topic],
with_metadata=with_metadata,
)
| beam.Map(lambda record: convert_kafka_record_to_dictionary(record))
)
if bq_dataset:
schema = "latitude:STRING,longitude:STRING,id:INTEGER"
if with_metadata:
schema += ",timestamp:STRING"
_ = get_col | beam.io.WriteToBigQuery(
bq_table_name, bq_dataset, project, schema
)
Next step in pipeline is to write the processed data in Big Query, using the beam.io.WriteToBigQuery connector. In this step data will be written to the Big Query table inside the specifed dataset passed in arguments, before starting the pipeline table does not exists, once the pipeline execution starts it will create table according to the message schema.
Step 4: Run the Code
Execute the script with required arguments on local or a GCP VM to build and submit the job to GCP DataFlow
note Make sure docker enginer is installed and running on machine before executing the script
Ensure to replace placeholders <...> with actual values.
python script.py \
--bootstrap_servers=<KAFKA_BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS> \
--topic=<KAFKA_TOPIC> \
--with_metadata \
--bq_dataset=<BIGQUERY_DATASET> \
--bq_table_name=<BIGQUERY_TABLE_NAME> \
--project=<GCP_PROJECT_ID> \
--runner DataflowRunner \
--region <region> \
--worker_zone <region> \
--staging_location gs://<staging-bucket>\
--temp_location gs://<staging-bucke>/temp \
--job_name kafka-streaming
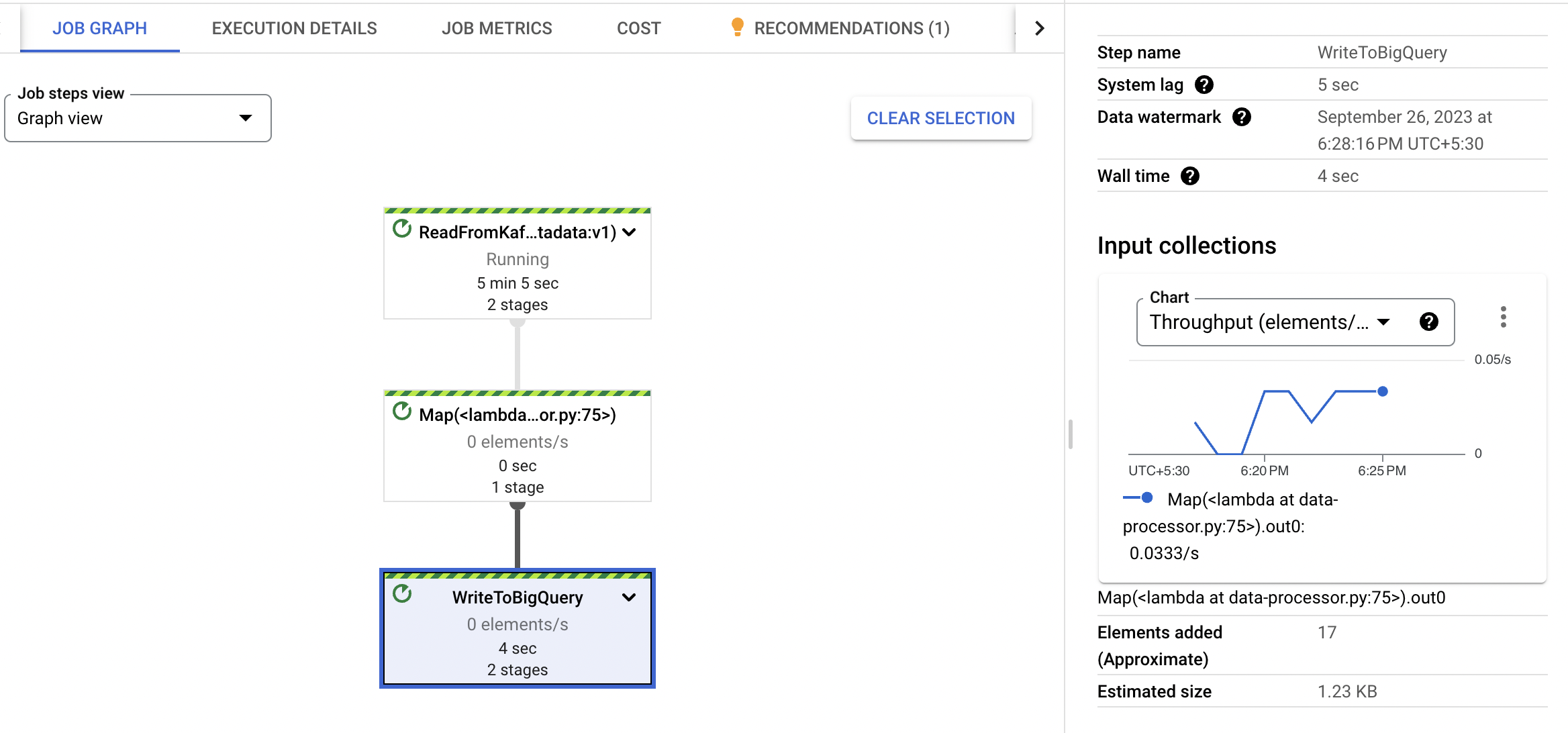
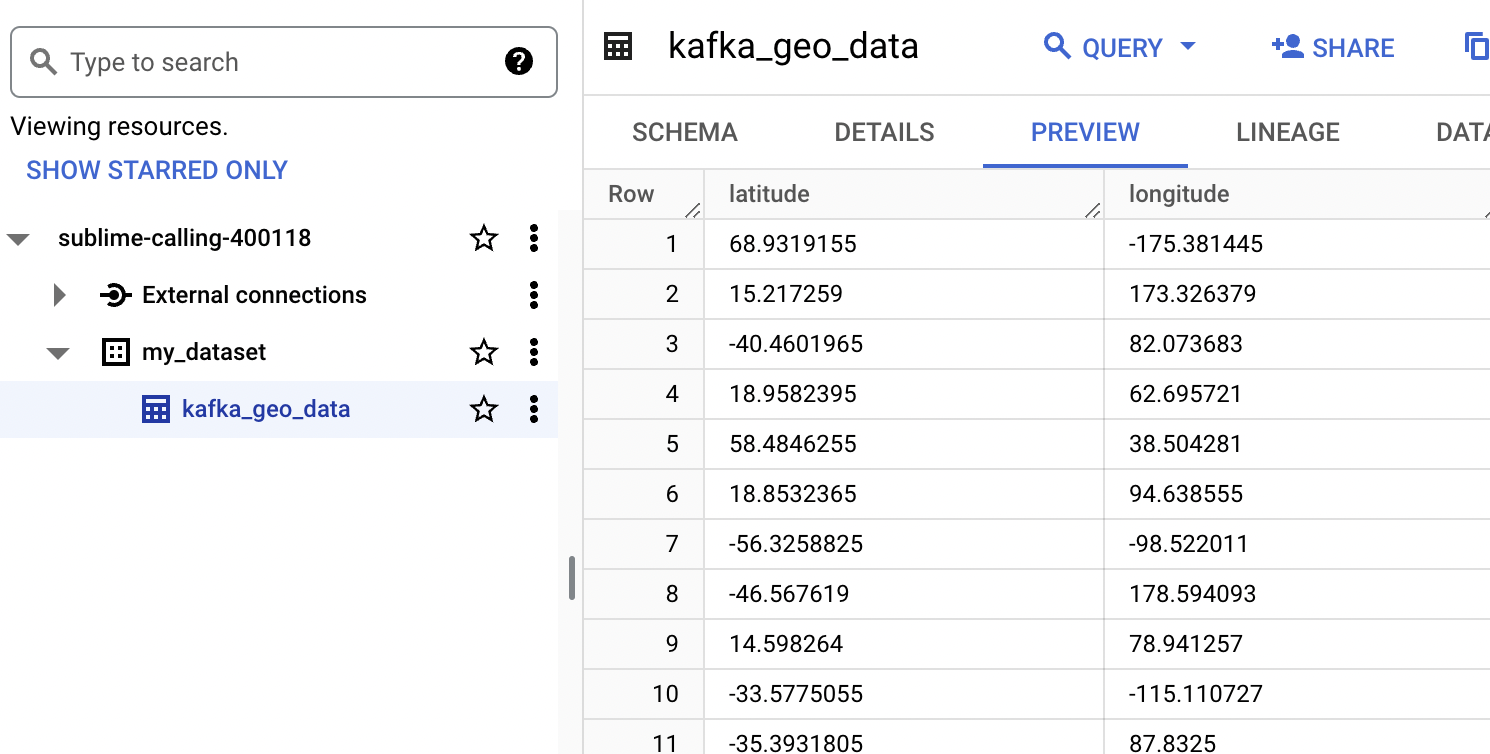
Step 5: Monitor Data Flow
Once the script is running, monitor the execution in the Dataflow section of the GCP console.
Check BigQuery for the data being written to the specified dataset and table.
Conclusion
This guide explained how to use Apache Beam to read data from Kafka and store it in BigQuery. You can further customise the pipeline according to your specific requirements and integrate additional data processing steps if necessary.
Github link for project code
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Rahul Das directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
