CSS Transitions
 dheeraj koranga
dheeraj korangaCSS transitions enable smooth changes to CSS property values over a specified duration, rather than having the changes happen instantly. This allows for more dynamic and visually appealing animations on a webpage.
Basic Syntax of CSS Transitions
The transition property is used to define which CSS properties should transition, the duration of the transition, the timing function, and any delay./* Transition Syntax */
/* Transition Syntax */
element {
transition: property duration timing-function delay;
}
div {
background-color: black;
height: 300px;
width: 300px;
border: 2px red solid;
transition: 2s;
}
div:hover{
background: red;
margin: 200px;
}
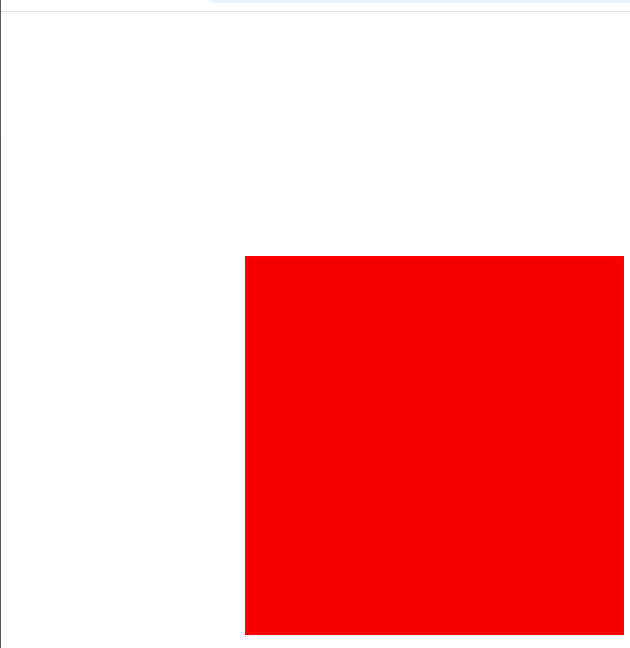
- On hovering it will move from left to right
Transition Shorthand
The transition shorthand property allows you to specify multiple transition properties in one line. The order of values is important:
Property: The CSS property to animate (e.g.,
width,background-color).Duration: The time the transition takes (e.g.,
2s,500ms).Timing Function: Defines the speed curve of the transition (e.g.,
ease,linear,ease-in,ease-out).Delay: The time before the transition starts (e.g.,
1s,200ms)
/* Transition Syntax */
element {
transition: property duration timing-function delay;
}
div{
transition: margin 2s ease-in 0.2s;
}
1. CSS Transform
CSS transforms allow you to move, rotate, scale, or skew elements without disturbing the document flow. Transforms work on 2D and 3D space.
Common Transform Functions:
rotate():Rotates an element clockwise or counterclockwise by a specified angle.
The value is in degrees (
deg), radians (rad), or turns (turn).
div {
background-color: black;
height: 300px;
width: 300px;
margin: 100px;
border: 2px red solid;
transform: rotate(45deg);
}
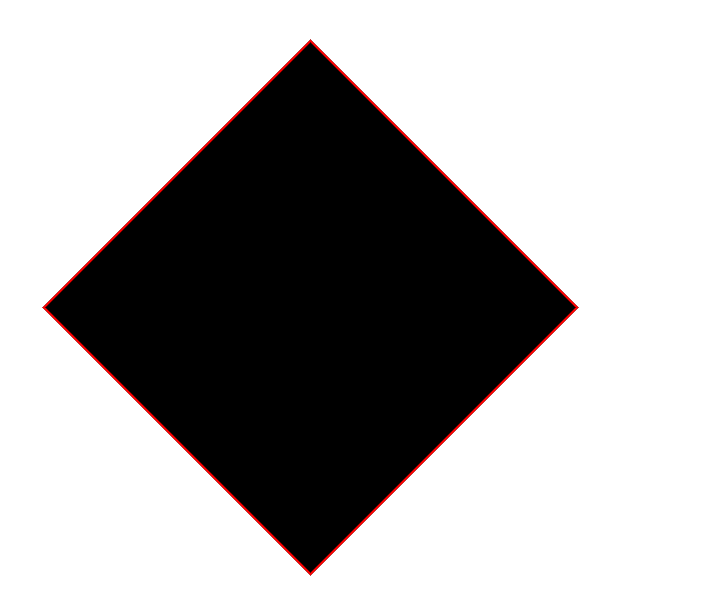
scale():
Scales an element up or down along the X and/or Y axis.
The value is a multiplier:
1means no scaling,0.5means 50% of the original size, and2means 200% of the original size.
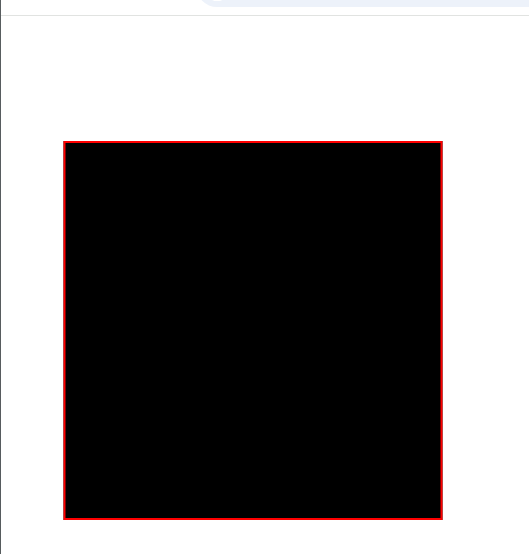
div {
background-color: black;
height: 300px;
width: 300px;
margin: 100px;
border: 2px red solid;
transform: scale(0.5,0.2);
}

translate():Moves an element from its current position by the specified X and Y values.
The values are in length units (
px,em,%, etc.).
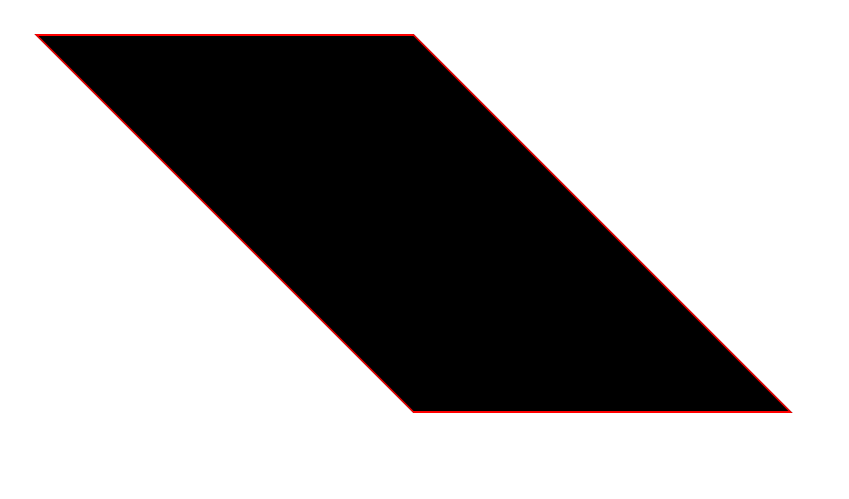
skew():Skews an element along the X and/or Y axis.
The value is in degrees and creates a slanting effect.

Using Transitions with Transforms
We can combine CSS transitions with transforms to create smooth animations.div {
div {
background-color: black;
height: 300px;
width: 300px;
border: 2px red solid;
transition: transform 2s ease-in 0.2s;
}
div:hover{
background: red;
margin: auto;
transition: skew(30deg) scale(1.2);
}
Summary of Key Concepts
Transition: Allows smooth changes to property values.
Shorthand:
transition: property duration timing-function delay;Common timing functions:
ease,linear,ease-in,ease-out,steps(n)
Transform: Allows manipulating elements with functions like
rotate(),scale(),translate(), andskew().Transform + Transition: Use them together to create animations like hover effects and dynamic changes.
These properties are essential for building visually dynamic and interactive web experiences.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from dheeraj koranga directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
