Unlocking AWS Cloud Essentials and Fundamentals ☁️
 sravani punreddy
sravani punreddy
In today’s tech-driven world, the cloud has become a pivotal solution for businesses of all sizes. Here’s a quick breakdown of AWS Cloud Essentials to help you understand why cloud computing is the future and how it operates:
What is Cloud & Why Do You Need It?
Cloud computing provides on-demand access to computing resources over the internet, eliminating the need for physical hardware. Instead of investing in costly infrastructure, businesses can scale resources up or down as needed, paying only for what they use. It offers cost-efficiency, scalability, and flexibility, making it essential for innovation and agility.
How Does Cloud Work?
Cloud works by hosting data, applications, and services on remote servers managed by cloud service providers. These servers communicate over the internet to deliver data to users and applications securely and quickly. AWS offers a range of cloud services like computing power (EC2), storage (S3), and databases (RDS), accessible via a web interface or APIs. You can think of cloud computing as renting server space and services remotely instead of owning and maintaining hardware on-premise.
Why AWS?
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a leader in cloud computing for several reasons:
Vast Services: AWS offers over 200 fully-featured services from data centers globally.
Scalability: Whether you're a startup or an enterprise, AWS can grow with your needs.
Security: AWS is designed to be one of the most secure cloud environments, offering data encryption, compliance, and real-time threat detection.
Cost-Effectiveness: With pay-as-you-go pricing, AWS allows businesses to avoid up-front capital expenses and long-term commitments.
Ruling Cloud Gains: A Comparative Analysis of Market Trends from 2023 to 2024
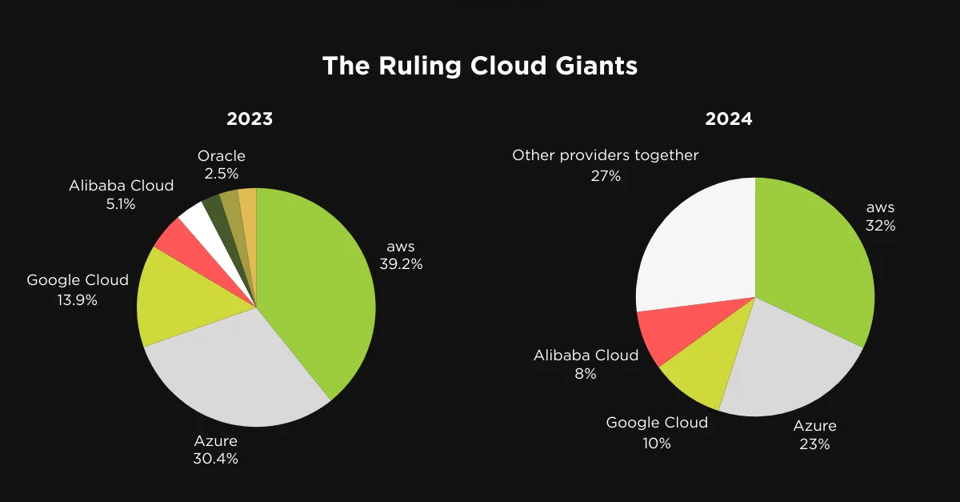
The cloud computing landscape is continuously evolving, driven by advancements in technology, shifting business requirements, and widespread adoption across various industries. As we analyze the projected market shares for cloud service providers (CSPs) in 2024, it is essential to compare these forecasts with the actual market state in 2023. This analysis provides valuable insights into the trends that are shaping the future of cloud computing.
Current Market Overview (2024)
As of 2024, the cloud market is characterized by the following major players:
Amazon Web Services (AWS): 32%
Microsoft Azure: 23%
Google Cloud: 10%
Alibaba Cloud: 8%
Others: 27%
AWS was the clear leader, with a substantial market share, followed closely by Azure and Google Cloud. The overall market was less fragmented, with fewer players capturing the total share.
Types of Servers (On-premises, Hybrid, Public/Private Cloud)
On-Premise: Traditional data centers where companies host servers locally. While offering control, it’s expensive and limited in scalability.
Hybrid Cloud: A mix of on-premise and cloud solutions, allowing businesses to store sensitive data on-site while using the cloud for other services.
Public Cloud: Cloud infrastructure offered by providers like AWS, accessible to multiple customers over the internet.
Private Cloud: Exclusive cloud infrastructure for one organization, ensuring privacy and control, either on-premise or hosted by a third-party provider.
AWS Global Infrastructure:
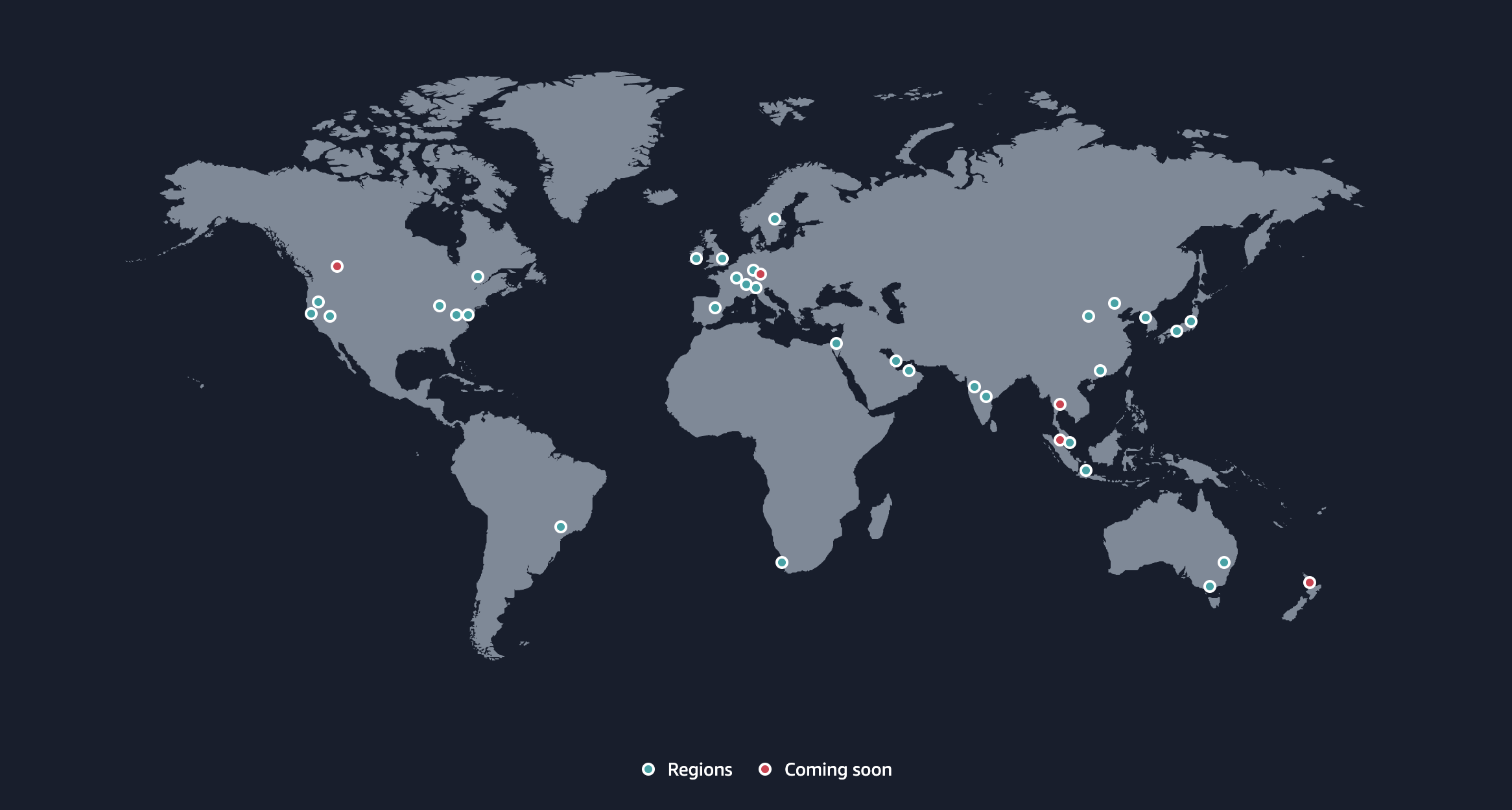
AWS is powered by a global network of data centers strategically located around the world to ensure low-latency, fault tolerance, and high availability.
Regions: A Region is a physical geographic area where AWS has clusters of data centers. These regions allow customers to deploy applications and store data closer to their end users, reducing latency and improving performance. Each AWS region is isolated from other regions to ensure data sovereignty and to meet compliance regulations.
AWS regions have atleast 3 AZs, ensuring fault tolerance, disaster recovery, and continuous uptime.
Availability Zones (AZs):
Within each AWS Region, there are Availability Zones (AZs). An AZ is a separate physical data center with independent power, cooling, and networking infrastructure. By spreading services across multiple AZs, AWS ensures high availability, fault tolerance, and disaster recovery.
Example: If you deploy your application across multiple AZs within a region, even if one AZ faces a failure (e.g., a power outage), your application can still run smoothly from the other AZs.
Global Reach: AWS has 34 geographic regions worldwide, with 108 Availability Zones, providing global coverage and secure access to its cloud services. 🌍
💡 AWS enables businesses to innovate faster, scale efficiently, and reduce IT costs while delivering robust security and reliability. If you're exploring cloud computing or want to take your first step into AWS, it’s time to dive in!
#AWS #CloudComputing #CloudEssentials #GlobalInfrastructure #CloudJourney
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from sravani punreddy directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
