AWS IAM for beginner's
 Aman Shaikh
Aman ShaikhThis is a core AWS service that helps us provide/control access to the AWS resources
Resources are the entities that you create in AWS , e.g. S3 bucket , Lambda function, etc.
Users attempt to perform action on this resources , e.g. Create S3 bucket
Now if the user has an authorization to perform the action on that resources is determined by a policy
Policy is basically a Json file , that have entries such as user has access to which resources
Now each user has its separate policy file
How many ways you can login to AWS and how does AWS knows which policy do you have ?
When we login AWS using console gives a prompt to login with IAM user :
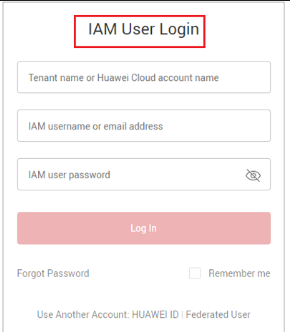
This way here AWS knows what is the policy attached to the user who is logging in
Using AWS CLI
Using AWS SDK
Now in either of the 3 cases AWS needs to know who are you and what are the policies attached to you/ what are the resources you can access, so how does AWS do that ?
This pretty clear for the #1 step that is using console , since you are providing user name and password, so AWS knows who you are and what are your polices
Now if you try to access it programmatically(Using AWS CLI or AWS SDK) how can AWS know it's you ?
Here comes the concept of Access keys and Secret Access keys
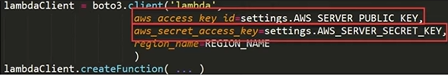
When you try to create your IAM user , AWS will give you 2 strings ,i) Access key ii) Secret access key
Now when you try to use AWS from CLI , you first need to configure it using "aws configure" command
It will ask you for your Access Key and Secret Access Key, then from this keys AWS will know who you are and what are yours policies/what are the resources you can access
If you want to access AWS using any programming language like Python, Java, etc. you can use AWS SDK for that .
Now this is similar to the AWS CLI you will need to enter access key and secret access key, so that AWS knows who you are and what are your policies
Eg: If you want to use it in Python ,you can use it using boto3 lib that python has for AWS SDK
Some other Imp concepts related to IAM :
- Okay Apart from this you can also attach the policy to a group, so if you add some one in that group he automatically gets that policy to him
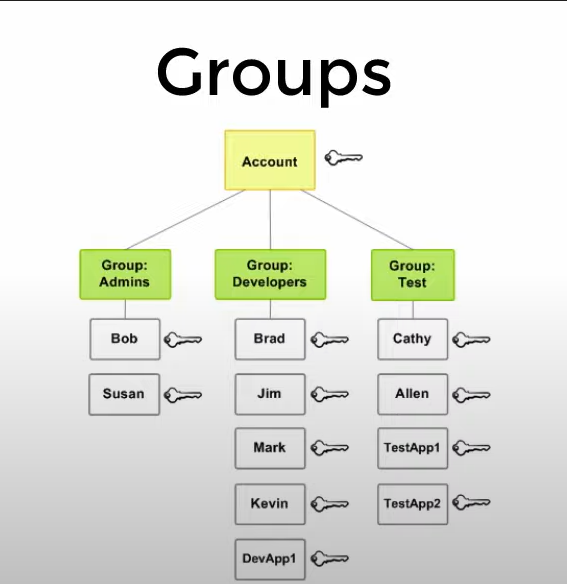
Groups cannot contain groups, but a single user can be in multiple groups
Roles :
In this we can give temporary access to either person or service
It can be given to a person to access something temporarily
It can also be given to a Lambda function or other services
Roles also have policy attached to them
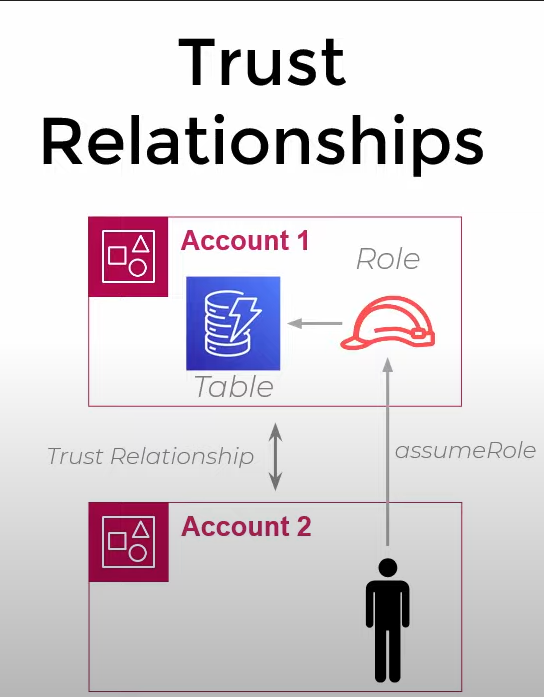
Trust Relationships:
Suppose in the same company you have 2 AWS accounts
In Acc1 there is one DynamoDB table and you are in Acc2 and want to access that table in Acc1 programmatically.
In this case we have to create a Role in Acc1 which will give us a temporary access to Acc1 and will have the policy to access that specific table
Then we attach this role to our user (assumeRole)
Tips is learnt :
Protect your root account , whatever you want to do create a user and do it
Give the minimal policies needed to do the tasks
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Aman Shaikh directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
