"Round Lens, Square Shot: Why Phone Cameras Capture Rectangular Images"
 Ayan
Ayan
When you look at the back of your smartphone, you'll often notice a small, circular lens housing the camera. Yet, when you take a picture, the resulting image is rectangular. This raises an interesting question: why do phone cameras have circular lenses if the images they produce are rectangular? The answer lies in a combination of optics, sensor design, and practical engineering choices that optimize the camera’s functionality.
The Role of Circular Lenses in Camera Optics
Camera lenses, including those on smartphones, are typically circular because of the way light behaves. Lenses are designed to focus light onto a sensor, and circular lenses are the most efficient shape for collecting light from all directions. The shape also allows the lens to focus light more uniformly onto the sensor, reducing optical aberrations that could distort the image.
Light enters the lens in all directions, and the curvature of the lens ensures that the rays of light are bent and focused onto a single point on the camera sensor. Since light travels in waves, and lenses deal with bending these waves, the most efficient and symmetrical way to manage this process is with a circular lens.
The Sensor: Rectangular by Design
Once the light passes through the lens, it needs to hit the camera’s sensor, which is the digital equivalent of photographic film. Most camera sensors are rectangular because this shape is practical for how images are displayed and used. Screens, print formats, and digital files generally use a rectangular aspect ratio, so it makes sense for the camera’s sensor to match this format.
Sensors are made up of millions of tiny pixels arranged in a grid, and it's easier to manufacture and work with rectangular sensors. The rectangular shape also aligns better with most modern display screens, which are also rectangular (such as TVs, monitors, and phone screens).
Why Not Use a Circular Sensor?
In theory, a circular sensor could capture light from the circular lens more efficiently, but in practice, there are several reasons why rectangular sensors are preferred:
Standardization: Rectangular sensors align with the rectangular aspect ratios used by almost all modern display devices. Whether it's 4:3, 16:9, or 3:2, these are all rectangular formats, and using a rectangular sensor ensures compatibility with these standards.
Cost and Simplicity: Manufacturing rectangular sensors is more cost-effective. A circular sensor would require a unique design, making it more expensive to produce. Additionally, rectangular sensors allow for more efficient use of space within the camera module, as they can fit neatly into a phone’s body.
Efficient Use of Data: A circular sensor would capture data around the edges that would typically be cropped out to display the image on a rectangular screen. This would lead to wasted data, increasing the processing and storage requirements without adding any benefit to the final image.
The Image Capture Process
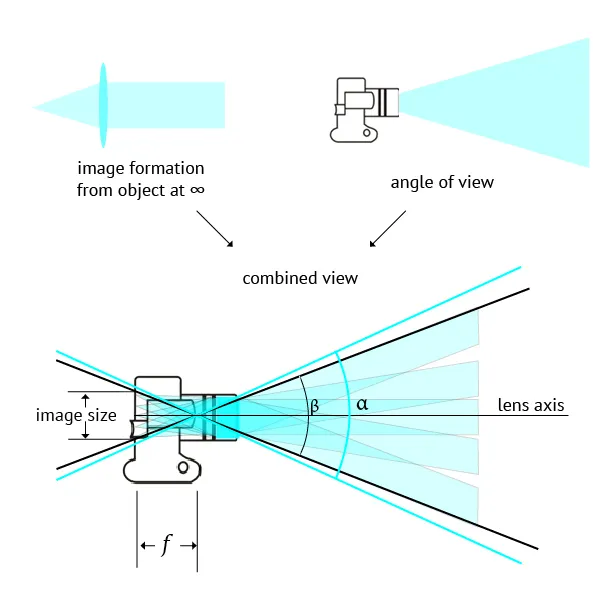
When a photo is taken, the circular lens gathers light and projects it onto the rectangular sensor. The sensor only captures the rectangular portion of the image that fits within its boundaries. While the lens captures a circular image (with light falling in a circular pattern), the camera's sensor only registers the portion that fits inside the rectangle. The areas outside the rectangle aren't captured, but they don't add anything necessary to the image, as they would either contain distorted light or be less useful for creating a clear picture.
A Practical Example: Cropping the Circle
Imagine shining a flashlight through a circular hole onto a flat surface. The beam of light is circular, but if you place a rectangular frame over it, only the part of the light that falls inside the frame is visible. The edges of the beam outside the frame are essentially discarded. The same principle applies to how the phone camera works. The circular lens projects light onto the sensor, and the sensor only records the part of the light that fits within its rectangular grid.
Engineering Balance: Circular Lens + Rectangular Sensor
Using a circular lens with a rectangular sensor strikes a balance between optical efficiency and the practical need to display rectangular images. This design allows cameras to capture high-quality images while maintaining compatibility with the devices we use to view and share them.
Conclusion
The reason phone cameras use circular lenses but produce rectangular images lies in the efficient design of both optical and digital components. Circular lenses capture and focus light more effectively, while rectangular sensors and image formats align with how we view and use photos in the real world. This blend of engineering choices ensures that phone cameras can provide high-quality images in a format that's easy to use, display, and share.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Ayan directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Ayan
Ayan
"I post blogs here in a simple way, so that a 5-year-old can read and understand them."