Virtualization in DevOps /How it helps/ Benefits and Challenges of Virtualization/ Day-2 / #DevopsLearning
 Pinnapareddigari Lasya priya
Pinnapareddigari Lasya priya
What is Virtualization?
Virtualization is the process of creating several virtual systems on a single server. This practice maximizes a physical machine’s capacity by distributing its resources between multiple users and environments.
DevOps teams use virtualization to create virtual machines (VMs), emulations of hardware and software configurations. Each VM has an operating system and acts as an independent computer even though it runs on a portion of the physical device. A virtual machine mimics all components of a computer, including:
CPU.
RAM.
Storage.
Networks.
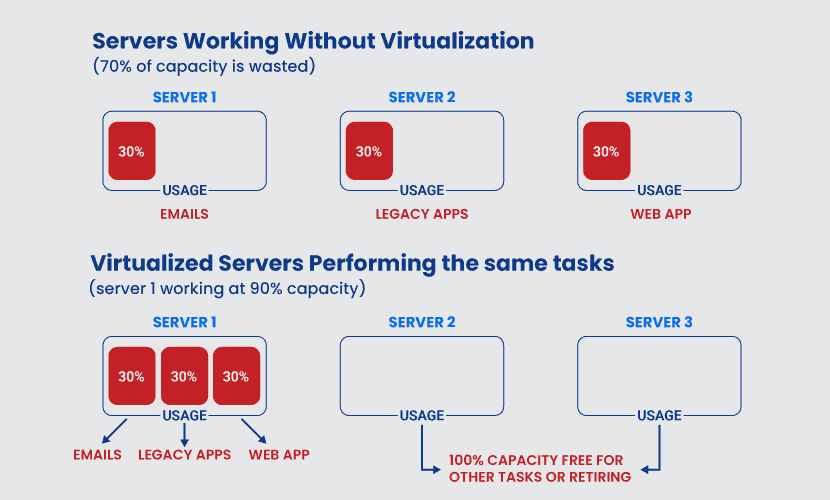
With virtualization, a piece of hardware can host numerous VM configurations simultaneously without performance issues. The main benefits of virtualization are:
More computing capabilities with fewer resources.
Running multiple independent systems on a single hardware.
Consistent environments throughout the continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) process.
DevOps teams use a hypervisor to manage virtual machines. A hypervisor, or a Virtual Machine Monitor (VMM), is a piece of software, firmware, or hardware that creates and runs VMs. The most popular VMMs are:
VMWare (ESXi).
AWS XEN.
Microsoft Hyper V.
Antsle OS.
Oracle VM Server.
POWER Hypervisor.
The hypervisor runs on top of a physical dedicated server or an operating system to emulate the underlying hardware.
Virtualization relies on cloud computing to ensure optimal performance at all times. Cloud allows a VM to scale up or down on-demand and in a matter of minutes to meet resource requirements.
How Does Virtualization Help DevOps?

Virtualization is a vital part of the DevOps software stack. Virtual machines allow a team to build, test, and deploy code within simulated environments without wasting computing resources. The benefits of virtualization include:
More agility, flexibility, and scalability during development.
Cost savings across the SDLC, primarily in terms of maintenance and testing.
Faster workloads and environment setups make the team more productive.
Virtualization in DevOps is essential in the development of complex cloud, API, and SOA systems. VMs are ideal for test-driven development (TDD) teams that prefer to start their bug hunt at the API layer.
DevOps and Virtualization: Benefits:
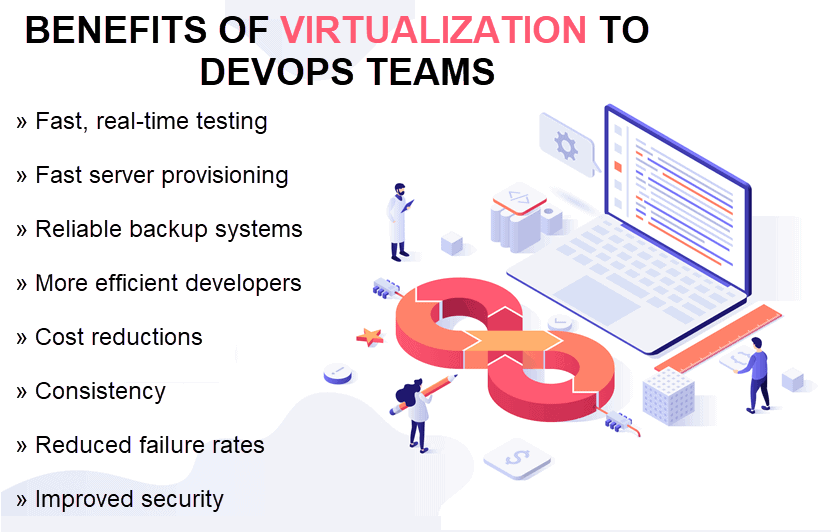
Faster and Better Real-Time Testing
Virtualization also allows development to happen alongside real-time testing. Real-time testing leads to:
High levels of accuracy.
Reduced deployment times.
Increased product stability.
The team can confidently check the effect of every new change in real-time and discover production defects early in the lifecycle. Using VMs for testing also reduces the time for retesting and rebuilding for production.
Fast Server Provisioning
Physical serves require time to set up. An operator must assemble a server, fit it on a rack, set it up, and place it into operation.
With virtualization, all an admin needs to do is assemble the virtual machine and transfer it to the target system. If necessary, this process can be automatic.
Faster and Easier Backup Systems
A loss of integrity or server data typically leads to data losses for most companies. With virtualization, however, a team can set up automatic data backups that occur every minute.
Virtualization features snapshots, complete images of virtual computer systems developers can reliably restore on any hardware.
More Efficient Teams
Whenever a team requires additional resources or environments, engineers can deploy a VM in a matter of minutes. Virtual instances are also flexible and scalable, so teams can do more with less while decision-makers can rely on efficient IT planning.
Virtualization providers keep the VM hardware and software up to date. There is no need for local updates or management, which allows DevOps teams to focus on other areas of the CI/CD. Experts estimate that a team saves between 50 and 60% on total productivity with virtualization.
A DevOps team can easily share and use virtual assets, allowing more efficient parallel development.
Cost Reductions
Virtualization saves money across the DevOps pipeline as:
Testing becomes cheaper.
The team no longer relies on environment sharing.
VMs require less energy than local hardware, lowering power utilization.
Less reliance on physical hardware lowers maintenance costs.
Standardization of environments across releases also reduces the cost of maintaining custom configurations.
Bare Metal Cloud provides the flexibility of virtual machines and the capabilities of dedicated servers. It’s cloud native, built to support infrastructure-as-code solutions such as Pulumi, Terraform, and Ansible, and optimized for DevOps-centric software development.
Environment Consistency
Working on virtual machines is more predictable than programming on bare metal, especially at scale. Physical hardware often exhibits slight differences due to:
Manufacturing processes.
Substitution of components.
Firmware differences.
Intermittent failures.
With a VM, the system’s configuration, device functioning, and memory state are all consistent. Teams use the same virtualization for both development and production, reducing the likelihood of configuration errors due to code pipeline transitions.
Additionally, the software has fewer latent defects (which are more reproducible even if they occur).
Reduced Failure Rates
Virtualization reduces check-in and release failure rates. DevOps teams often design automated tests that simulate the real-world use of the software. These tests run automatically whenever an engineer submits code for check-in, so bugs rarely end up in a release.
Large-scale virtualization also allows the team to set up simultaneous testing on different release and patch levels. These setups improve both product compatibility and interoperability.
Relying on virtualization is beneficial when the team must repeatably test against a dependent third-party component. By virtualizing an ERP or payment gateway, a test accounts for all the simulated data and software responses of the real-world dependent.
Improved Security
Virtualization provides failure-tolerant, consistent, and predictable environments that improve configuration control, safety assurance, and cybersecurity.
VMs are ideal for high-risk tasks. Risky processes run in isolated virtual containers away from other processes and data, limiting the potential blast radius.
A team can also set up VLANs to virtually separate operations. This form of network segmentation improves security as an intruder cannot move freely through a compromised system.
DevOps and Virtualization: Challenges
Despite offering many benefits, virtualization in DevOps still poses some problems. While VMs speed up development and testing times, setting up and using these machines still requires time.
Also, some teams have experienced data breaches due to remote access and virtualized applications. These features can increase the attack surface if not set up correctly.
However, the biggest obstacle for virtualization in DevOps is the knowledge gap. To effectively adopt VMs, a company must either hire new staff or invest in extensive training. Both options are expensive, especially for large DevOps projects.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Pinnapareddigari Lasya priya directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
