DevOps Monitoring Project
 Bala
Bala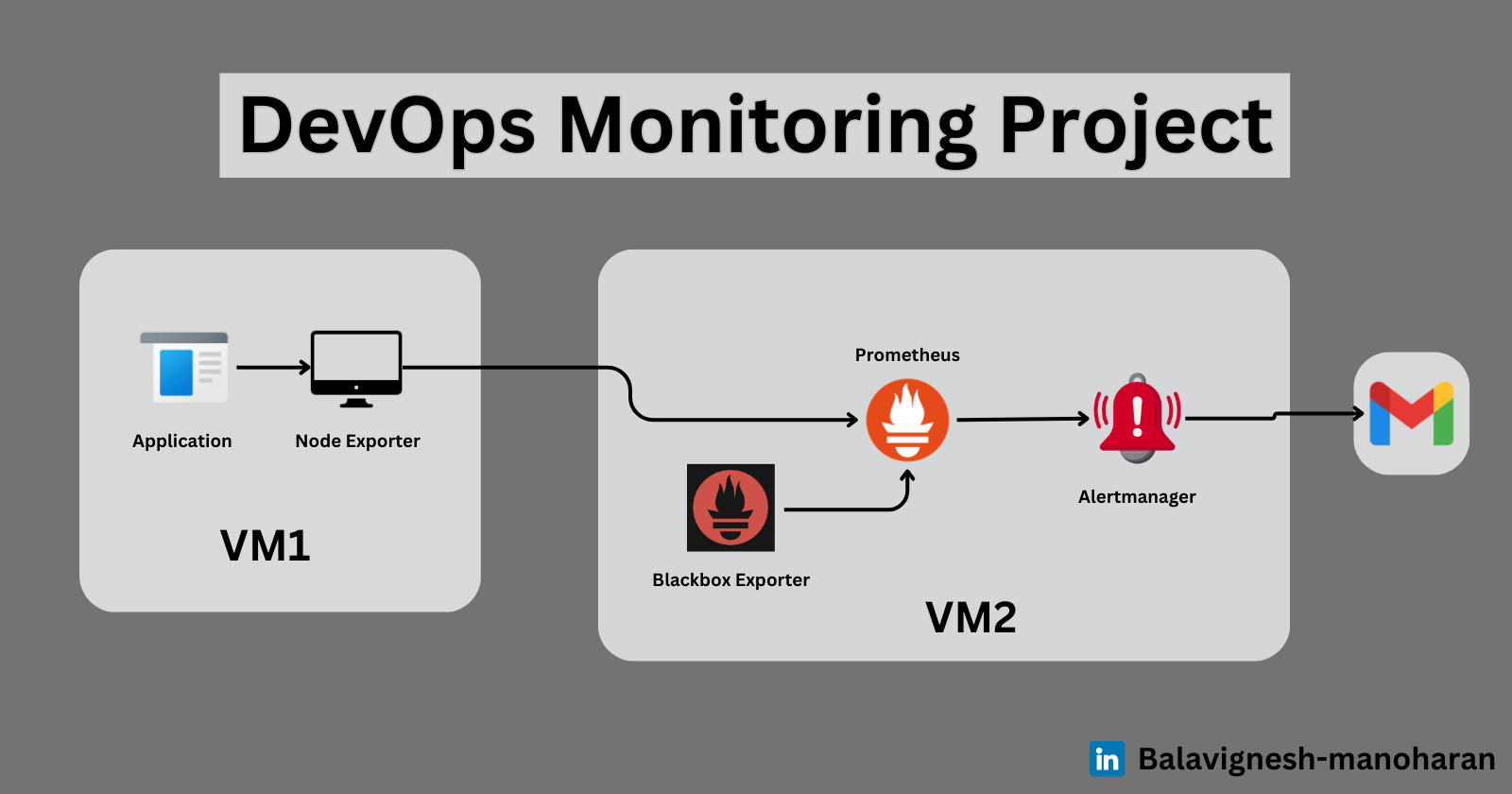
Introduction: Monitoring is a crucial part of the DevOps lifecycle, ensuring that the infrastructure, application and services run in its optimal state.
In this blog, we will see how to set up and configure monitoring tools for a DevOps project such as Node Exporter, Blackbox Exporter and Alert Manager and send notification to the team via email.
Pre-requisites:
AWS Account
Basic Monitoring Understanding
Security Ports:
Prometheus: Port 9090
Node Exporter: Port 9100
Blackbox Exporter: Port 9115
Alertmanager: Port 9093
Application: Port 8080
Tools Overview:
Prometheus
It is an open source application used for event monitoring and alerting. It records metrics in a time series database.
Node Exporter
It is an agent that gathers the system metrics such as CPU / Disk / Network and exposes them in a format which can be ingested by Prometheus.
Black Box Exporter
It is used for endpoint monitoring, allowing you to check endpoints and generate uptime and availability metrics.
Alert Manager
The Alertmanager handles the alerts sent by a client applications such as promethues server.
Steps:
Go to the AWS Console, and launch two Ubuntu instances with instance type as t3.medium and set the storage as 20GB and rest you can keep as the default.
One instance we will have our application and this application we need to monitor, the other application is where we install the tools such as the node exporter, blackbox exporter and alert manager.
Rename both the instances accordingly.
Open the first instance using putty or mobaxterm, in which we will install all the tools starting with prometheus, node exporter and blackbox exporter.
Open prometheus.io and click on download.
- In the next page, select the prometheus link for your OS. Right click on the link and select the copy link address.
Open your instance and first run the below command
sudo apt updatePaste the link address which you had copied earlier and run
wget https://github.com/prometheus/prometheus/releases/download/v2.53.2/prometheus-2.53.2.linux-amd64.tar.gz
Once downloaded, extract using tar the file which you had downloaded.
tar -xvf prometheus-2.53.2.linux-amd64.tar.gz
Next we will install the blackbox exporter which you can find below in the same documentation.
Select the link address and go to your terminal and paste it and download the package with wget like earlier.
Install and extract the same way you did for Prometheus.
Next, Install the alert manager which is also available in the same documentation.
Install and extract the same way you have done for earlier tools.
Now, Go to your second VM and update using below command.
sudo apt updateInstall node exporter in this VM, go to the same Prometheus documentation and you can find node exporter package, copy link address and paste and extract in your VM using the same method.
Open the node exporter folder, where you can find the node exporter file which is executable.
Run the file using below command.
./node_exporter &This
&will run the service in background, and now access the node exporter using the Public IP of your instance with port9100. Open the port9100in the security group.Clone the java application and go inside the application.
Install java using command below command
sudo apt install openjdk-17-jre-headless
Now install maven using below command
sudo apt install maven -y
Build the project of your application using the command
mvn packageOnce the build is completed, go inside the target folder and run the jar file.
To run the application use the below command
java -jar database_service_project-0.0.2.jarOpen a new browser and copy the public Ip with the port 8080 to see the application running successfully.
Now we need to monitor this website. Go to the monitoring instance in which we have installed all the required tools.
Open the Prometheus folder and run the Prometheus file using the below command.
./prometheus &Copy the Public IP with Port
9090and Prometheus is running.
Go to the Prometheus folder and create a new file called alert_rules.yaml and copy the below contents.
--- groups: - name: alert_rules rules: - alert: InstanceDown expr: up == 0 for: 1m labels: severity: critical annotations: summary: Endpoint {{ $labels.instance }} down description: "{{ $labels.instance }} of job {{ $labels.job }} has been down for more than 1 minute." - alert: WebsiteDown expr: probe_success == 0 for: 1m labels: severity: critical annotations: description: The website at {{ $labels.instance }} is down. summary: Website down - alert: HostOutOfMemory expr: (node_memory_MemAvailable / node_memory_MemTotal) * 100 < 25 for: 5m labels: severity: warning annotations: summary: Host out of memory (instance {{ $labels.instance }}) description: |- Node memory is filling up (< 25% left) VALUE = {{ $value }} LABELS: {{ $labels }} - alert: HostOutOfDiskSpace expr: (node_filesystem_avail{mountpoint="/"} * 100) / node_filesystem_size{mountpoint="/"} < 50 for: 1m labels: severity: warning annotations: summary: Host out of disk space (instance {{ $labels.instance }}) description: |- Disk is almost full (< 50% left) VALUE = {{ $value }} LABELS: {{ $labels }} - alert: HostHighCpuLoad expr: (100 - (avg by (instance) (irate(node_cpu_seconds_total{mode="idle"}[5m]))) * 100) > 80 for: 5m labels: severity: warning annotations: summary: Host high CPU load (instance {{ $labels.instance }}) description: |- CPU load is > 80% VALUE = {{ $value }} LABELS: {{ $labels }} - alert: ServiceUnavailable expr: up{job="node_exporter"} == 0 for: 2m labels: severity: critical annotations: summary: Service Unavailable (instance {{ $labels.instance }}) description: |- The service {{ $labels.job }} is not available VALUE = {{ $value }} LABELS: {{ $labels }} - alert: HighMemoryUsage expr: (node_memory_Active / node_memory_MemTotal) * 100 > 90 for: 10m labels: severity: critical annotations: summary: High Memory Usage (instance {{ $labels.instance }}) description: |- Memory usage is > 90% VALUE = {{ $value }} LABELS: {{ $labels }} - alert: FileSystemFull expr: (node_filesystem_avail / node_filesystem_size) * 100 < 10 for: 5m labels: severity: critical annotations: summary: File System Almost Full (instance {{ $labels.instance }}) description: |- File system has < 10% free space VALUE = {{ $value }} LABELS: {{ $labels }}Save the file and now open prometheus.yaml file
Go to the alert files section and provide the name of the alert file which you had just created in the previous step.
Run the alert manager by going inside the alert manager folder and run using command.
./alertmanager &Copy the Public IP with Port
9093and see if the alert manager is running.
Restart the Prometheus service to see if the rules are populated.
To restart we will kill the prometheus service using command which will give the PID of the prometheus.
pgrep prometheusKill “PID” to kill the process and again start it using command “
./prometheus &”Reload the Prometheus page again and go to rules to see all the rules displayed.
Open the Prometheus,yml file and set the target for the alert manager. Just uncomment the alertmanager and provide the IP of the alert manager.
Inside the scrape metrics, add the following lines as the node exporter targets and save the file.
scrape_configs: # The job name is added as a label `job=<job_name>` to any timeseries scraped from this config. - job_name: "prometheus" # metrics_path defaults to '/metrics' # scheme defaults to 'http'. static_configs: - targets: ["localhost:9090"] - job_name: node_exporter static_configs: - targets: - 13.201.170.34:9100 - job_name: blackbox metrics_path: /probe params: module: - http_2xx static_configs: - targets: - http://prometheus.io - https://prometheus.io - http://13.201.170.34:8080 relabel_configs: - source_labels: - __address__ target_label: __param_target - source_labels: - __param_target target_label: instance - target_label: __address__ replacement: 15.206.188.156:9115Restart the Prometheus service again as we did earlier.
Once the prometheus site is up, go to targets and you can see the node exporter is up and running.
Now we need to add the black box exporter, go to the official documentation of Prometheus and scroll down to black box exporter and click on the github link provided along with it.
Scroll down in the github repo and you will find the scrape configs, copy it and paste it in yaml lint site as we need to modify it.
scrape_configs: - job_name: 'blackbox' metrics_path: /probe params: module: [http_2xx] # Look for a HTTP 200 response. static_configs: - targets: - http://prometheus.io # Target to probe with http. - https://prometheus.io # Target to probe with https. - http://example.com:8080 # Target to probe with http on port 8080. relabel_configs: - source_labels: [__address__] target_label: __param_target - source_labels: [__param_target] target_label: instance - target_label: __address__ replacement: 127.0.0.1:9115Replace your application IP address in the targets section, and also the black box IP(VM) in the last line which states replacement IP.
Restart again the Prometheus service.
Check the targets section in Prometheus site, and you will see black box is added but service is down.
Let us start the black box exporter using command
./blackbox _exporter &Copy the public Ip with port 9115 and run it in the new browser to see black box exporter running.
We can see that the black box exporter is running and the target is fetched successfully.
- Now all the service is running once you refresh.
Let us configure the email notification for the services, for that first we need to generate an app password from our account.
Before that you need to turn on “Two step verification” from the security section in https://myaccount.google.com/
Now create an app password and copy and use it in your file.
Create a file alertmanager.yml inside the alert manager folder and paste the content for the email notification.
--- route: group_by: - alertname group_wait: 30s group_interval: 5m repeat_interval: 1h receiver: email-notifications receivers: - name: email-notifications email_configs: - to: example@gmail.com from: monitoring@example.com smarthost: smtp.gmail.com:587 auth_username: example@gmail.com auth_identity: example@gmail.com auth_password: wdmg ndpc xweb copp send_resolved: true inhibit_rules: - source_match: severity: critical target_match: severity: warning equal: - alertname - dev - instanceRestart alert manager using command “./alertmanager.yml &”
Restart Prometheus again.
Now everything is set, just check the targets in the Prometheus site for confirmation.
Check the alerts in the Prometheus site for all the configured alerts.
- Now to test, just stop your website and check the Prometheus server, it will show the site is down and in a few mins you will also get an email stating the website is down.
- Also the mail has been fired to the given recipient mail address.
- Now stop the node exporter and you can see the service is unavailable and the second mail has been received.
- Once the instance and node exporter is down, we can see that the alerts have been active and the mail has been fired.
- This covers everything about the monitoring project.
Conclusion: In this blog we have discussed and implemented few of the monitoring tools and saw how it is useful in the DevOps environment. These tools allows you to track and report the performance of your application and infrastructure in real time. With these tools you can detect the issues early and respond quickly.
If you found this post useful, give it a like👍
Repost♻️
Follow Bala for more such posts 💯🚀
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Bala directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
