Basics Content Delivery Network (CDN)
 OBULIPURUSOTHAMAN K
OBULIPURUSOTHAMAN K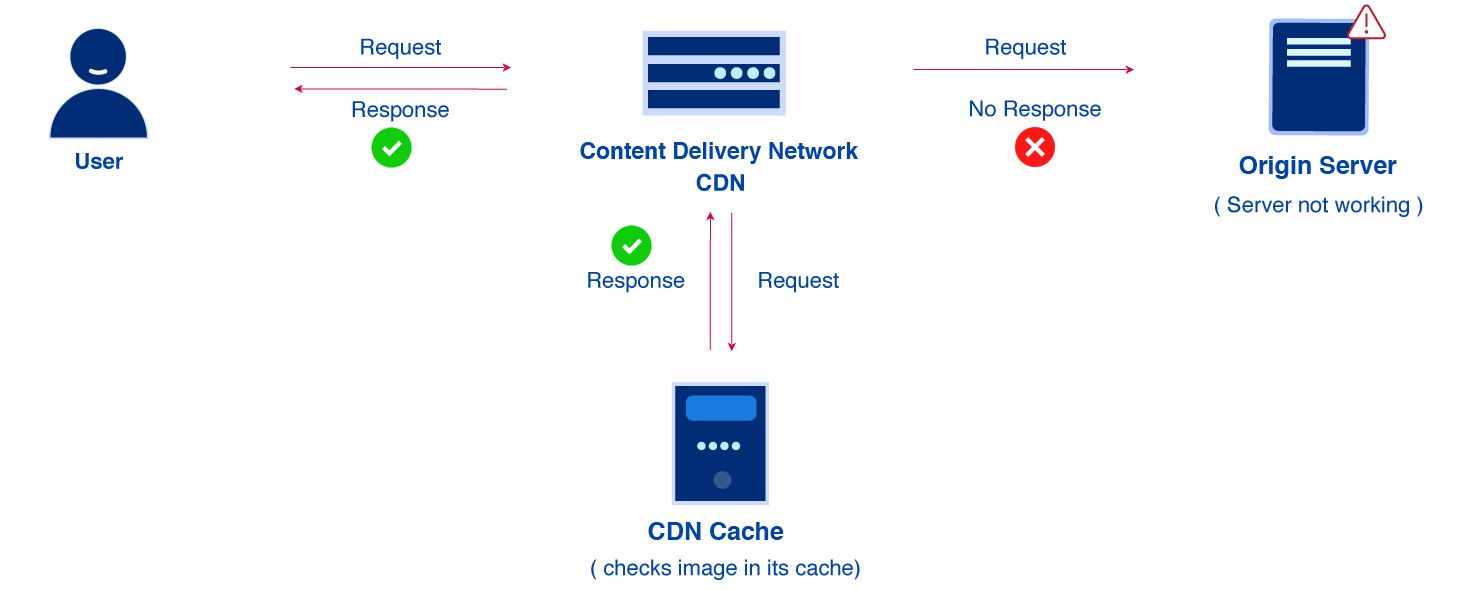
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) :
Imagine you have built an app used by millions of users worldwide.
Your app also serves video content, but all your videos are hosted in one geographical location.
Due to the large physical distance, users in other locations experience significant latency and buffering while watching videos. This is expected since the data takes time to travel from the server to the client.
One popular solution to this issue is to place these video files closer to user locations.
This is what a Content Delivery Network (CDN) does.
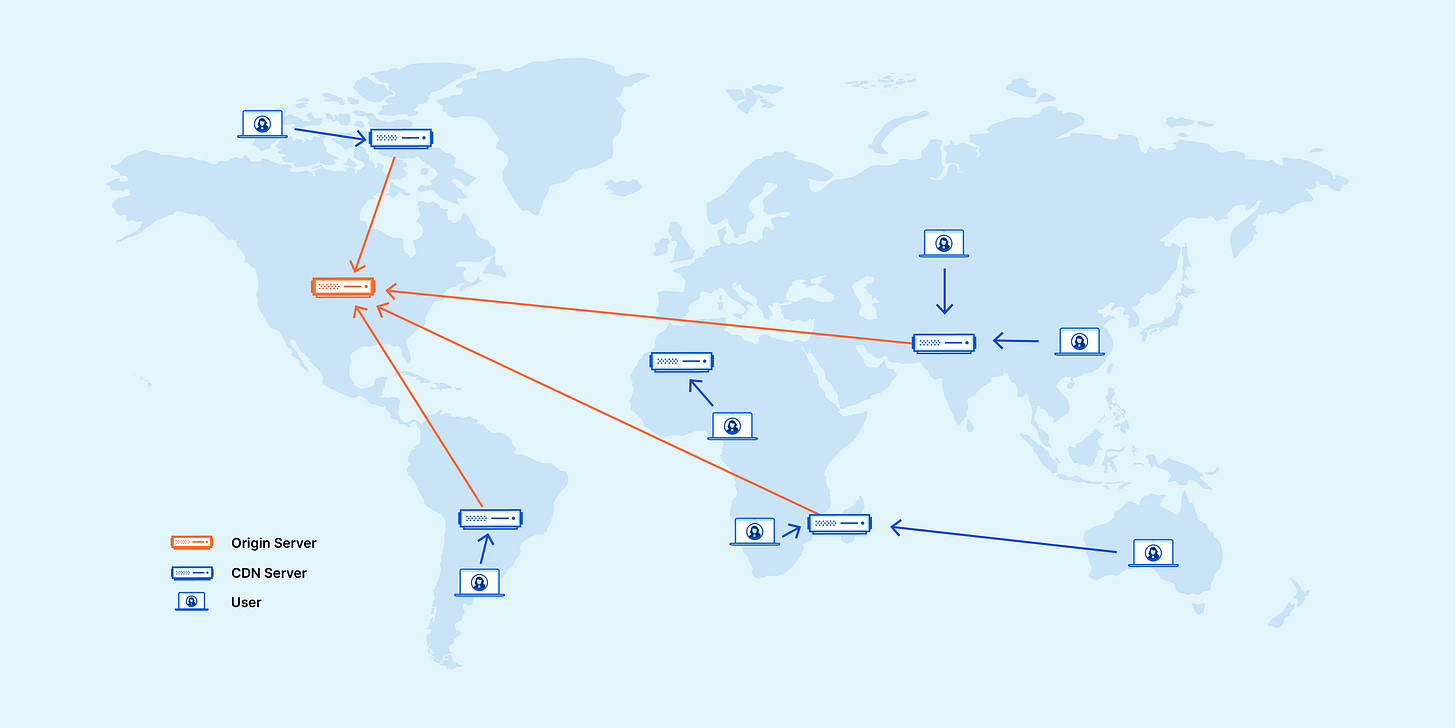
What is CDN ?
A CDN is a geographically distributed network of servers that work together to deliver web content (like HTML pages, JavaScript files, stylesheets, images, and videos) to users based on their geographic location.
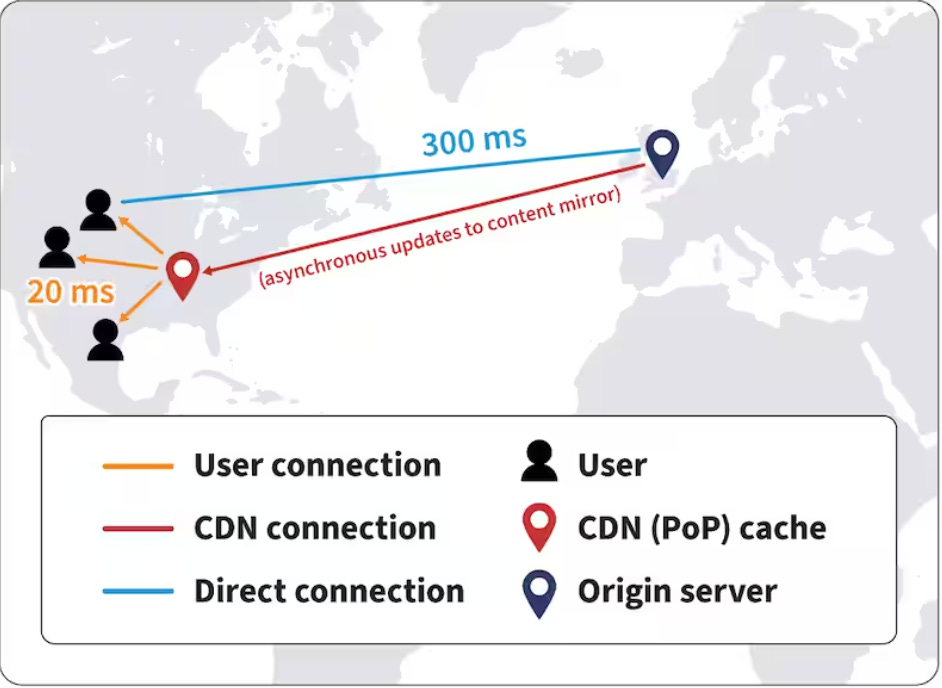
The primary purpose of a CDN is to deliver content to end-users with high availability and performance by reducing the physical distance between the server and the user.
When a user requests content from a website, the CDN redirects the request to the nearest server in its network, reducing latency and improving load times.
How Does a CDN Work ?
Content Caching: When a user requests content, the CDN caches this content in servers located closer to the user, known as edge servers. Subsequent requests for the same content are served from these edge servers, reducing the load on the origin server.
Content Delivery: If the edge server has the requested content cached, it delivers it directly to the user. If not, it retrieves the content from the origin server, caches it for future requests, and then delivers it to the user.
Content is Refreshed: CDNs periodically update cached content to ensure users receive the latest version.
Benefits of using a CDN :
Improved Website Load Times: By serving content from servers closer to the user's geographic location, CDNs significantly reduce latency and improve website load times.
Reduced Bandwidth Costs: By offloading traffic from the origin server, CDNs reduce bandwidth costs and server load, potentially lowering overall infrastructure expenses.
Increased Content Availability and Redundancy: With content distributed across multiple servers, CDNs provide a failover mechanism that ensures content remains available even if one or more servers go offline.
Enhanced Website Security: Many CDNs offer security features such as DDoS protection, SSL/TLS encryption, and secure token authentication, safeguarding your content and data.
Better User Experience: Faster load times and increased reliability translate to a better user experience, which can lead to higher engagement and conversion rates.
Global Reach: CDNs make it easier to deliver content to users worldwide, regardless of their location.
Scalability: CDNs can handle traffic spikes more efficiently than traditional hosting, making them ideal for websites with fluctuating traffic patterns.
Types of Content Delivered By CDNs : While CDNs can deliver various types of content, they are particularly effective for:
Static Content: Includes images, CSS files, JavaScript files, and other static assets that do not change frequently.
Dynamic Content: Personalized content that changes based on user interactions, such as user-specific data or real-time information.
Streaming Media: Video and audio content delivered in real-time to users.
Software Downloads: Large files such as software updates, applications, and games.
Use Cases of CDNs :
E-commerce: Ensures fast loading times and high availability during peak shopping periods, enhancing the shopping experience.
Media and Entertainment: Delivers high-quality streaming media to a global audience with minimal buffering.
Gaming: Reduces latency and improves download speeds for game patches and updates.
Software Delivery: Accelerates the distribution of software updates and applications to users worldwide.
Popular CDN Providers :
Akamai: One of the oldest and largest CDN providers, known for its extensive global network and robust security features.
Cloudflare: Offers a comprehensive suite of performance and security services, including a free tier for smaller websites.
Amazon CloudFront: Integrated with AWS, providing seamless scalability and extensive integration with other AWS services.
Fastly: Known for its real-time content delivery and edge computing capabilities.
Google Cloud CDN: Leverages Google’s global network infrastructure for high performance and reliability.
A Content Delivery Network is an essential tool for any online service aiming to deliver content quickly and reliably to a global audience.
By understanding how CDNs work, the benefits they offer, and how to choose and implement the right one, you can significantly enhance the performance, security, and scalability of your web applications.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from OBULIPURUSOTHAMAN K directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

OBULIPURUSOTHAMAN K
OBULIPURUSOTHAMAN K
As a Computer Science and Engineering graduate, I have cultivated a deep understanding of software development principles and technologies. With a strong foundation in Java programming, coupled with expertise in frontend and backend development, I thrive in crafting robust and scalable solutions. Currently, I am leveraging my skills as a Java Full Stack Engineer at Cognizant, where I am involved in designing and implementing end-to-end solutions that meet the complex requirements of our clients. I am passionate about leveraging emerging technologies to drive innovation and deliver tangible business value. My goal is to continually enhance my expertise and contribute to the advancement of software engineering practices in the industry.