Future of Cloud Networks
 Aakashi Jaiswal
Aakashi Jaiswal
Before getting into Cloud Networking, let’s first have a glimpse about
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing are the services that are provided over the internet or the cloud. It allows users to access computing resources on-demand, such as storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics, without the need to buy, own, or maintain physical resources.
Through Cloud Computing, people can have these benefits:
-They can access any service from anywhere, just with the internet connection.
-Users can scale their business as per their requirements.
-Users can pay only for the cloud service they are using.
Some of the applications of Cloud computing are like Gmail, movie streaming on Netflix and even playing cloud hosted games.
There are even different types of Cloud services:
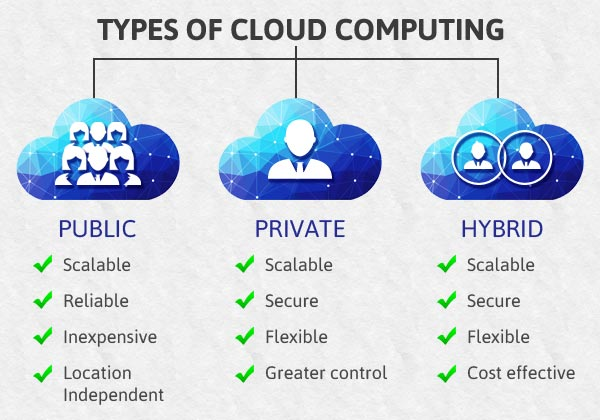
-Public: Wide number of users accessing a host of remote servers that are connected to form a single, all-encompassing network.
-Private: Reserved for individual users.
-Hybrid: hybrid clouds combine the devoted resources of a private cloud with the managed infrastructure that a public cloud.
What is Cloud Networking?
![]()
Cloud networking is the use of the cloud based services to deploy a network which connects an organization’s employees, resources and applications.
Traditionally, organizations use their own private network hardware components to create an isolated wide area network(WAN) for secure communication and application deployment.
The setup and management process is expensive as well as complicated. A third party service provider manages and maintains networking hardware and infrastructure.
Benefits of Cloud networking:
-Efficient network management.
-Increased scalability
-Easier security
-Improved monitoring and maintenance
How does cloud networking work?
Traditionally, business would rent a server in a nearby data center.
Today, cloud networking configurations use cloud-based virtual servers in the region. And they connect to the office sites by using cloud-based virtual private network and gateway.
Cloud networking is virtual network components, topologies, and configurations that run on a cloud provider’s physical networking infrastructure. You define and manage your networks as software.
You can create your own virtual local area networks (LANs) and wide area networks (WANs) with cloud resources.
Virtualization
Cloud networking services are possible because of virtualization. This virtualization means that the only limits to the possibilities of cloud networking are the capacity and capabilities of the underlying physical infrastructure.
A cloud service provider can multiplex a network cable with a large capacity. And they can create several different virtual private network links operating on it and share the capacity. Providers define the logically isolated virtual links in software and offer different capacities in different service packages.
Virtual private clouds
Combining other cloud resources with a cloud network is known as a virtual private cloud (VPC). With a VPC, you can define a virtual private cloud network and run cloud network resources within its bounds. You have internet-based remote access through a virtual private network and a software-defined gateway. A virtual private cloud is logically isolated from the public cloud. VPC is like our own Virtual data center.
Hybrid cloud networking
Within cloud networking, not all networking components and resources need to be cloud-based.
For example, cloud networking configurations can connect to on-premises data centers and site branches through traditional networking infrastructure and the public internet.

What's the difference between cloud networking and cloud computing?
Cloud networking is just one cloud infrastructure component that's available as a service from a cloud computing provider.
Cloud computing traditionally offers access to a range of rented, virtualized IT infrastructure, such as servers, storage, and networking. A cloud provider owns and runs the underlying physical resources.
These resources are offered as a service to customers through software-based network management. The physical infrastructure itself is distributed across the world through virtualization. This means that multiple customers can run logically isolated private infrastructure on the same underlying physical hardware.
Cloud computing has now expanded beyond hardware-based infrastructure services to other products such as tools, platforms, and serverless computing.
Future of Cloud Network:

-Distributed cloud
This model will extend cloud services to different locations, which will allow for real-time data processing and compliance with local regulations.
-Quantum computing
This model will use quantum physics to process data, which will allow for faster processing of large amounts of data
-Cloud TV
Cloud TV is expected to become more popular and eventually replace traditional TV.
-Green cloud computing
This model will aim to reduce the carbon footprint and energy consumption of cloud computing by using alternative materials and optimizing data center operations.
-Serverless computing
This model will allow businesses to automatically scale resources based on demand, which will reduce costs and simplify deployment.
Also, the integration of Internet Of Things(IOT), edge computing, adoption of hybrid will happen to take place.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Aakashi Jaiswal directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Aakashi Jaiswal
Aakashi Jaiswal
Coder | Winter of Blockchain 2024❄️ | Web-Developer | App-Developer | UI/UX | DSA | GSSoc 2024| Freelancer | Building a Startup | Helping People learn Technology | Dancer | MERN stack developer
