IAM: Identity and Access Management (Short notes)
 Fatima Jannet
Fatima JannetTable of contents
- IAM Introduction: Users, Groups, Policies
- IAM: Permission
- IAM Policies Structure
- IAM - Password Policy
- Multi Factor Authentication - MFA
- MFA devices options in AWS
- What is AWS CLI?
- What’s the AWS SDK?
- IAM Security Tools
- IAM Guidelines & Best Practices
- Shared Responsibility Model for IAM (Lot of question comes in the CCP exam regarding this)
- Questions
- End.
Disclaimer: This blog is a quick rundown of the theory for the AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner (CCP) exam. I’d recommend hands-on practice to really get the hang of things! Hands-on experience is highly recommended
IAM Introduction: Users, Groups, Policies
IAM = Identity and Access Management, Global service
Root account created by default, shouldn’t be shared or used
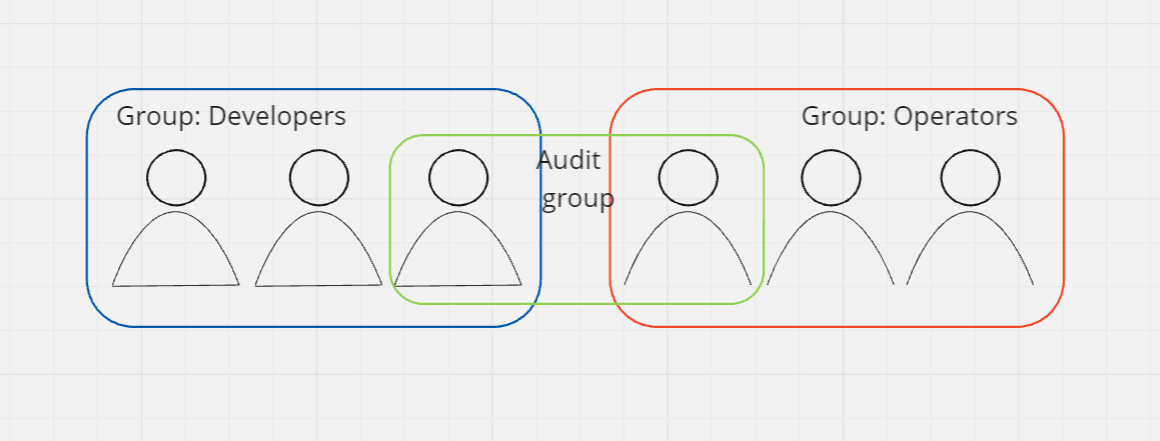
Users are people within your organization, and can be grouped
Groups only contains users, not other groups
Users don’t have to belong to a group, and user can belong to multiple groups
IAM: Permission
Users or Groups can be assigned JSON documents called policies.
These policies define the permissions of the users
In AWS, you don't let everyone do everything, as that would be disastrous. A new user could launch many services, costing you a lot of money or posing security risks. Instead, AWS uses the principle of least privilege. This means you only give users the permissions they need.
IAM Policies Structure
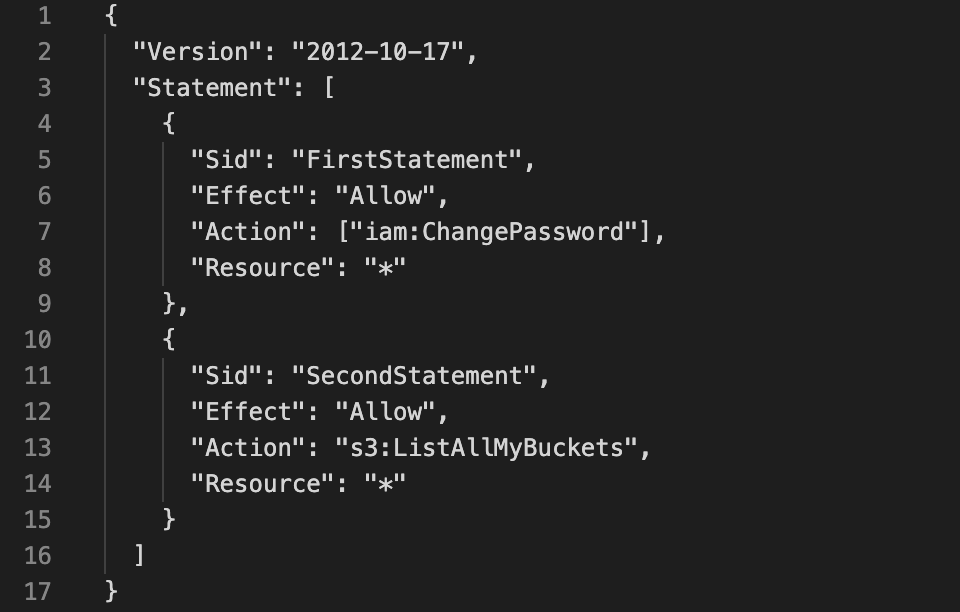
Consists of
Version: Policy language version always include “2012-10-17”
Id: an identifier for the policy (optional)
Statement: one or more individual statements (required)
Statement consists of
Sid: an identifier for the statement (optional)
Effect: whether the statement allows or denies access (allow, deny)
Principle: account/user/role to which this policy applied to
Action: list of actions this policy allows or denies
Resources: list of resources to which the actions applied to
Condition: conditions for when this policy is in effect (optional)
IAM - Password Policy
Strong password = higher security for your account
In AWS, you can setup a password policy:
set a minimum pass length
require specific uppercase letter
lowercase letter
numbers
non-alphanumeric characters
Allow all IAM users to change their own passwords
Require users to change their password after some time (password expiration)
prevent password re-use
[Access management → Account settings → Password policy → edit]
Multi Factor Authentication - MFA
Users have access to your account and can possibly change configurations or delete your resources in your AWS account
You want to protect your Root Accounts and IAM users
MFA = password you know + security device you own

Main benefit of MFA:
if a password is stolen or hacked, the account is not compromised
MFA devices options in AWS
Virtual MFA device (support for multiple tokens on a single device)
google authenticator (phone only)
Authy (phone only)
Universal 2nd Factor (U2F) security key (support for multiple root and IAM users using a security key)
- YubiKey (3rd party)
What is AWS CLI?
A tool that enables you to interact with AWS services using commands in your command-line shell
Direct access to the public APIs of AWS services
You can develop scripts to manage your resources
It’s open-source https://github.com/aws/aws-cli
Alternative to using AWS management console
What’s the AWS SDK?
AWS software development kit (SDK)
Language-specific APIs (set of libraries)
Enables you to access and manage AWS services programmatically
Embedded within your application
Supports
SDKs (JavaScript, Python, PHP, Ruby, Java, Go, Node,js, C++)
Mobile SDKs (Android, iOS..)
IoT device SDKs (embedded C, Arduino, ….)
Example: WS CLI is built on AWS SDK for python
IAM Security Tools
IAM Credential Report (account-level)
- a report that lists all your account’s users and the status of their various credentials
IAM Access Advisor (user-level)
Access advisor shows the service permissions granted to a user and when those services were last accessed
You can use this information to revise your policies
[Access report → Credential report → Download credential report (open via excel)]
IAM Guidelines & Best Practices
Don’t use the root account except for AWS account setup
One physical user = one AWS User
Assign users to groups and assign permissions to groups
Create strong password policy
Use and enforce the use of MFA
Create and use Roles for giving permissions to AWS services
Use Access Keys for Programming Access (CLI/ SDK)
Audit permissions of your account using IAM Credentials Report & IAM Access Advisor
Shared Responsibility Model for IAM (Lot of question comes in the CCP exam regarding this)
AWS
Infrastructure (global network security)
Configuration and vulnerability analysis
Compliance validation
You
users, groups, roles, policies, management and monitoring
Enable MFA on all accounts
Rotate your keys often
Use IAM tools to apply appropriate permissions
Analyze access patterns and review permissions
Questions
What is a proper definition of IAM Roles?
- An IAM entity that defines a set of permission for making AWS service requests, that will be used by AWS services
Which of the following is an IAM Security Tool?
IAM Credential Report
IAM root account manager
IAM service report
IAM security advisor
What are IAM Policies?
- An IAM policy is an entity that, when attached to an identity or resource, defines their permissions.
End.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Fatima Jannet directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
