Demystifying Test Driven Development
 Dinesh T
Dinesh T
Introduction
As a developer, when trying to solve a problem through coding, the typical approach is to design the flow of the program. However, if unexpected data is passed, the code may fail, breaking the entire program. In TDD, instead of focusing solely on designing the logic, the programmer first writes the test cases before starting to code. This approach results in more robust code.
Why Test Driven Development (TDD)
In Software Development UI/UX design drives the Application. similarly, In TDD Test Cases Drive the design of the code. TDD will make our code more robust and confident. Kent Beck, the father of extreme programming once said,
TDD encourages simple designs and inspires confidence to your code.
TDD in a Nutshell
Test Driven Development (TDD) is a software development approach where It emphasizes a "test-first" philosophy to guide the development process, ensuring that every new feature or functionality is covered by a corresponding test.
Importance of Testing in software development
Let’s examine the statistics on how software development improves by implementing Test-Driven Development (TDD). Researchers at the Department of Computer Science at North Carolina State University introduced developers to TDD and then asked for their feedback on the approach.
The results showed that 92% of the developers believed that TDD leads to higher-quality code, 79% thought that TDD encourages simpler design, and 71% found the approach to be notably effective.
Brief overview of the article's structure
In this blog we will be walking through
Introduction to testing
TDD Approach Red, Green, Refactor Workflow
How to write test assertions that ensure the code behaves as expected.
Test Fixtures to load the consistent initial state during each test
Generating our FAKE data using Factory and Fakes Class
How to test the sample data in the production-ready systems.
Case Studies and Real-world Application
Introduction to Testing
Testing Verifies that your software works as expected
Testing prevents future code breaks and compatibility issues. by emphasising the Testing Overall Development time can be reduced Significantly
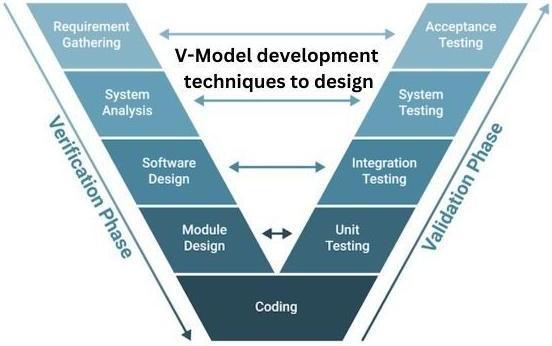
Test Levels and Release Cycles
The software testing process includes four levels: Unit, Integration, System, and User Acceptance Testing and the level of testing that developers perform varies throughout the phases of the traditional release cycle.
Key components of TDD: Tests, Code, Refactor
Red, Green, and Refactor are fundamental practice in a Test-driven Development. The workflow encourages writing tests first, which guide the design and implementation of code. The core philosophy is to focus on correctness first, then optimize for quality.
TDD cycle helps maintain a high level of test coverage and ensures the code remains clean and functional over time. Red, Green, Refactor workflow includes three steps which is a cycle
TDD cycle explained: Red, Green, Refactor
Red: Write the Failing unit test case for the code you wish you had.
Green: write just enough code to pass the test case.
Refactor: Refactor the code to improve the code quality.
By breaking the development process into smaller cycles, the Red-Green-Refactor encourages writing well-tested, clean, and maintainable code, which is crucial for scalable and robust software systems.
TDD Methodology
Test Assertions
Test Assertions are an essential part of writing unit tests. They help verify that the code behaves as expected by checking if the actual method matches the expected output.
Assertions serve as checkpoints in tests, and when an assertion fails, it indicates that there's a problem with the code. and there are several methods to check if Tests are passed or failed they are as follows
assertEqual(a,b)
assertNotEqula(a,b)
assertTrue(x)
assertFalse(x)
assertIn(a, b)
assertNotIn(a, b) and much more..
Test Fixtures
Test Fixtures establish a known initial state before and after each test. Test Fixtures are helpful for many testing situations, such as creating Mock Objects and loading a database with known data set.
Test Fixtures operates at three level: Module, Test Case, Test level.
click me for Practicing Test Fixtures.
Generating Fake Data
Creating and maintaining a huge test data set requires overhead time and can be cumbersome so we can also generate Fake Data in Python unit test from the Factory Faker Class
Benefits of Test Driven Development
To create a DevOps Pipeline, all the Tests should be automated

Improved code quality and design
Early bug detection and reduced debugging time
Facilitation of better collaboration and communication
Enhanced documentation and code coverage
Common Misconceptions about TDD
TDD is time-consuming and slows down development
TDD only tests existing code rather than design purposes
TDD is only suitable for large projects
TDD guarantees bug-free software
Implementing TDD in Practice
Setting up a TDD environment: Tools and frameworks
Click me for TDD Environment setup
Writing effective tests: Best practices and strategies
Test cases help developers identify and fix parts of their code that can break
Click me for practicing Test Assertions.
Click me for practicing Test Fixtures
Click me for practicing Test Coverage
Challenges and Limitations of TDD
Overhead of writing and maintaining tests
Learning curve for adopting TDD approach
Potential for neglecting non-functional testing aspects
Balancing pragmatism and purity in test writing
Case Studies and Real-World Applications

Spotify – Continuous Delivery and TDD
Overview: Spotify, a global music streaming service, implemented TDD as part of their continuous delivery pipeline. With millions of users, Spotify needed to ensure that their platform was robust, scalable, and bug-free.
TDD Use: Developers at Spotify use TDD extensively to maintain the reliability of new features and minimize bugs in production. Unit tests are written for every small piece of functionality, ensuring that changes don’t break existing systems.
Outcome: By integrating TDD with their agile development practices, Spotify reduced the time it took to deliver new features while maintaining the quality and stability of their platform.
Conclusion
In Conclusion, Test-Driven Development (TDD) enhances software quality by prioritizing a test-first approach, promoting simple design, and improving collaboration. Despite challenges, its benefits, like early bug detection and enhanced documentation, make it valuable. Real-world applications, such as Spotify's use of TDD, demonstrate its effectiveness in maintaining platform stability and accelerating feature delivery. Overall, TDD is crucial for developing high-quality software systems.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Dinesh T directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Dinesh T
Dinesh T
Passionate and committed DevOps Engineer with a solid grasp of computer science basics 💻, containerization 🐳, cloud tech ☁️, micro-services architecture 🏗️, and DevOps methodologies 🚀. Proficient in enhancing and overseeing CI/CD pipelines 🔄 and managing resilient cloud infrastructure 🌐 for maximum availability. I’m constantly broadening my expertise in DevOps, Cloud, and Technology 📚, and love sharing my insights with the community 🌍 in a more captivating and concise way.