How Does a Computer Network Work?
 Aakashi Jaiswal
Aakashi Jaiswal
Computer networking is a fascinating and essential part of our modern world. It allows various devices, like computers, smartphones, and even smart appliances, to communicate and share information seamlessly.
What is a Computer Network?
At its core, computer networks, a collection of interconnected devices that can exchange data and resources. This can range from a small home network with a few devices to vast systems like the Internet that connect millions globally. The main goal of networking is to facilitate communication and resource sharing among devices.
Types of Computer Networks
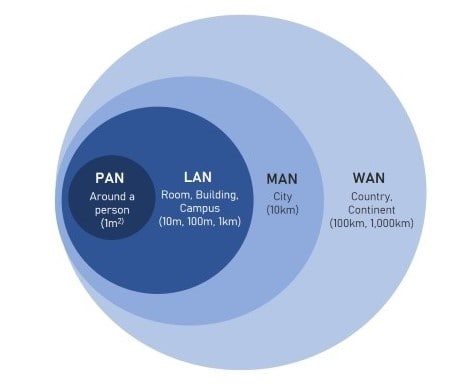
Local Area Network (LAN): This is typically used in homes or offices to connect computers and devices over a short distance. LAN’s allow users to share files and printers easily.
Wide Area Network (WAN): These networks cover larger geographical areas, connecting multiple LAN’s. The Internet is the most well-known example of a WAN.
Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN): This type uses wireless technology (like Wi-Fi) to connect devices without physical cables.
Personal Area Network (PAN): This is used for connecting personal devices, such as linking your smartphone to your laptop via Bluetooth.
Virtual Private Network (VPN): A VPN provides secure connections over the Internet, allowing users to access their home or office network remotely.
Key Components of Computer Networks

Understanding the components that make up a computer network is crucial:
Routers: These devices forward data between different networks, acting like traffic directors that ensure information reaches its destination efficiently.
Switches: Switches connect multiple devices within the same network, allowing them to communicate directly with one another.
Access Points: These are used in wireless networks to connect devices without cables.
Cables: Physical connections like Ethernet cables or fiber optics are essential for wired networks.
IP Addresses: Each device on a network has a unique identifier known as an IP address, which helps in routing data correctly.
When you send an email or browse the web, your device communicates with others through these networks. Data is broken down into smaller packets that travel across various paths until they reach their destination. Routers determine the best route for these packets based on current network conditions.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Aakashi Jaiswal directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Aakashi Jaiswal
Aakashi Jaiswal
Coder | Winter of Blockchain 2024❄️ | Web-Developer | App-Developer | UI/UX | DSA | GSSoc 2024| Freelancer | Building a Startup | Helping People learn Technology | Dancer | MERN stack developer