Understanding DNS: The Internet’s Phonebook
 Ashwin R
Ashwin R
Hey there! Today, let’s chat about DNS—no, not the “Did Not Submit” kind, but the Domain Name System. If you’ve ever wondered how typing a simple web address gets you to a website, you’re in the right place!
What is DNS?
Imagine you’re trying to visit your favorite website, like www.google.com. When you type that into your browser, your computer needs to know where to find it. But here’s the thing: computers don’t understand words like we do. They only understand numbers! That’s where DNS comes in.
Think of DNS like the phonebook of the internet. Just like you look up a name in a phonebook to find a phone number, DNS helps your computer find the right “address” for the website you want to visit.
How Does DNS Work?
Let’s break it down step by step. When you hit enter after typing a URL, here’s what happens:
Local Cache Check: First, your computer checks its memory (called a cache) to see if it already knows the IP address for the website. If it does, awesome! You’re ready to go. If not, it’s like asking for directions.
Recursive DNS Server: If your computer doesn’t have the address, it asks a DNS server for help. This server is called a recursive DNS server. It’s like that friend who knows all the good shortcuts and can find anything.
Root Name Server: The recursive server asks a special type of DNS server called a root name server. This server knows where to find the top-level domain (TLD) servers.
Top-Level Domain (TLD) Server: TLDs are the last part of a domain name, like .com, .org, or .net. The TLD server knows where to go based on the domain extension. So, if you’re looking for a .com website, it directs the request to the right server.
Authoritative Name Server: Finally, the recursive server reaches the authoritative name server. This server has the actual IP address you need. It sends that back to your computer, and voilà! Your browser loads the website you wanted.
This whole process happens in a blink of an eye—like magic!
What Are TLDs?
So, what exactly are TLDs? The Top-Level Domain is the part of a web address that comes after the last dot. For example, in www.google.com, the TLD is .com. There are many different TLDs:
.com: Originally meant for commercial businesses but now used by everyone.
.org: Typically used by non-profit organizations.
.net: Originally intended for network providers but is now widely used.
.edu: Restricted to educational institutions.
.gov: Reserved for government entities.
TLDs help categorize websites and can also indicate what kind of organization or entity they belong to.
Real-Life Scenarios
Let’s make this relatable. Imagine you’re at a café, sipping coffee, and you want to look up a new recipe. You type in the URL, and thanks to DNS, it pops right up. But what if you recently switched your website’s hosting? You change your DNS settings, and now your friends are trying to access the site. Some see the old version, while others see the new one. Confusing, right?
Or picture this: you’re trying to log in to your bank account, and instead of landing on your bank’s site, you’re redirected to a sketchy page that looks almost identical. This is a classic case of DNS spoofing. It’s where hackers trick you into thinking you’re on a legitimate site when you’re actually not. Super scary!
The Not-So-Great Side of DNS
Now, let’s talk about the not-so-great parts. DNS can be targeted by bad actors. One infamous attack happened in 2016, known as the Dyn DDoS attack. Hackers targeted a DNS provider called Dyn, causing major websites like Twitter, Netflix, and Reddit to go down. It was like the internet had a massive hiccup!
And then there’s DNS spoofing again. Imagine you think you’re entering your bank’s URL, but you’re actually redirected to a fake site designed to steal your information. That’s why it’s essential to stay aware and be cautious online!
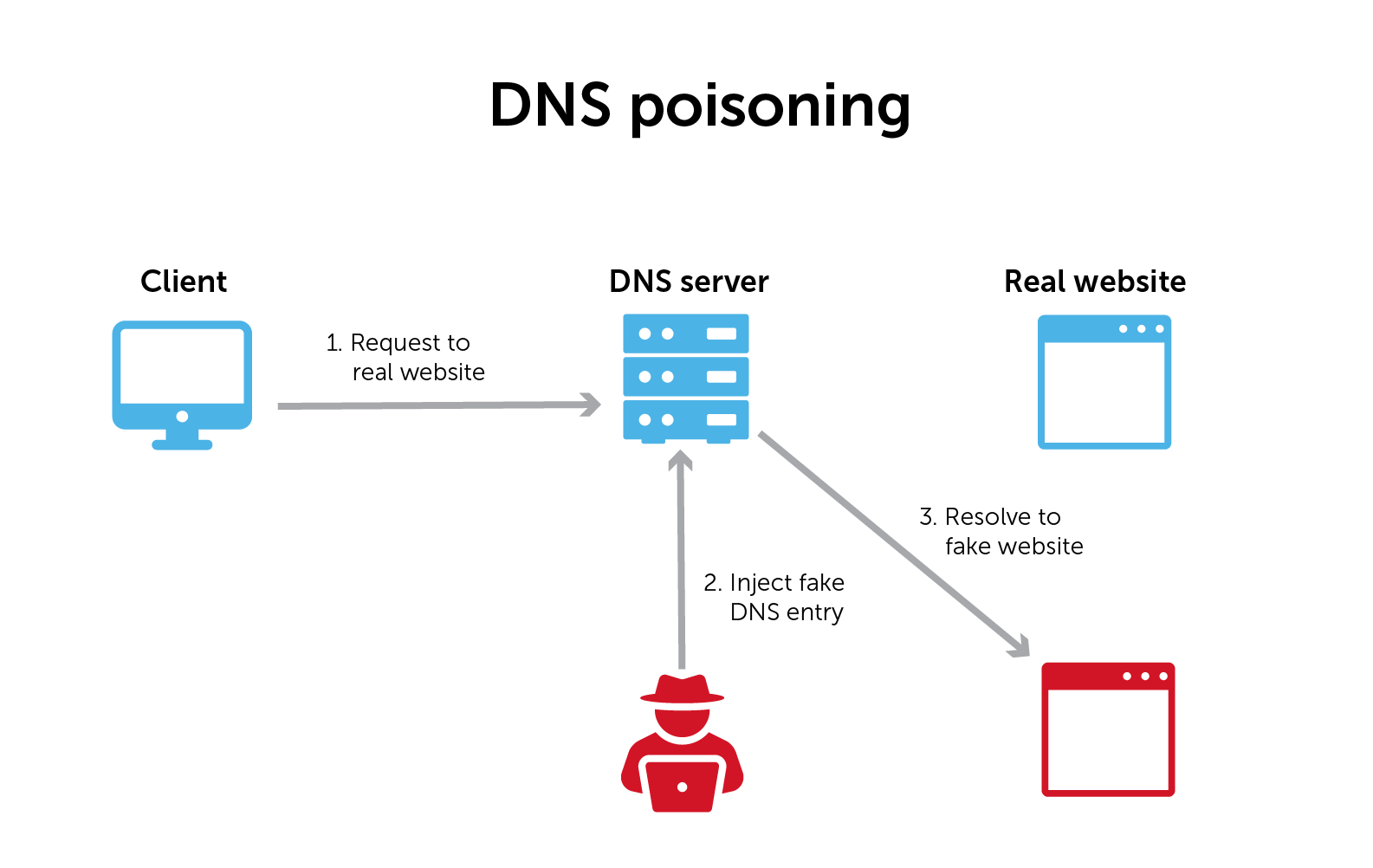
Why Should You Care?
You might be wondering, “Why do I need to know about DNS?” Well, understanding DNS can help you troubleshoot issues when things go wrong. Like when your favorite website won’t load—knowing about DNS can help you figure out if it’s a caching issue or something else.
Plus, being aware of DNS security can protect you from potential threats. The more you know, the safer you are online!
So, the next time you’re casually browsing the web, take a moment to appreciate all the behind-the-scenes action going on with DNS. It’s not just a bunch of tech jargon; it’s what keeps our online experience smooth and user-friendly.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Ashwin R directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
