Linked List (1) - Basic Structure & Print List
 KiwiChip
KiwiChip영어 부연 설명:
prepend: adding an element to the front of a list (Linked List 맨 앞에 요소 추가)
append: adding an element to the end of a list (Linked List 맨 뒤에 요소 추가)
The basic structure of a Linked List
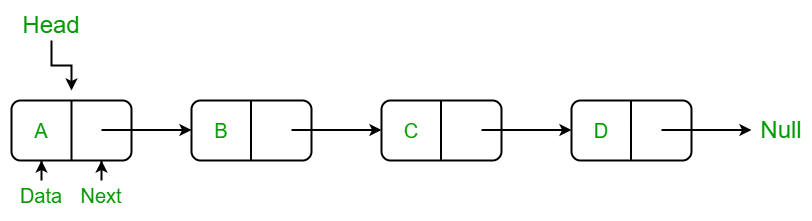
Image: https://media.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/uploads/20220829110944/LLdrawio.png
The basic structure of a Linked List can be described as follows:
Linked List의 기본 구조는 다음과 같다:
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self, value):
create new Node
def append(self, value):
create new Node
add Node to end
def prepend(self, value):
create new Node
add Note to beginning
def insert(self, index, value):
create new Node
insert Node
Each function (like __init__, append, prepend, and insert) needs to create a new node, which is why we start by defining a Node class.
각 함수(__init__, append, prepend, insert)는 새로운 노드를 생성해야 하므로, 먼저 Node 클래스를 정의한다
Node Class
class Node:
def __init__(self, value):
self.value = value
self.next = None
The Node class represents each individual node in the linked list. It contains two attributes: value, which stores the data of the node, and next, which points to the next node in the list.
Node 클래스는 링크드 리스트 안의 각각의 노드를 나타낸다. 이 클래스는 value와 next 두 가지 속성을 가지고 있다. value는 노드의 데이터를 저장하고, next는 다음 노드를 가리킨다.
LinkedList Class
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self, value):
new_node = Node(value)
self.head = new_node
self.tail = new_node
self.length = 1
my_linked_list = LinkedList(4)
print('Head:', my_linked_list.head.value) # Head: 4
print('Tail:', my_linked_list.tail.value) # Tail: 4
print('Length:', my_linked_list.length) # Length: 1
The LinkedList class handles the overall structure of the list. It creates a new node using the Node class and sets this node as both the head and tail of the list since it's the only element at this point. The length of the list is initialized as 1.
LinkedList 클래스는 전체 리스트 구조를 다룬다. Node 클래스를 사용하여 새로운 노드를 생성하고, 이 노드를 리스트의 head와 tail로 설정한다. 현재는 리스트에 하나의 요소만 있으므로 길이는 1로 초기화된다.
Here’s an example of creating a new linked list:
다음은 새 링크드 리스트를 생성하는 예시이다:
Print List Function
def print_list(self):
temp = self.head # Set a temporary pointer (temp) to the head of the list to start traversal
while temp is not None: # Iterate through the list until the end (temp is None)
print(temp.value) # Print the value of the current node (temp)
temp = temp.next # Move the temporary pointer (temp) to the next node in the list
The print_list function starts from the head of the list and prints the value of each node. It moves to the next node using temp.next until it reaches the end, indicated when temp becomes None.print_list 함수는 리스트의 head부터 시작하여 각 노드의 값을 출력한다. temp.next를 사용해 다음 노드로 이동하며, temp가 None이 될 때까지 반복한다. None은 리스트의 끝을 의미한다.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from KiwiChip directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

KiwiChip
KiwiChip
I'm currently learning Python and studying RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation).