Cloud/DevOps Project - 2
 Biswanath Sah
Biswanath Sah🌐 Static Website Hosting on AWS S3 Using Terraform 🚀
Are you ready to bring your static website online? 🌍 In this guide, I'll walk you through deploying a static website to AWS using Terraform - an awesome tool that lets you manage your infrastructure as code! 🖥️
By the end of this tutorial, you'll have your website up and running on Amazon S3, complete with automated infrastructure management. No more clicking around in the AWS console; everything will be handled by Terraform’s code-based approach. 🙌
Let's dive in! 🏊♂️
🛠️ Tools and Technologies Need
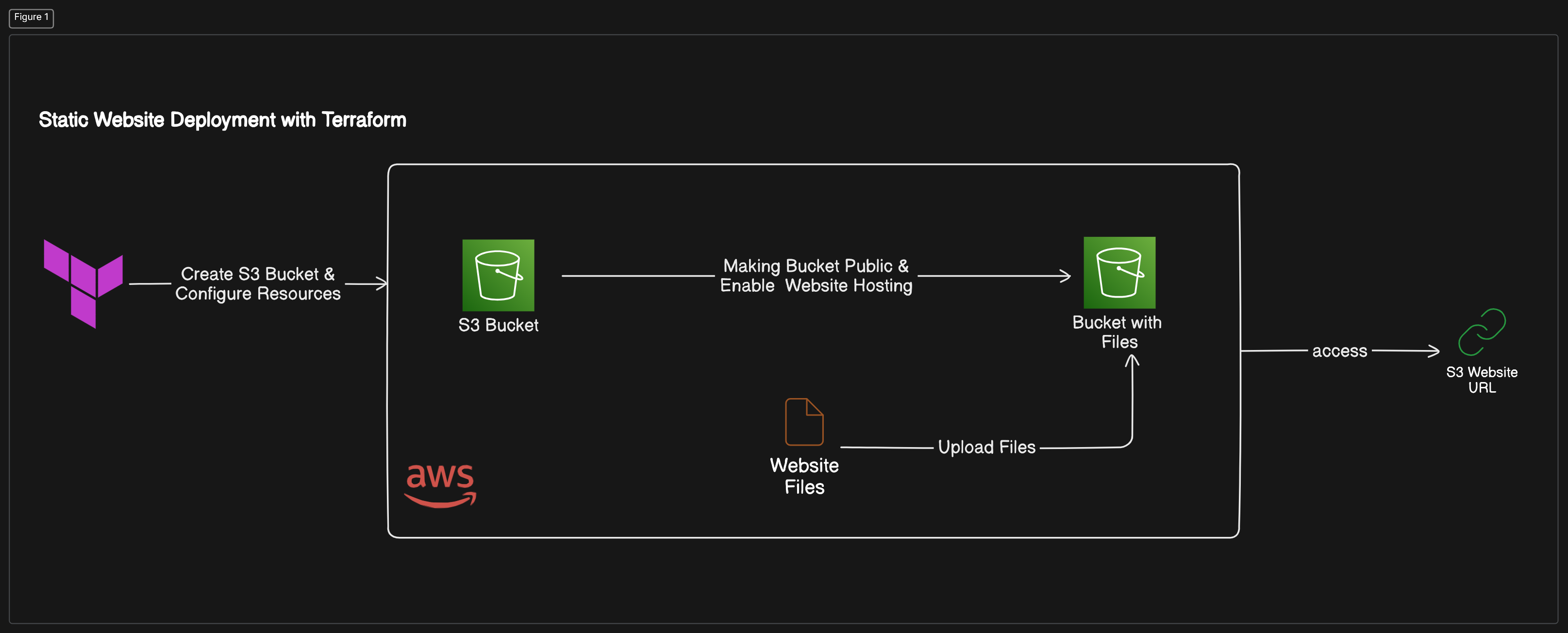
Terraform: Think of it as your infrastructure assistant. 🧑💻 With Terraform, you can easily create, change, and version your infrastructure using simple configuration files.
Essential Commands:
terraform init: Prepares your workspace to run Terraform by setting up the environment. 🛠️terraform plan: Gives you a sneak peek 👀 of the changes Terraform will make, so you can confirm before applying.terraform apply: Executes your configuration and makes your infrastructure live. 🎉
Amazon S3: Simple Storage Service(S3) is Amazon’s highly scalable and durable object storage service. It’s designed to store and retrieve any amount of data from anywhere on the web, making it perfect for hosting static websites.
📜 Step-by-Step Guide
Initialize Your Terraform Environment 🔄
- Start by running
terraform initin your project directory. This command sets up Terraform by downloading necessary plugins and modules, making your environment ready for the next steps.
- Start by running
Set Up Your Terraform Configuration Files 📂
Now, create three essential files:
main.tf: This file contains the definitions for your AWS resources, like the S3 bucket and access policies.provider.tf: Here, you specify the AWS provider and the region you’ll be using.variables.tf: This file allows you to define variables to make your code more modular and easier to update in the future.
Configure Your S3 Bucket 🪣
- In
main.tf, define your S3 bucket resource and set up public access. You’ll also enable static website hosting and specify yourindex.htmlas the entry point.
- In
Upload Your Website Content 🖼️
- Now, upload your HTML files, images, and any other static assets to the S3 bucket. You can automate this with Terraform or use the AWS CLI for quick uploads.
Plan and Apply with Terraform 🔍➡️🚀
Run
terraform planto review the changes Terraform will make in your AWS account. This is a good way to double-check before deploying.Then, run
terraform apply -auto-approveto make your website live! 🌐
Visit Your New Website 🎉
- In the AWS S3 console, navigate to your S3 bucket, go to Properties, and find the Static website hosting URL. Open it up in your browser, and voila! Your website is now live on AWS. 🎊
💡 Wrapping Up
With Terraform, you’ve not only deployed a static website, but you’ve also adopted a modern, efficient way of managing infrastructure. 🔥 Next time, try adding more Terraform configurations to expand site or integrate additional AWS services.
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Biswanath Sah directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by
