Introduction to Heaps - Max Heap vs Min Heap [2024] Guide | Day #15
 Bonaventure Ogeto
Bonaventure Ogeto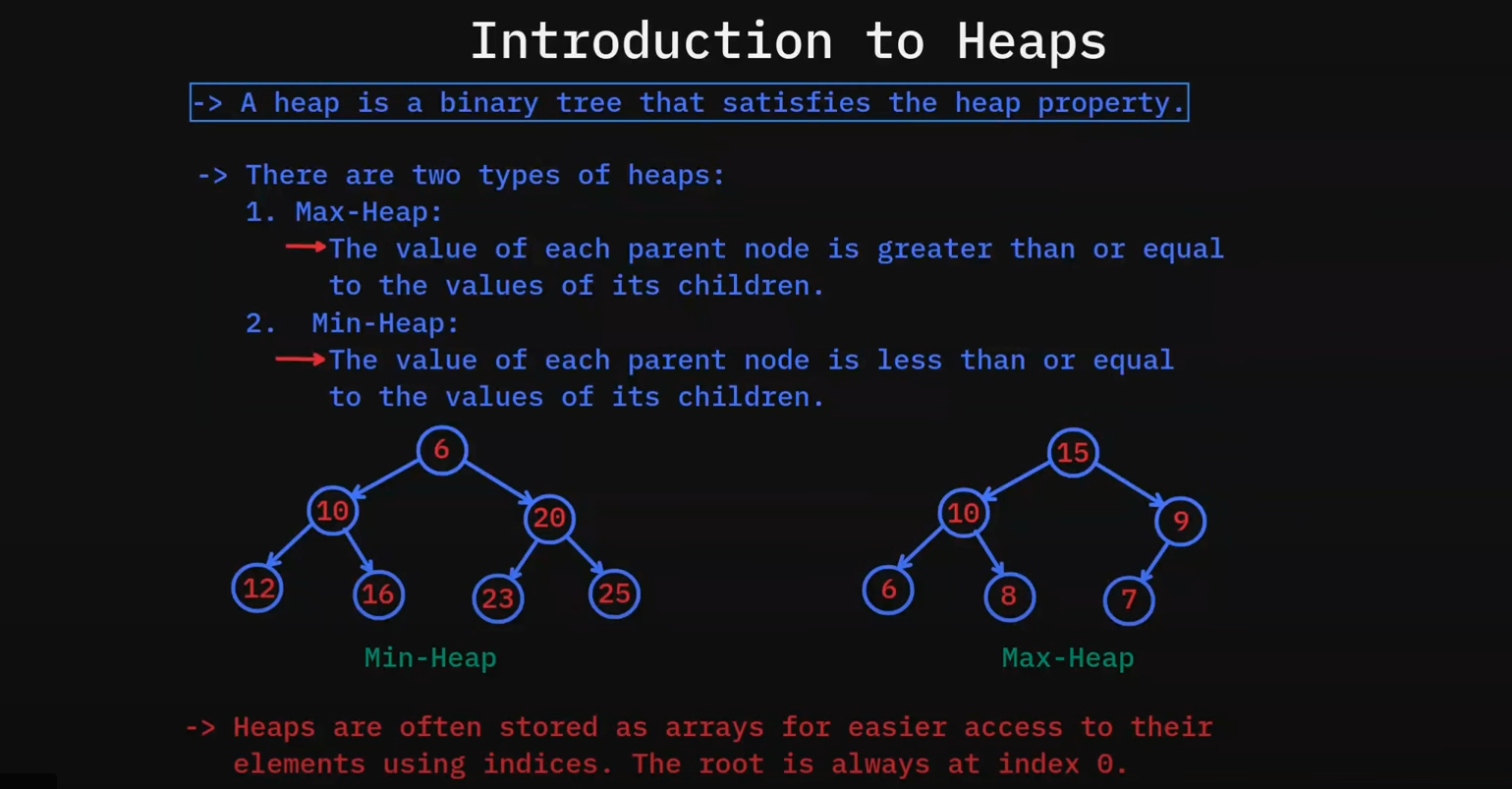
Key Takeaways
Learn what heaps are and their fundamental properties
Master both Max Heap and Min Heap implementations
Understand heap operations with O(log n) time complexity
Implement heaps in Python and JavaScript
Apply heaps to solve real-world problems efficiently
%[https://youtu.be/Uc5bV3mC_y4?si=9Is7CJCIj59OCx_Q]
What are Heaps?
A heap is a specialized tree-based data structure that satisfies the heap property. It's a complete binary tree where each parent node maintains a specific ordering relationship with its children.
Key Properties of Heaps
Complete Binary Tree: All levels are filled except possibly the last level
Heap Property: Parent-child relationship follows a specific order
Array Representation: Can be efficiently stored in arrays
Zero-based Indexing:
Left child: 2i + 1
Right child: 2i + 2
Parent: (i - 1) // 2
Types of Heaps
Max Heap
In a Max Heap, the parent node is always greater than or equal to its children.
# Max Heap Property
parent.value ≥ max(leftChild.value, rightChild.value)
Example Max Heap:
100
/ \
80 70
/ \ /
50 60 65
Min Heap
In a Min Heap, the parent node is always less than or equal to its children.
# Min Heap Property
parent.value ≤ min(leftChild.value, rightChild.value)
Example Min Heap:
10
/ \
30 20
/ \ /
50 40 25
Heap Operations
1. Insertion (Add)
class MaxHeap:
def __init__(self):
self.heap = []
def parent(self, i):
return (i - 1) // 2
def insert(self, key):
self.heap.append(key)
self._sift_up(len(self.heap) - 1)
def _sift_up(self, i):
parent = self.parent(i)
if i > 0 and self.heap[i] > self.heap[parent]:
self.heap[i], self.heap[parent] = self.heap[parent], self.heap[i]
self._sift_up(parent)
2. Delete (Extract) Max/Min
def extract_max(self):
if not self.heap:
return None
max_val = self.heap[0]
self.heap[0] = self.heap[-1]
self.heap.pop()
if self.heap:
self._sift_down(0)
return max_val
def _sift_down(self, i):
max_index = i
left = 2 * i + 1
right = 2 * i + 2
if left < len(self.heap) and self.heap[left] > self.heap[max_index]:
max_index = left
if right < len(self.heap) and self.heap[right] > self.heap[max_index]:
max_index = right
if i != max_index:
self.heap[i], self.heap[max_index] = self.heap[max_index], self.heap[i]
self._sift_down(max_index)
3. Heapify Process
def build_max_heap(array):
heap = MaxHeap()
heap.heap = array[:]
# Start from last non-leaf node
for i in range(len(array) // 2 - 1, -1, -1):
heap._sift_down(i)
return heap
JavaScript Implementation
class MinHeap {
constructor() {
this.heap = [];
}
parent(i) {
return Math.floor((i - 1) / 2);
}
leftChild(i) {
return 2 * i + 1;
}
rightChild(i) {
return 2 * i + 2;
}
insert(value) {
this.heap.push(value);
this.siftUp(this.heap.length - 1);
}
siftUp(i) {
while (i > 0 && this.heap[this.parent(i)] > this.heap[i]) {
[this.heap[i], this.heap[this.parent(i)]] =
[this.heap[this.parent(i)], this.heap[i]];
i = this.parent(i);
}
}
}
Applications & Use Cases
1. Priority Queues
Task scheduling in operating systems
Event-driven simulation
Emergency room patient management
2. Sorting Algorithms
K-way merge
K closest points
3. Graph Algorithms
Prim's minimum spanning tree
Best-first search
Performance Analysis
| Operation | Time Complexity |
| Insert | O(log n) |
| Delete | O(log n) |
| Peek | O(1) |
| Build | O(n) |
Space Complexity
Array Implementation: O(n)
Additional Operations: O(1)
Best Practices & Common Pitfalls
Best Practices
Choose the Right Heap Type
Use Max Heap for:
Finding maximum elements
Descending order sorting
Use Min Heap for:
Finding minimum elements
Ascending order sorting
Optimization Strategies
# Efficient array access def get_children(self, i): return [2*i + 1, 2*i + 2]Error Handling
def extract_min(self): if not self.heap: raise IndexError("Heap is empty") # ... rest of implementation
Common Pitfalls
Incorrect parent-child relationship calculation
Not maintaining complete binary tree property
Forgetting to update heap size after operations
FAQs
Q1: When should I use a Max Heap vs Min Heap?
Choose Max Heap when you need quick access to maximum elements, and Min Heap when you need quick access to minimum elements.
Q2: Can a heap contain duplicate elements?
Yes, both Max and Min heaps can contain duplicate elements while maintaining their respective heap properties.
Q3: What's the difference between a binary search tree and a heap?
A BST maintains left-right ordering for all nodes, while a heap only maintains parent-child ordering.
Summary & Key Points
Heap Types
Max Heap: Parent > Children
Min Heap: Parent < Children
Core Operations
Insertion: O(log n)
Deletion: O(log n)
Peek: O(1)
Implementation Tips
Use array representation
Maintain complete binary tree property
Handle edge cases properly
Next Steps
Practice implementing both heap types
Solve heap-related coding problems
Explore heap variations (Fibonacci heap, Binomial heap)
Study heap applications in real systems
Subscribe to my newsletter
Read articles from Bonaventure Ogeto directly inside your inbox. Subscribe to the newsletter, and don't miss out.
Written by

Bonaventure Ogeto
Bonaventure Ogeto
Software Engineer & Technical Writer